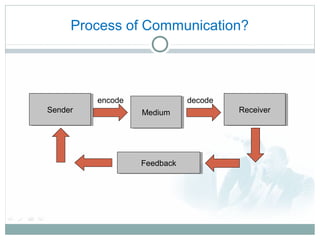
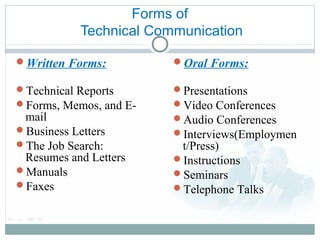
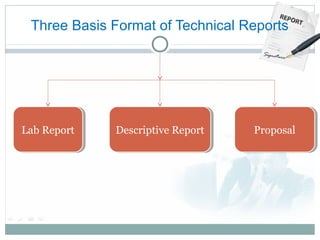
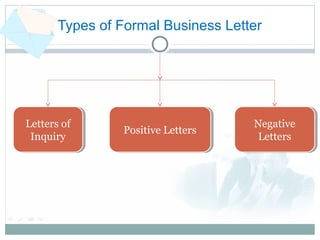
Technical communication involves conveying scientific, engineering, or other technical information through various written and oral forms. It aims to define, create and deliver information for the safe, efficient and effective use of products. The key characteristics of technical communication are that it is clear, correct, concise, consistent and comprehensive. Some common forms of technical communication include technical reports, forms, memos, emails, business letters, resumes, manuals, presentations, video/audio conferences, instructions and seminars. These forms are used to inform, instruct and influence audiences through factual information tailored to specific technical topics and users.