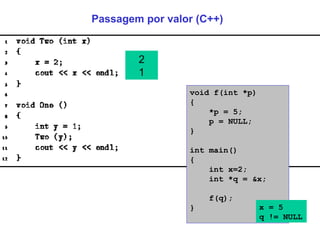
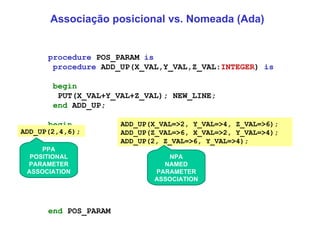
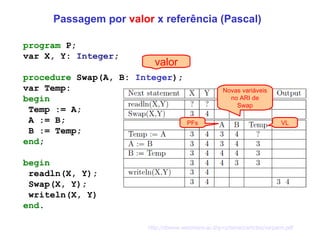
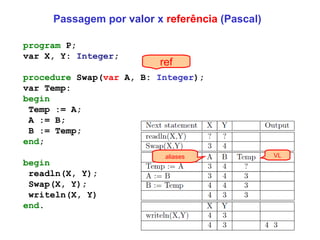
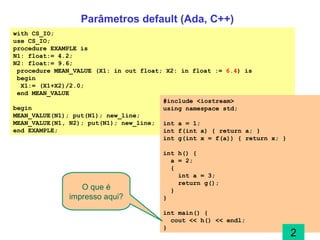
The document discusses different parameter passing techniques in programming languages, including pass by value, pass by reference, and pass by result/value-result. It provides examples in languages like C, C++, Java, C#, Pascal, Ada to illustrate how each technique works and the differences between them. It also covers topics like parameter modes (in, out, in-out), parameter arrays, and variable arguments.
![Paradigmas de Linguagens de Programação Paradigma Imperativo [Passagem de parâmetros] Aula #4 (CopyLeft)2009 - Ismar Frango ismar@mackenzie.br](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/75/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-1-2048.jpg)



![Passagem por referência (C++) 2 2 void f(int A[]) { A[0] = 5; } int main() { int B[10]; B[0] = 2; f(B); cout << B[0] << endl;} 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-6-320.jpg)


![Passagem por valor (Java) public class Teste{ private static void aloca(String x) { x="Hello";} public static void main(String args[]) { String b="World"; aloca(b); System.out.println(b); } } World](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-12-320.jpg)
![Passagem por valor (Java) public class Teste{ private static String aloca(String x,String y) { x=x+y; return x;} public static void main(String args[]) { String a="Hello, "; String b="World"; String c = aloca(a,b); System.out.println(c==a); String d="World"; String e=new String("World"); System.out.println(b==d); System.out.println(b==e); String f=e.intern(); System.out.println(b==f); } } false true false true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-13-320.jpg)


![O que ocorre aqui? public class Teste2 { public static void foo (String x) { x+=" World"; } public static void main(String []a) { String y = new String("Hello"); foo (y); System.out.println(y); } } Hello public class Teste3 { public static void foo (StringBuilder x) { x.append(" World"); } public static void main(String []a) { StringBuilder y = new StringBuilder(); y.append("Hello"); foo (y); System.out.println(y); } } Hello World](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-16-320.jpg)
![Passagem e Alocação Java vs. C vs. C# class Elefante { public int peso=1000; //:-( Thou shalt not do this! } public class Teste{ public static void main(String args[]) { Elefante dumbo = new Elefante(); dumbo.peso=2000; Elefante dumbinho = dumbo; dumbinho.peso=500; System.out.println(dumbo.peso); } } 500 Java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-17-320.jpg)
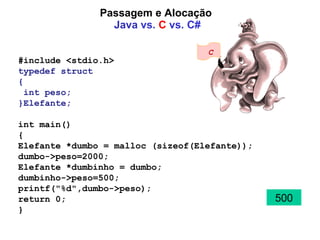

![Java vs. C vs. C# using System; public struct Elefante { public int peso; } public class testecs { public static void Main(string []a) { Elefante dumbo = new Elefante(); dumbo.peso=2000; Elefante dumbinho = dumbo; dumbinho.peso=500; Console.WriteLine (dumbo.peso); } } 2000 C#](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-20-320.jpg)
![Java vs. C vs. C# using System; public class Elefante { public int peso; } public class testecs { public static void Main(string []a) { Elefante dumbo = new Elefante(); dumbo.peso=2000; Elefante dumbinho = dumbo; dumbinho.peso=500; Console.WriteLine (dumbo.peso); } } 500 C#](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-21-320.jpg)
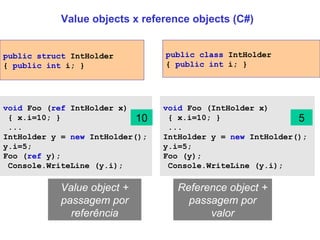
![Passagem por referência (C#) void Foo ( ref StringBuilder x) { x = null ; } ... StringBuilder y = new StringBuilder(); y.Append ( "hello" ); Foo ( ref y); Console.WriteLine (y== null ); using System; using System.Text; public class testecsref { public static void Foo1 ( ref Elefante x) { x.peso=1000 ;} public static void Foo2 (Elefante x) { x.peso=0 ;} public static void Main(string []a) { Elefante dumbo=new Elefante(); Foo1 ( ref dumbo); Console.WriteLine (dumbo.peso); Foo2 (dumbo); Console.WriteLine (dumbo.peso); } } public class Elefante { public int peso; } public struct Elefante { public int peso; } 1000 0 1000 1000 Qual a diferença entre passar um value object por referência e um reference object por valor? true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-22-320.jpg)



![Parameter arrays –”params” (C#), ... (Java) void ShowNumbers ( params int [] numbers) { foreach ( int x in numbers) { Console.Write (x+ " " ); } Console.WriteLine(); } ... int [] x = {1, 2, 3}; ShowNumbers (x); ShowNumbers (4, 5); static int sum (int ... numbers) { int total = 0; for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) total += numbers [i]; return total; } C# Java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-27-320.jpg)
![Parâmetros variáveis (C++) void myprintf( char *format, ... ){ va_list vl; int i; va_start ( vl, args ); for( i = 0; args[i] != '\0'; ++i ){ union any_t { int i; float f; char c; } any; if( args[i]=='i' ){ any.i = va_arg( vl, int ); printf( "%i\n", any.i ); } else if( args[i]=='f' ){ any.f = va_arg( vl, float ); printf( "%f\n", any.f ); }else if( args[i]=='c' ){ any.c = va_arg( vl, char ); printf( "%c\n", any.c ); } else{ throw SomeException; } va_end( vl ); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-28-320.jpg)
![Parâmetros read-only (C++) class IntList { public: const Print (ostream &o); }; void f(const IntList &L) { L.Print(cout); } bool Compare(const vector <int> & A) // precondition: A is sorted { int k; for (k=1; k<A.size(); k++) { if (A[k-1] == A[k]) return true; } return false; } E se aqui não fosse const?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-30-320.jpg)
![Macros #define MAXLINE 100 char line[MAXLINE]; ... getline(line, MAXLINE); #define A 2 #define B 3 #define C A + B int x = C * 2; O que acontece aqui? Por que não tem ponto-e-vírgula?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-31-320.jpg)
![Pass-by-name (ALGOL) procedure double(x); real x; begin x := x * 2 end; double(C[j]) C[j] := C[j] * 2. real procedure Sum(j, lo, hi, Ej); value lo, hi; integer j, lo, hi; real Ej; begin real S; S := 0; for j := lo step 1 until hi do S := S + Ej; Sum := S end; Sum(i, 1, n, x[i]*i) Como simular isso em C++ ou Java?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-32-320.jpg)
![Pass-by-name (ALGOL) procedure swap (a, b); integer a, b, temp; begin temp := a; a := b; b:= temp end; swap(x, y) temp := x; x := y; y := temp swap(i, x[i]) temp := i; i := x[i]; x[i] := temp Antes i = 2 x[2] = 5 Depois i = 5 x[2] = 5 x[5] = 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-33-320.jpg)



![#define TAM 10 void change ( int v[ ], int &ntx) { for (;ntx>0;ntx--) v[ntx]=ntx---1; } int main() { int k[TAM],i=0,; for (;;) { if (i==TAM) break ; k[i++]= i*2;} change(k,i); for (;;) { if (i>TAM) break ; cout<<k[i++]<<endl;} } 0 2 1 6 3 10 5 14 7 18 9 C++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-37-320.jpg)
![using namespace System; double average( ... array<Int32>^ arr ) { int i = arr->GetLength(0); double answer = 0.0; for (int j = 0 ; j < i ; j++) answer += arr[j]; return answer / i; } int main() { Console::WriteLine("{0}", average( 1, 2, 3, 6 )); } Visual C++ (.NET) 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-38-320.jpg)


![public class TestY { public static void differentArray(float[] x) { x = new float[100]; x[0] = 26.9f; } public static void main(String a[]) { float[ ] xx = new float[100]; xx[0] = 55.8f; differentArray(xx); System.out.println("xx[0] = " + xx[0]); } } Java 55.8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-41-320.jpg)
![procedure sub1(x: int; y: int); begin x := 1; y := 2; x := 2; y := 3; end; sub1(i, a[i]); Algol a={2,3}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp4-090827150114-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-4-42-320.jpg)