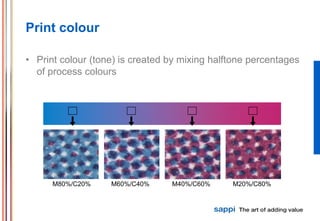
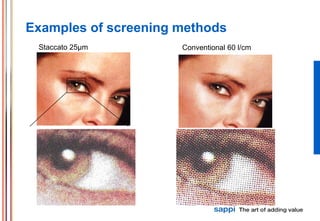
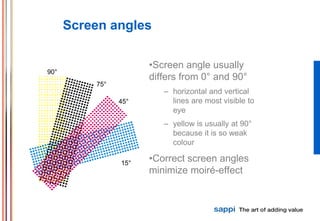
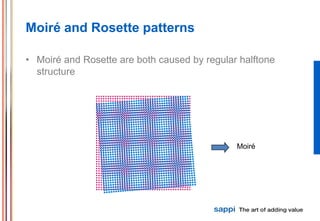
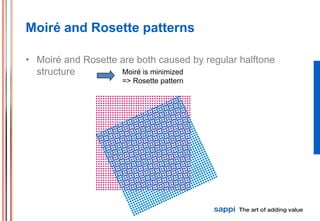
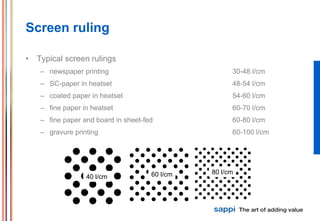
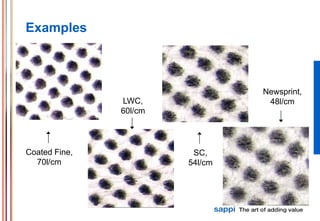
The document discusses the processes involved in printing, particularly the formation of colors using halftones with cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks (CMYK). It describes various screening methods, including conventional and stochastic screening, and details the impact of print density and screen angles on print quality. Additionally, it highlights typical screen rulings for different types of paper, emphasizing the need for higher rulings for finer detail rendering.