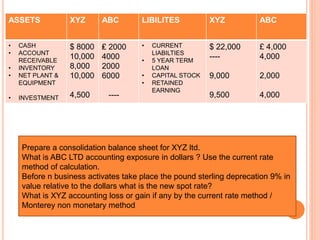
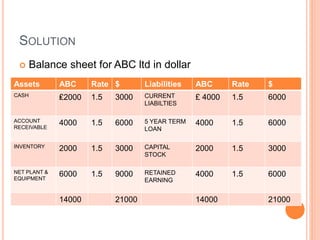
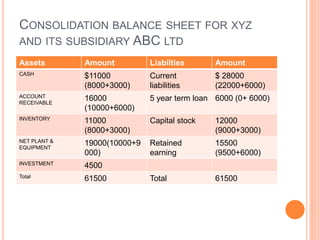
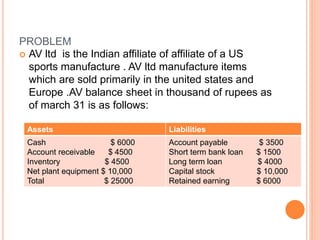
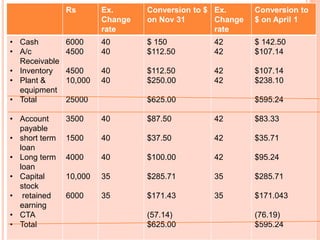
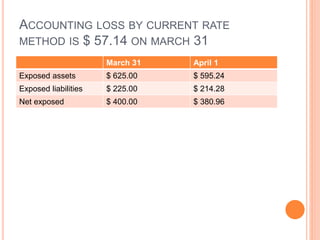
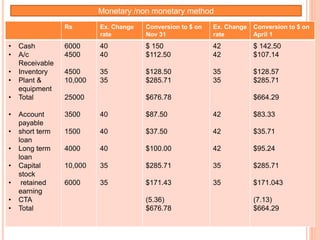
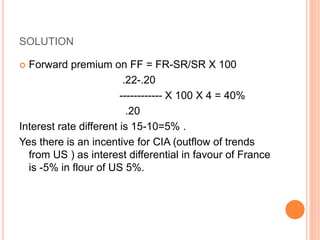
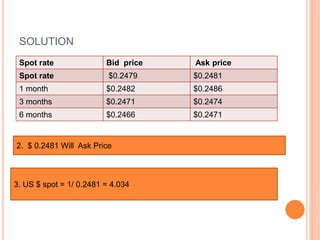
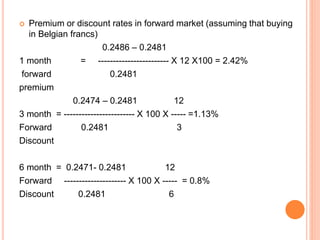
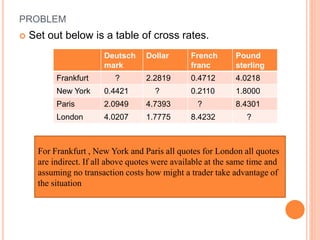
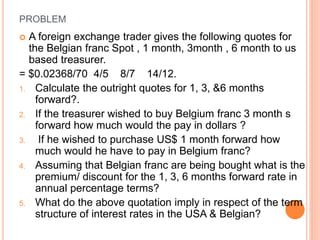
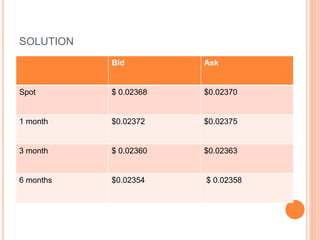
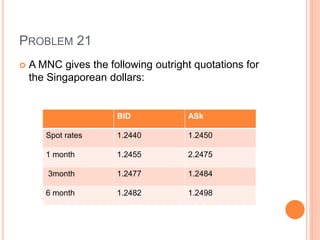
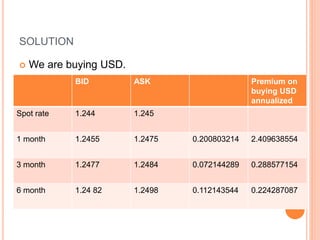
An American investor purchased securities in the Indian market investing $1 million USD. The document calculates the rate of return for the investor under different scenarios where the annual return on the Indian securities is 20%, 25%, and 50%. It also considers a second problem where an American investor wants to invest in Indian securities with a given beta and calculates the expected rate of return and risk. The document then provides exchange rate calculations and examples involving cross rates, spot rates, forward rates, and premiums/discounts. It summarizes international financial management concepts.































































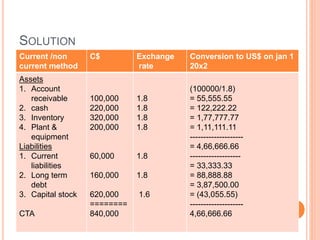
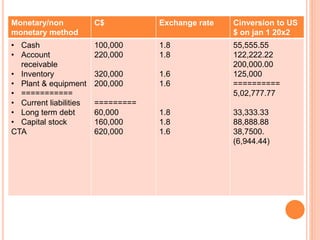
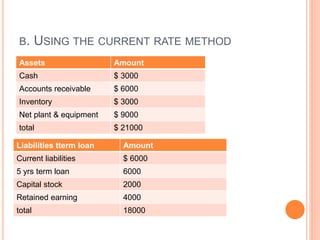
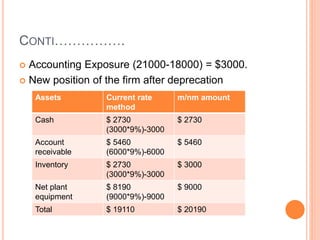
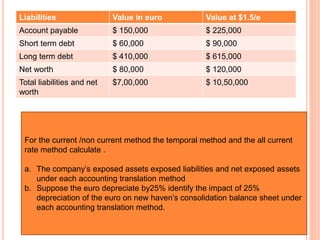
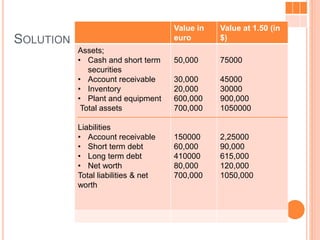
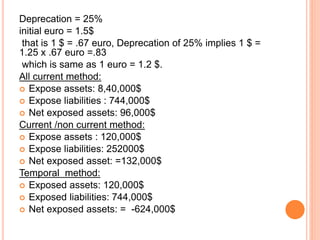
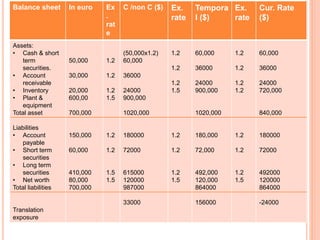
![As per current rate method
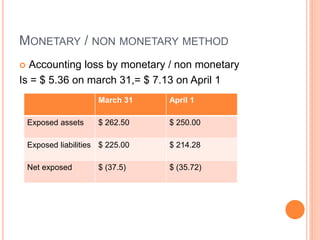
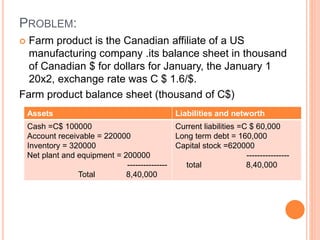
Accounting exposure on Jan 1 20x2 is as follows
Exposed asset = US$ 4,66,666.66.
Exposed liabilities = US $ 1,22, 222.22.
Accounting exposure = 3,44,444.45
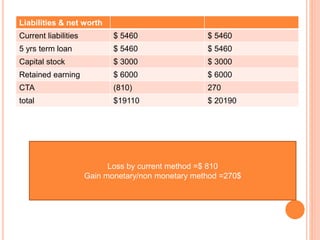
Accounting loss as show as in CTA (Cumulative Translation
Adjustment) account is =US $ 43,055.55
Cumulative Translation Adjustment :- Cumulative Translation
Adjustments are an integral part of the financial statements for firms
with international market exposure.
An entry in the comprehensive income section of a translated
balance sheet summarizing the gains/losses resulting from varying
exchange rates over the years. A CTA entry is required under the
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) No.52 rule as a
means of helping investors differentiate between actual operating
gains/losses and those generated via translation.
(Opening Functional Balance x (Current month-end rate - Previous
month-end rate)] + [Sum(Transactions in month) x (Current month-end
rate - current average rate)]
) x [-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ifmproblems-141114001859-conversion-gate02/85/Ifm-problems-80-320.jpg)