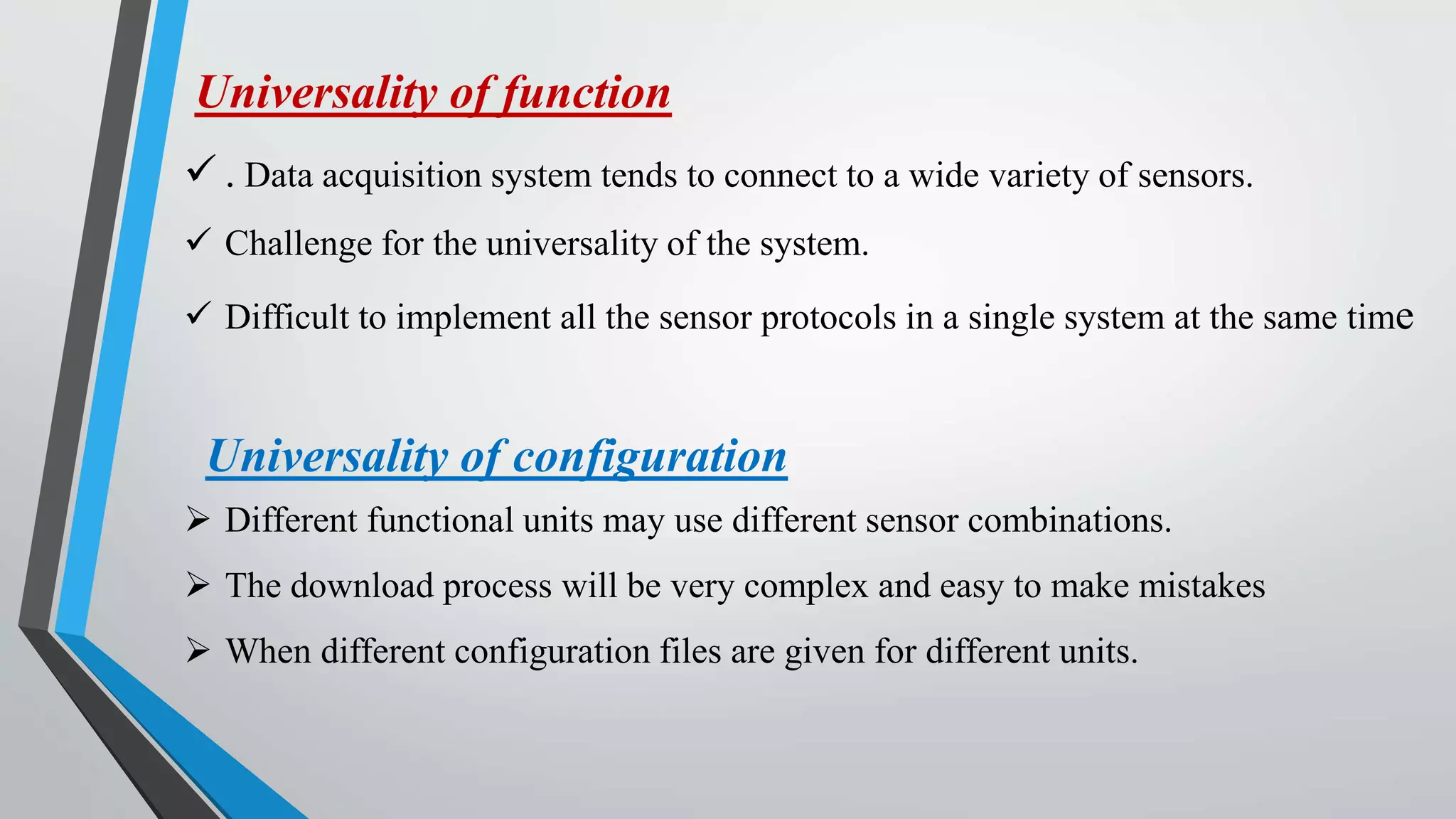
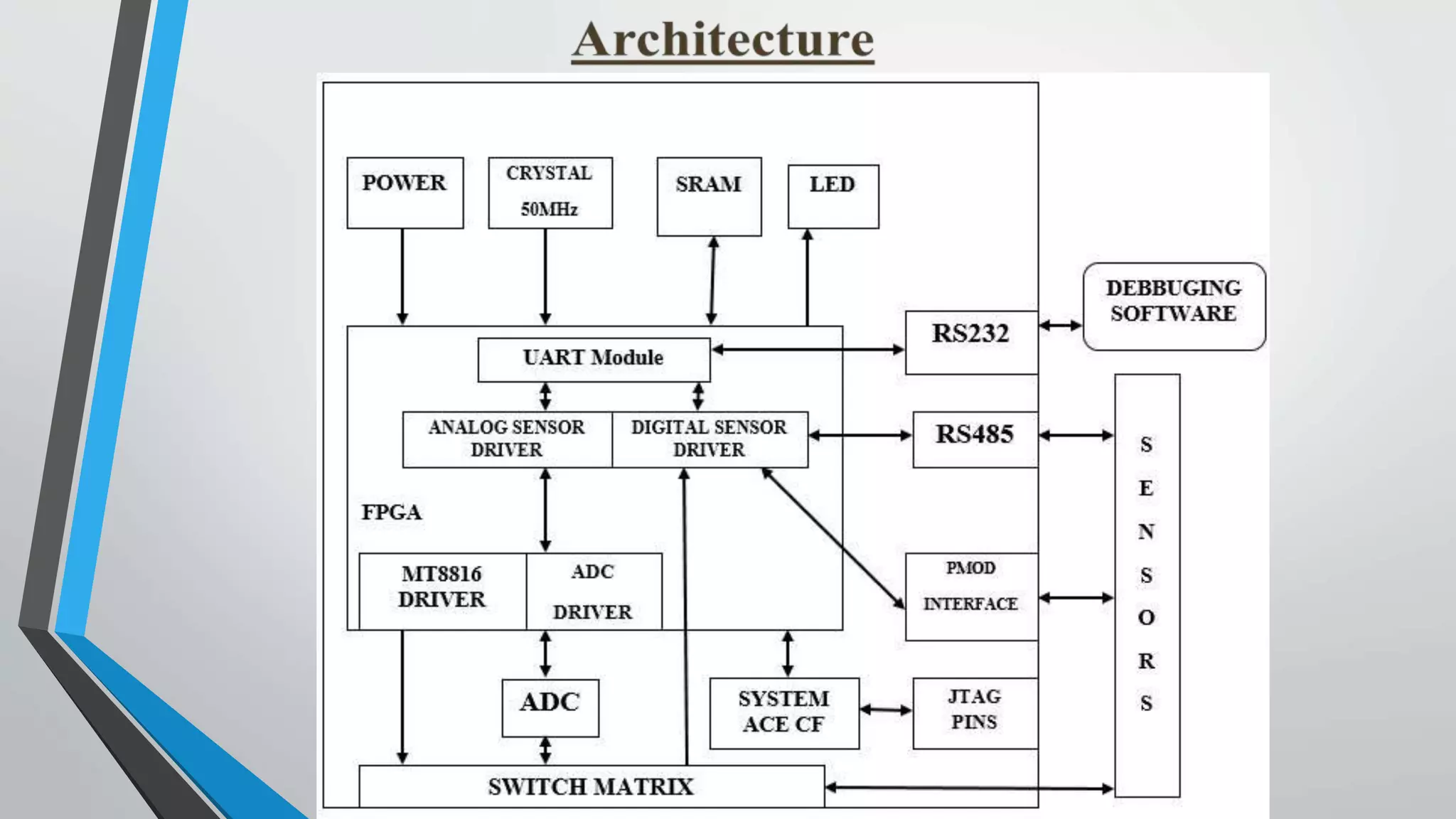
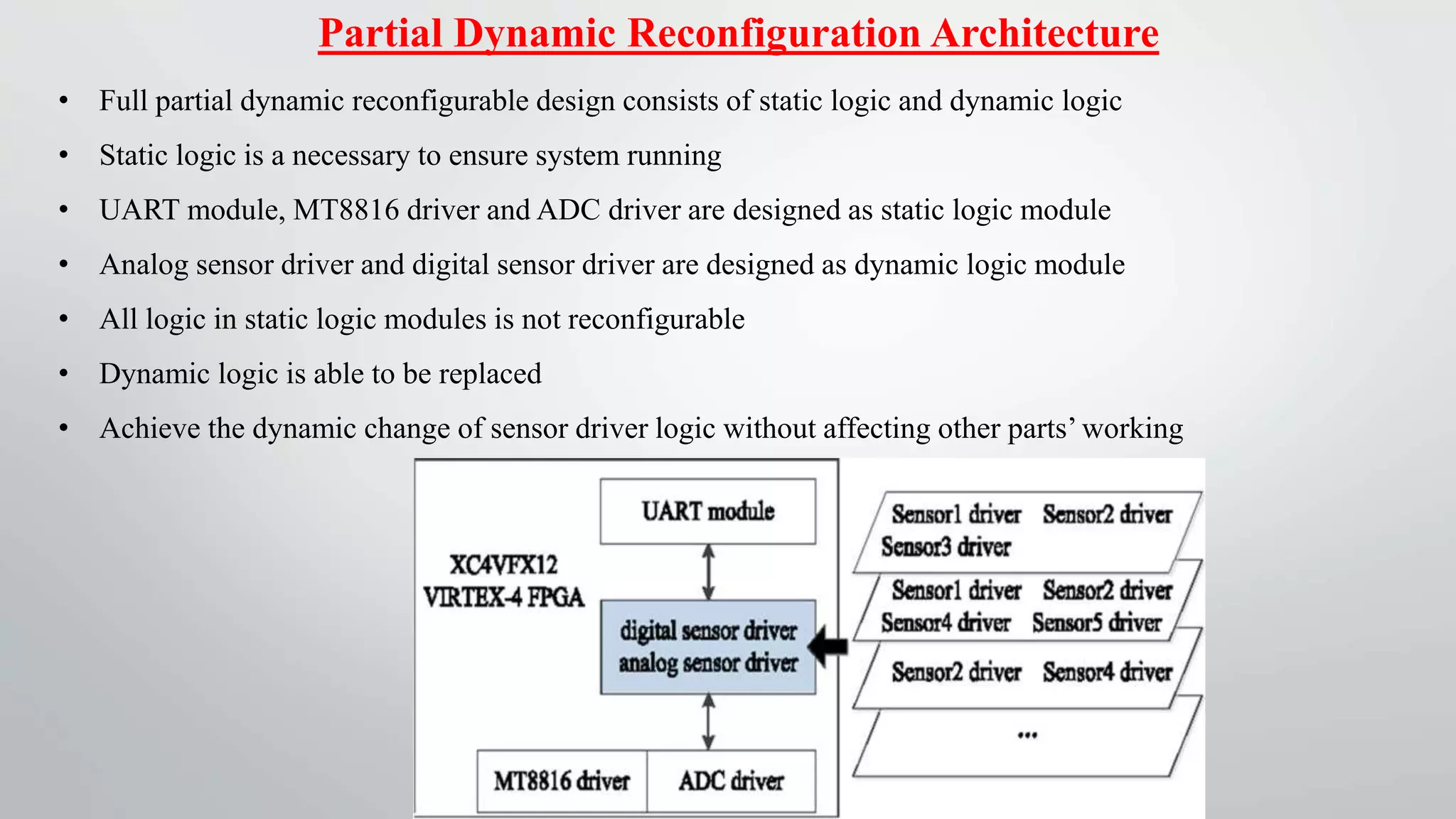
This document proposes a reconfigurable sensor data acquisition system based on FPGA for industrial computerization and control. The system uses FPGA reconfiguration technology to allow dynamic switching of sensor protocols and functions without powering off. It achieves static reconfiguration through an FPGA-controlled switch matrix and dynamic reconfiguration by storing configuration files on an FPGA configuration flash card. This provides flexibility to change sensor connections and logic online for improved real-time performance, universality, and continuous operation.























![References
• [1] Shuang Bao, Hairong Yan, Qingping Chi, Zhibo Pang, and Yuying Sun, “FPGA-
Based Reconfigurable Data Acquisition System for Industrial Sensors”, IEEE
Transactions On Industrial Informatics, Vol. 13, No. 4, August 2017
• [2] A. Tisan and J. Chin, “An End-user Platform For FPGA-based Design And Rapid
Prototyping Of Feedforward Artificial Neural Networks With On-chip
Backpropagation Learning,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat., vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 1124–
1133, Jun. 2016.
• [3] Q. Chi, H. Yan, C. Zhang, Z. Pang, and L. D. Xu, “A Reconfigurable Smart
Sensor Interface For Industrial WSN In IoT Environment,” IEEE Trans. Ind.
Informat., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 1417–1425, May 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpgaacquisition-190519032620/75/Fpga-acquisition-29-2048.jpg)
![Cont…
• [4] J. Mangala and J. Manikandan, “FPGA Implementation Of Reconfigurable
Modulation System,” in Proc. 2015 Int. Conf. Adv. Comput., Commun. Informat.,
Aug. 2015, pp. 493–500.
• [5] S. Agarwal, A. Rani, V. Singh and A. P. Mittal, "FPGA Based Wireless
Emergency Medical System for Developing Countries," 2015 Annual Global Online
Conference on Information and Computer Technology (GOCICT), Louisville, KY,
2015, pp. 80-84.
• [6] Z. Wang, Y. Yao, L. Chen, F. Li and G. Jin, "A reconfigurable ethernet-based
data acquisition and processing system for particle physics experiments," 2016
IEEE-NPSS Real Time Conference (RT), Padua, 2016, pp. 1-4.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpgaacquisition-190519032620/75/Fpga-acquisition-30-2048.jpg)
