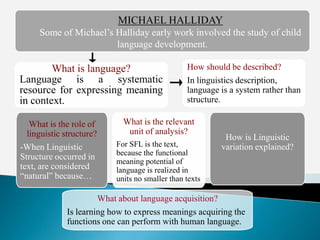
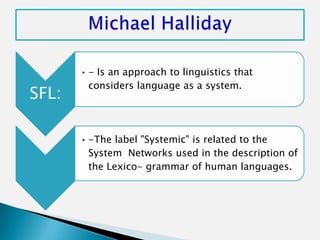
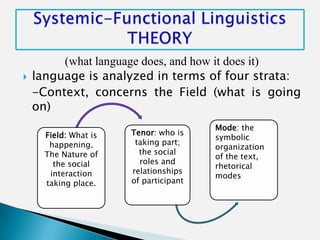
This document discusses the work of Australian linguist Michael Halliday and his theory of Systemic Functional Linguistics (SFL). [Halliday identified seven language functions that children acquire: instrumental, regulatory, interactional, personal, heuristic, imaginative, and representational.] Halliday's approach analyzes language in terms of context (field, tenor, mode), semantics, and lexico-grammar. Central to SFL is the use of "system networks" to represent linguistic choices. According to Halliday, language is a functional system organized to express three primary meanings: ideational, interpersonal, and textual.