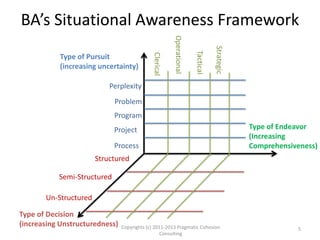
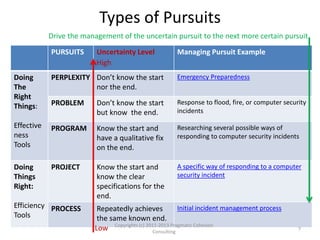
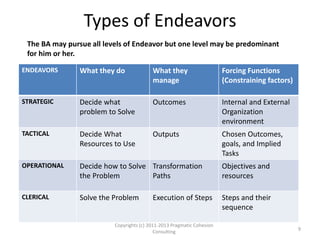
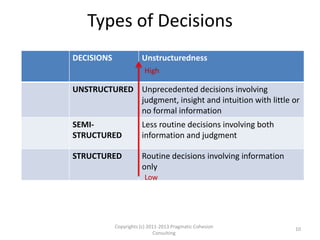
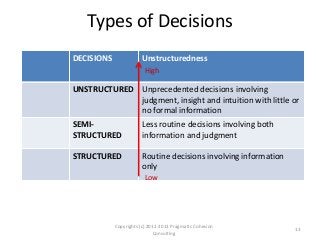
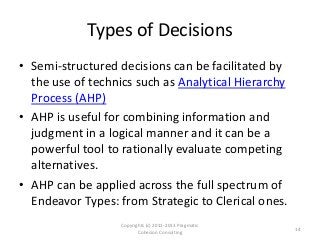
The document outlines a framework for assessing business analysts' situational awareness through three dimensions: type of pursuit, type of endeavor, and type of decision. It argues that as the complexity of these dimensions increases, the experience and skill level of the business analyst become more critical. The framework aims to help business analysts identify their current situational awareness and navigate complex decision-making scenarios effectively.

![Situational Awareness Wikipedia
Definition
• Situation awareness is the perception of environmental
elements with respect to time and/or space, the
comprehension of their meaning, and the projection of their
status after some variable has changed, such as time, or some
other variable, such as a predetermined event. It is also a field
of study concerned with perception of the environment
critical to decision-makers in complex, dynamic areas from
aviation, air traffic control, power plant operations, military
command and control, and emergency services such as fire
fighting and policing; to more ordinary but nevertheless
complex tasks such as driving an automobile or bicycle. [may
this author add Business Analysis ?]
Copyrights (c) 2011-2013 Pragmatic Cohesion
Consulting
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/frameworkforassessingbusinessanalystssituationalawareness-130502132312-phpapp02/85/Framework-for-assessing-business-analysts-situational-awareness-2-320.jpg)