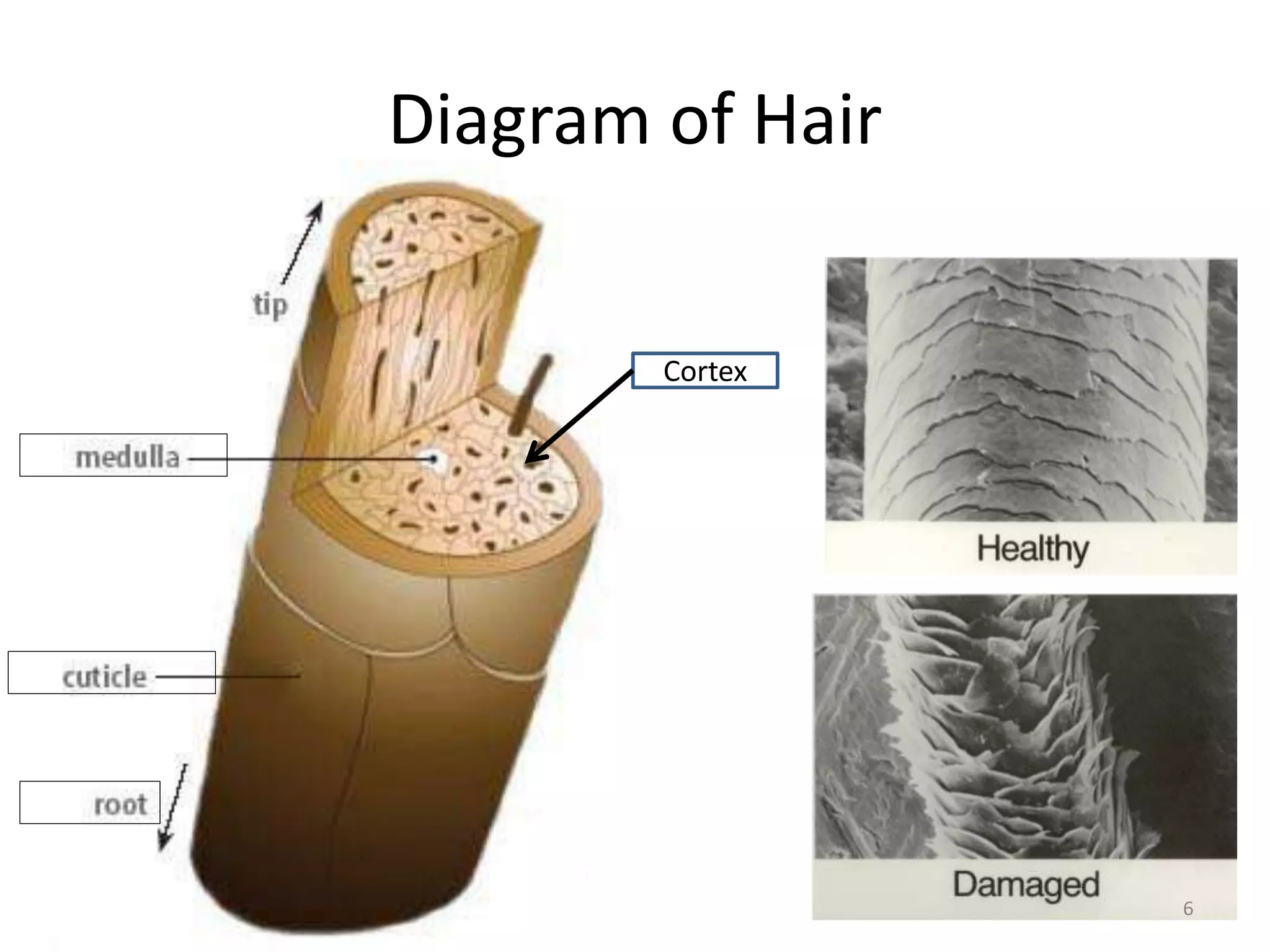
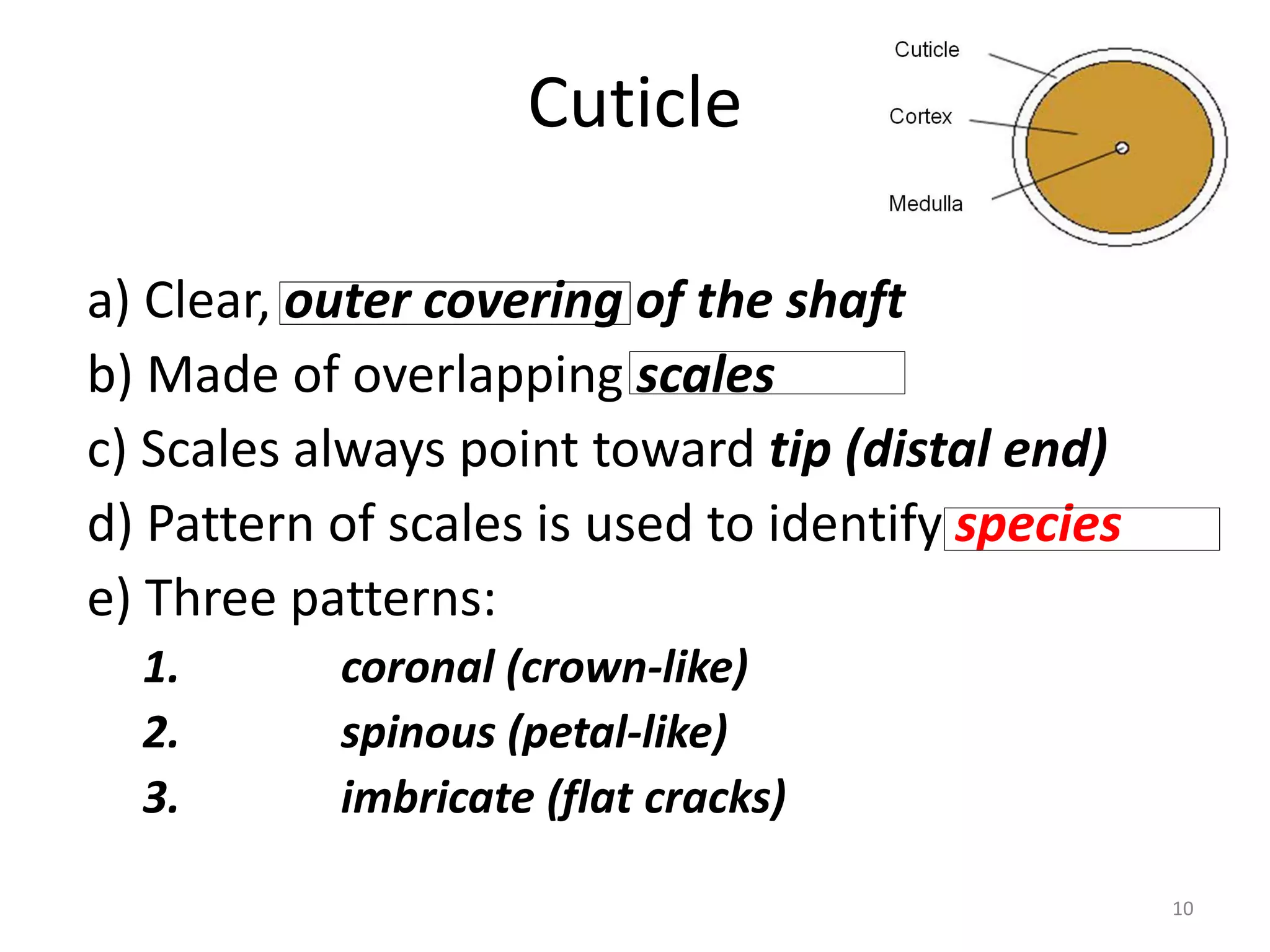
This document provides information about hair evidence in criminal investigations. It discusses how hair is one of the most common types of trace evidence found at crime scenes. Hair can be used to corroborate other evidence, narrow the list of suspects, and detect drugs or poison. The document then describes the structure and composition of hair, including the cuticle, cortex, and medulla. It explains how hair growth cycles through anagen, catagen, and telogen phases. Guidelines are provided for properly collecting hair evidence from crime scenes and known individuals.