The document summarizes key features of Muslim historiography:
- It began with biographies of the Prophet Muhammad using isnad (chain of transmission) to verify accounts. This established history as a science with critical methods.
- Early histories used chronology and theological views, interpreting history as God's divine plan.
- Key forms included khabar (brief accounts of single events), annalistic (year-by-year), dynastic, and tabaqat (generations).
- Early works focused on the Prophet's military campaigns (maghazi) and life (sirah/seerah).
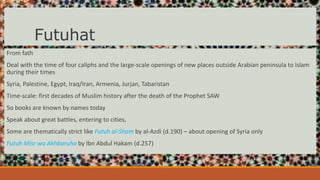
- Futuhat covered the era of the Four Righteous Caliphs and the