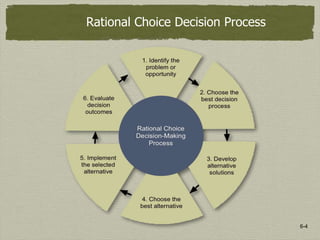
1) Decision making is defined as a conscious process of choosing among alternatives to move toward a desired outcome. The rational choice process involves identifying problems, choosing a decision process, developing and identifying alternatives, choosing the best alternative, implementing it, and evaluating the results.
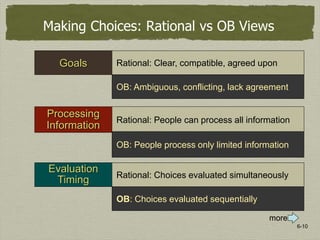
2) Problem identification can be challenging due to stakeholder framing, perceptual defenses, mental models, and lack of decisive leadership. Evaluating alternatives involves bounded rationality since people can only process limited information and aim for satisfactory rather than optimal solutions. Emotions and intuition also influence decision making.
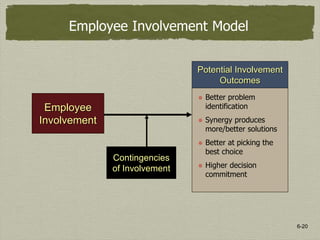
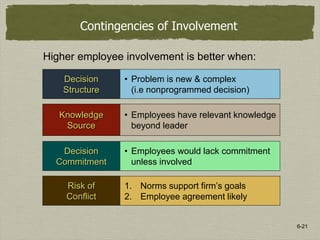
3) Employee involvement in decision making can lead to better problem identification, more alternatives, choosing better options, and higher commitment. It works best when employees have relevant knowledge