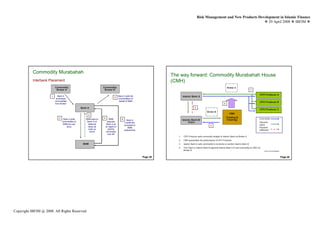
This document discusses new product development in Islamic finance. It begins with providing market updates and statistics on the growth of the Islamic finance industry globally and domestically. It then discusses recent developments, contemporary issues, and the new product development process. Some of the key issues highlighted include the need for more standardized Islamic financial contracts, improving liquidity and infrastructure, and developing products that meet market needs and comply with shariah principles. The document stresses the importance of collaboration between shariah and finance experts to continue advancing the industry.
















































































![Risk Management and New Products Development in Islamic Finance
29 April 2008 IBFIM
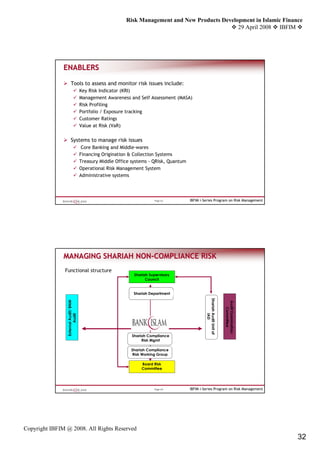
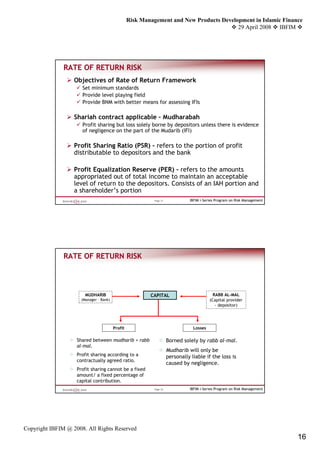
IFSB CAPITAL ADEQUACY STANDARD
IFSB RWCR - Standard Formula
Eligible Capital > 8.00%
Total RWA (Credit + Market Risks) + Operational Risk PSIA is
Profit
Less Sharing
RWA funded by PSIA (Credit + Market Risks) Investment
Account
Page 51 IBFIM i-Series Program on Risk Management
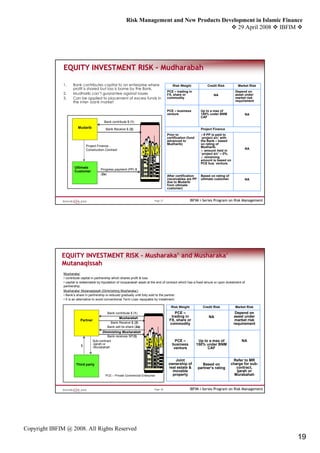
IFSB CAPITAL ADEQUACY STANDARD
IFSB RWCR - Supervisory Discretion Formula
Eligible Capital
Total RWA (Credit + Market Risks) + Operational Risk
Less
RWA funded by Restricted PSIA (Credit + Market Risks)
Less
(1 – α)[RWA funded by Unrestricted PSIA (Credit + Market Risks)]
Less
α [RWA funded by Profit Equalisation Reserve (PER) and Investment Risk Reverse (IRR)
of Unrestricted PSIA (Credit + Market Risks)]
Page 52 IBFIM i-Series Program on Risk Management
Copyright IBFIM @ 2008. All Rights Reserved
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05072209fullriskmanagementandnewproductsdevelopme-120408031618-phpapp02/85/Full-Risk-management-and-new-products-developme-91-320.jpg)