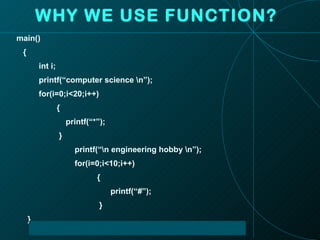
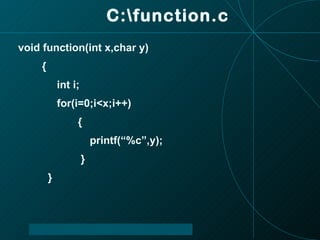
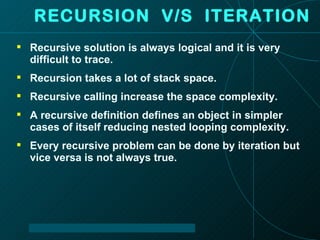
The document discusses functions in the C programming language, including their definitions, declarations, and types. It provides examples of function implementations, outputs, and explores concepts like recursion and argument passing. Additionally, it touches on the differences between recursion and iteration in programming.