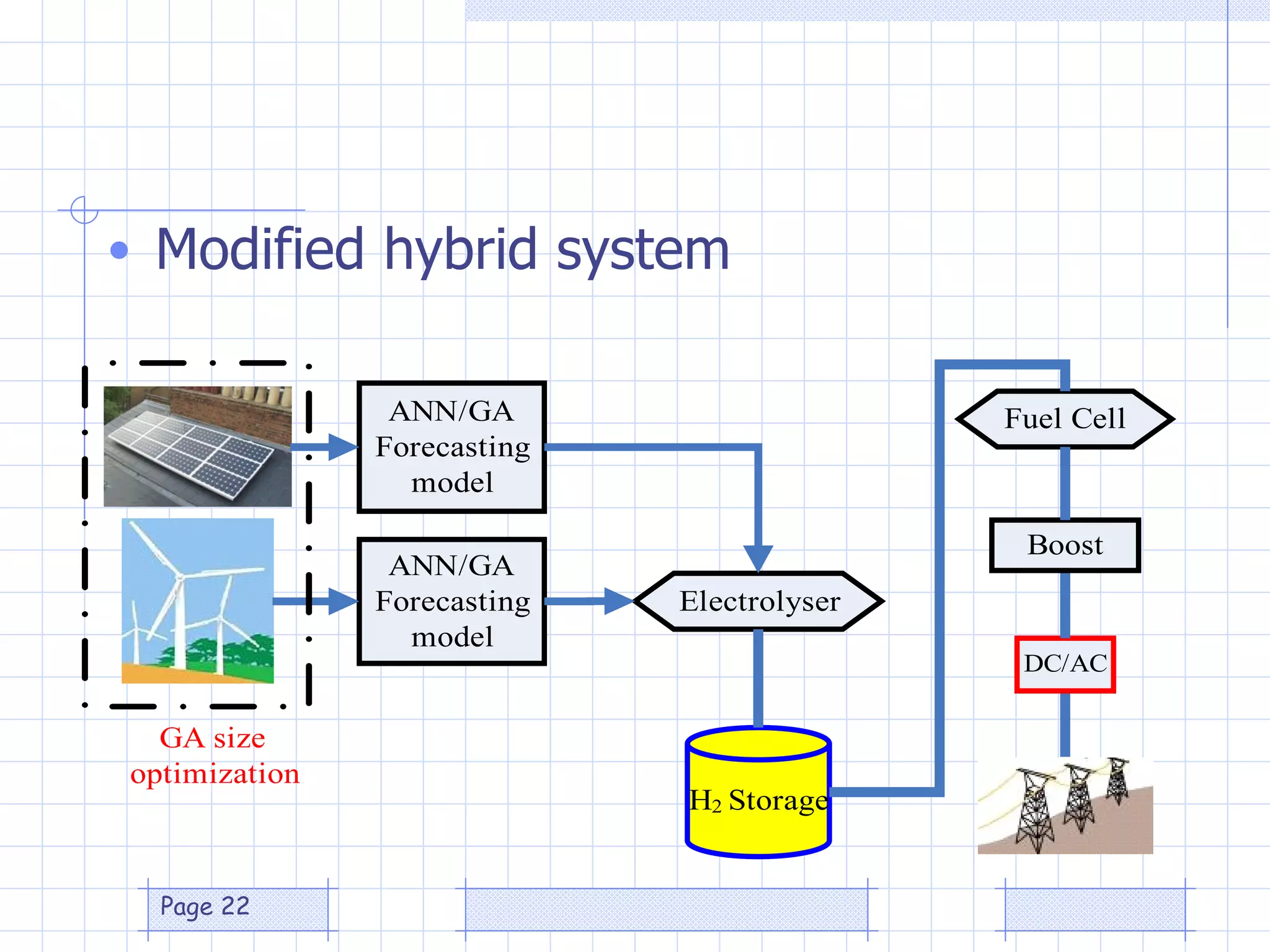
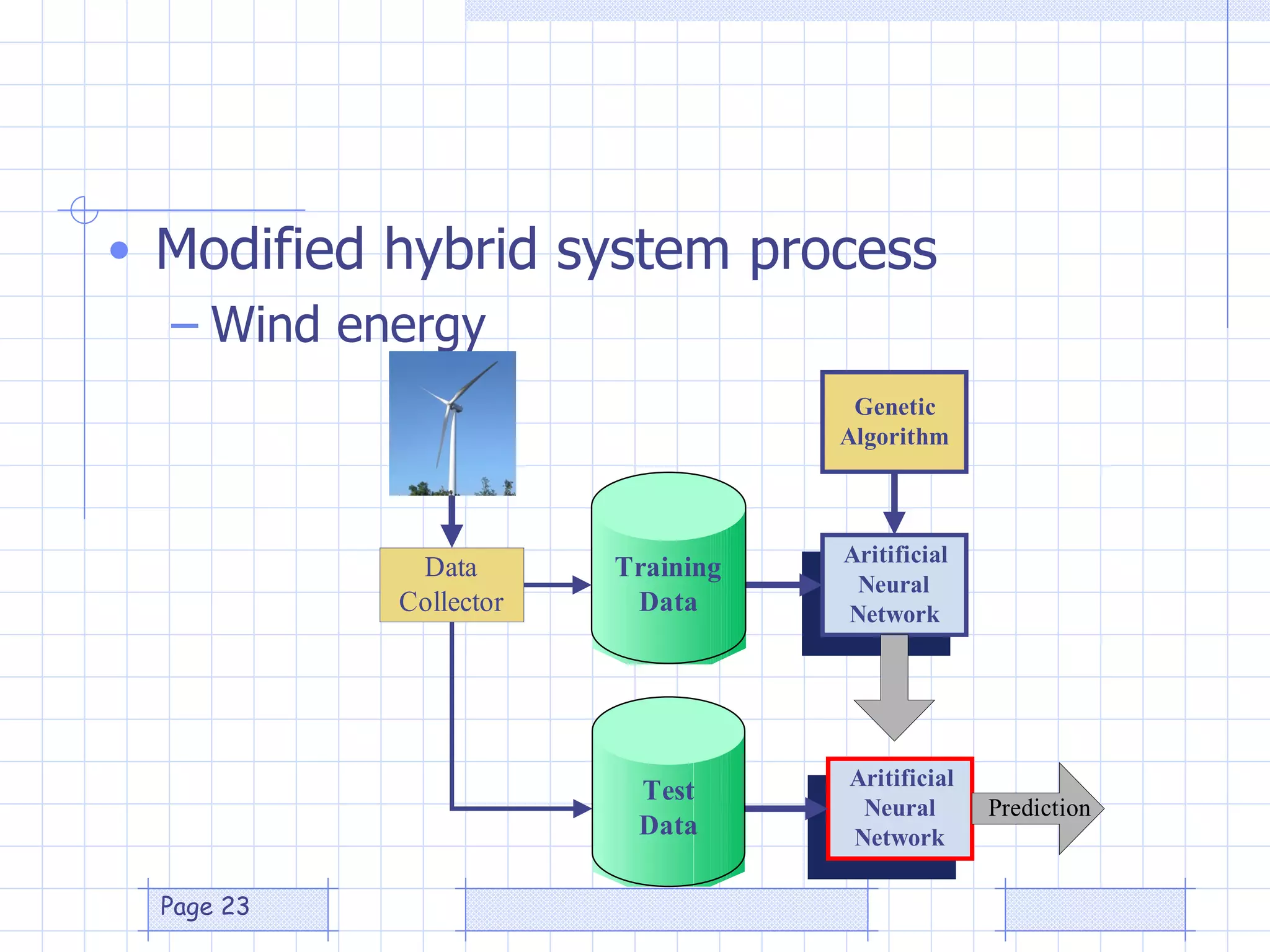
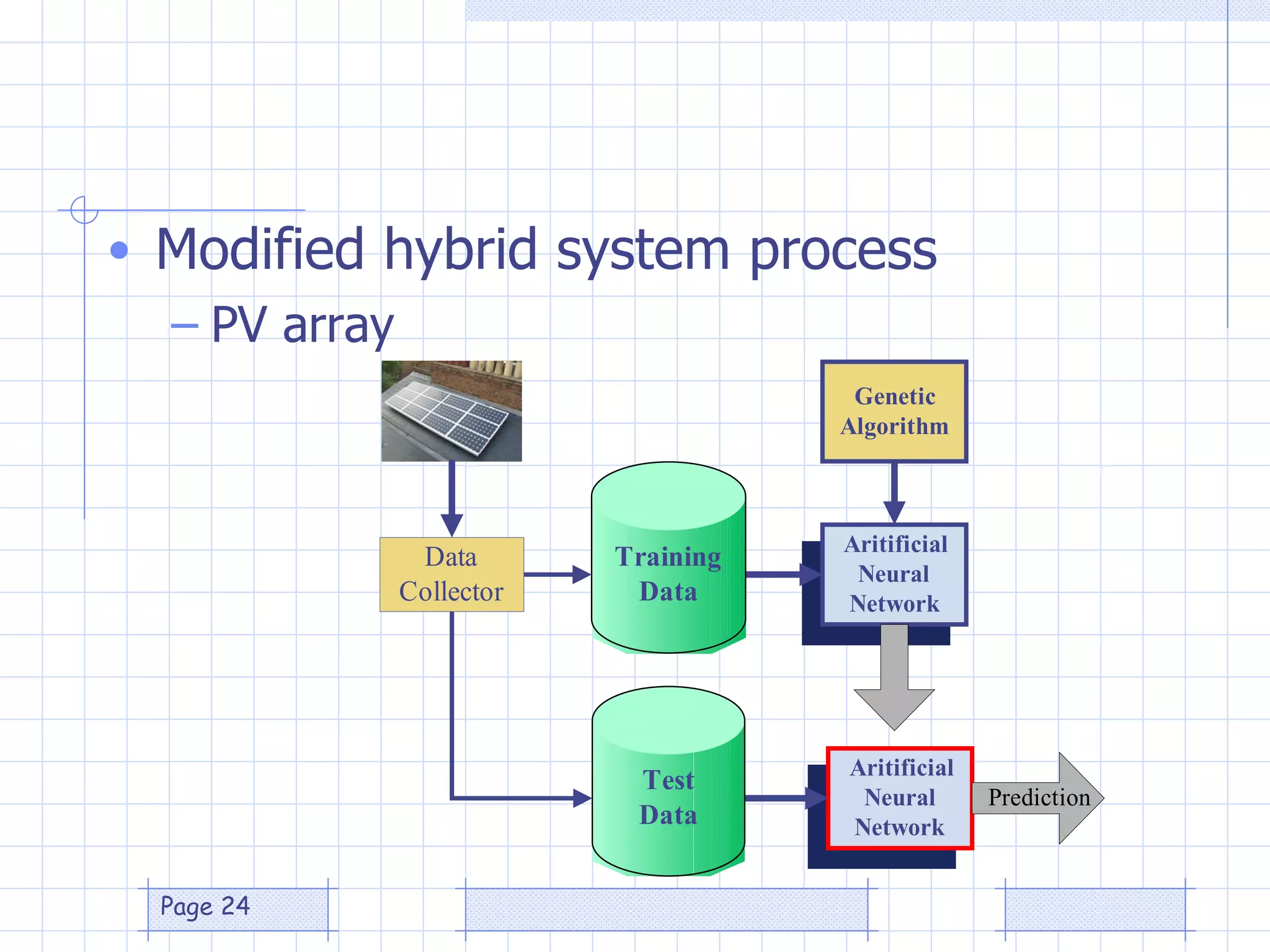
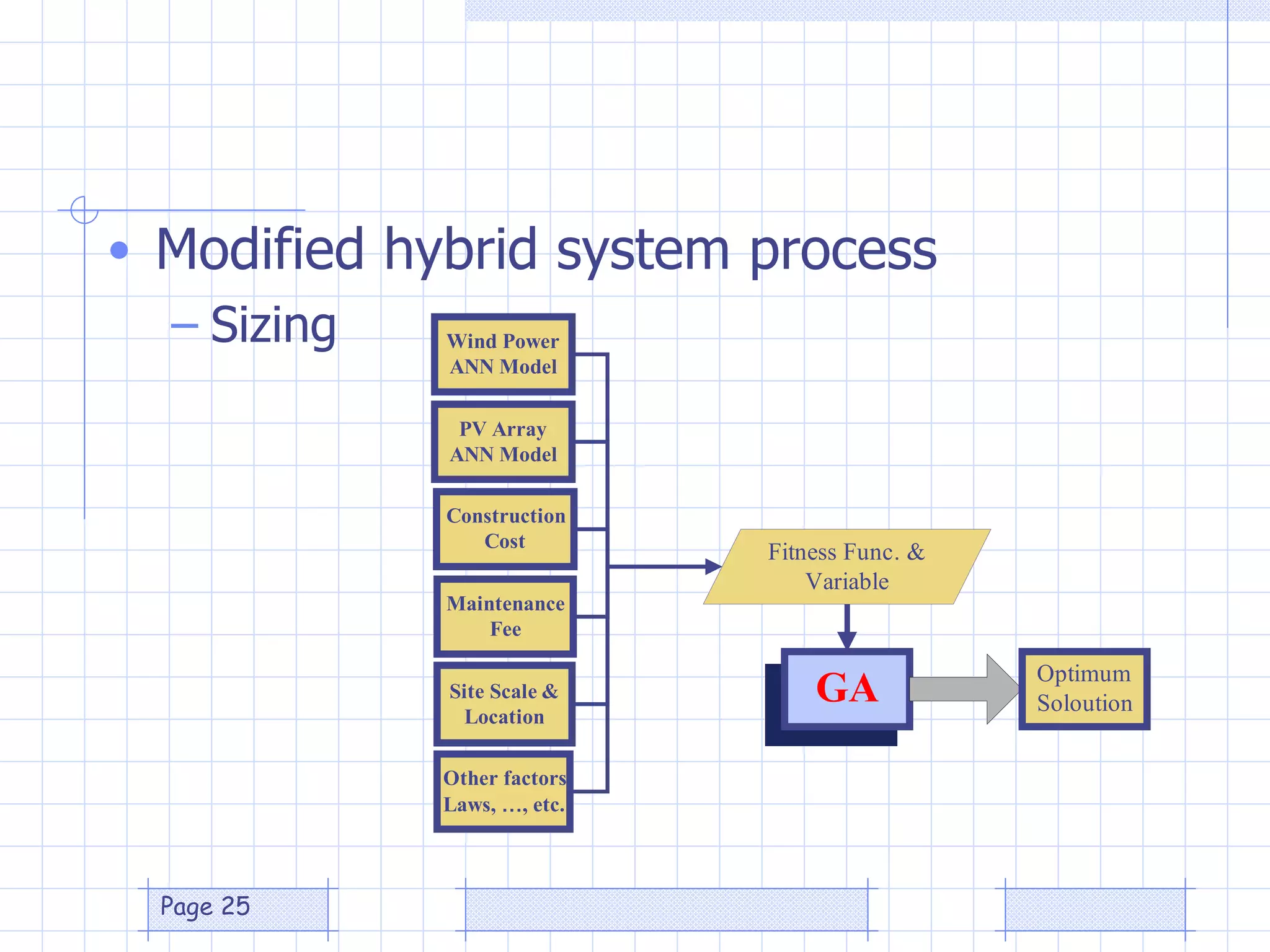
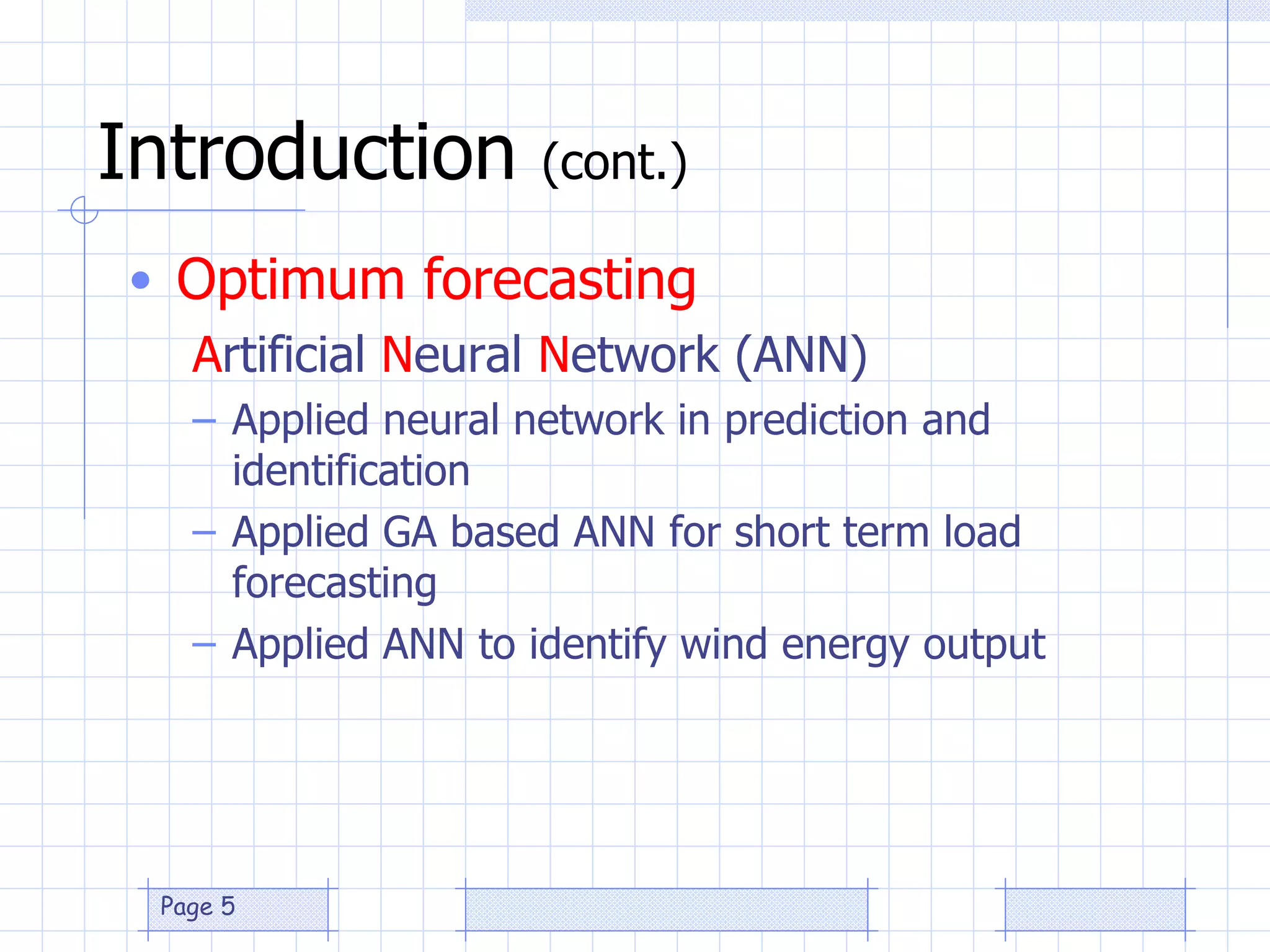
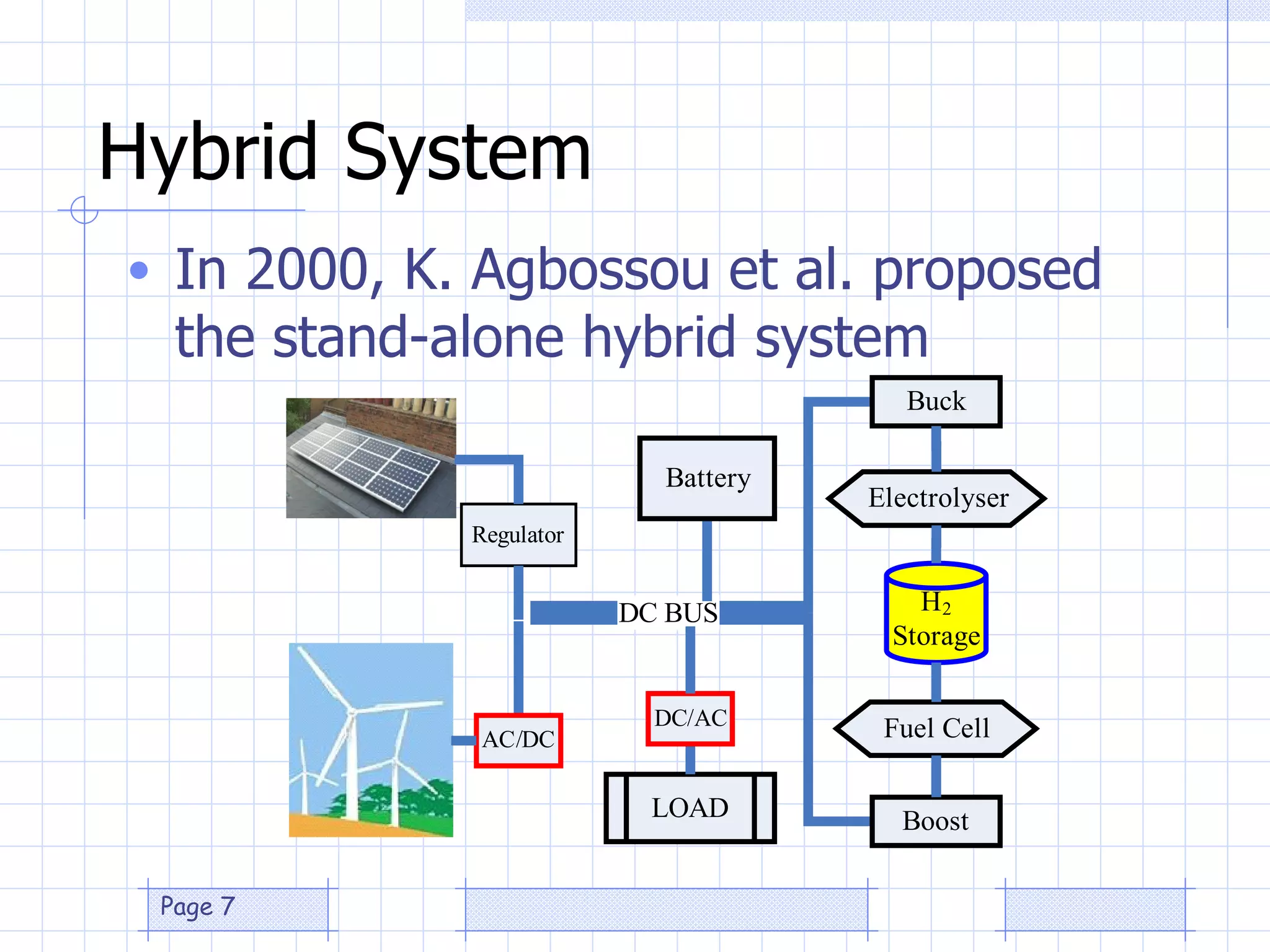
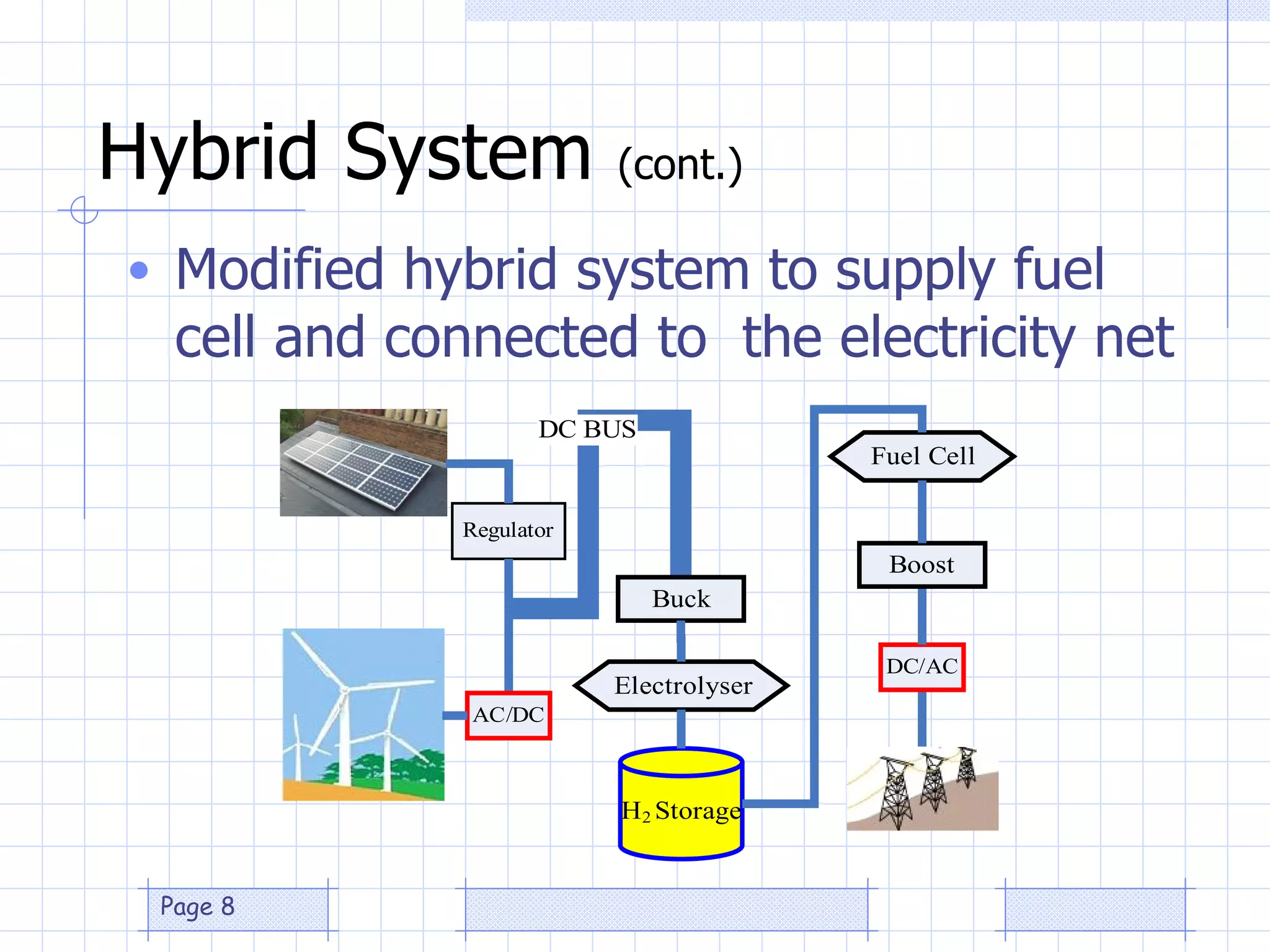
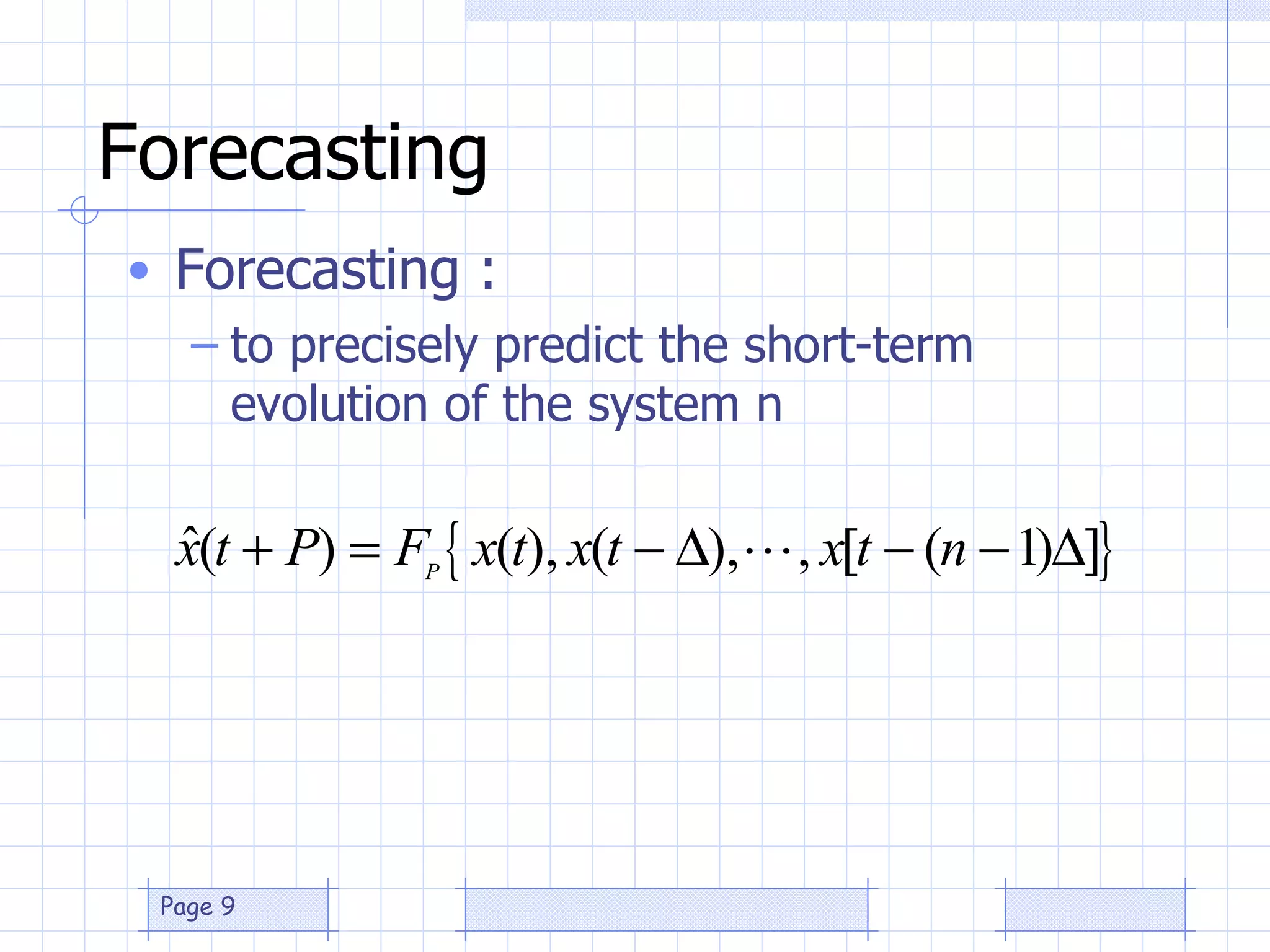
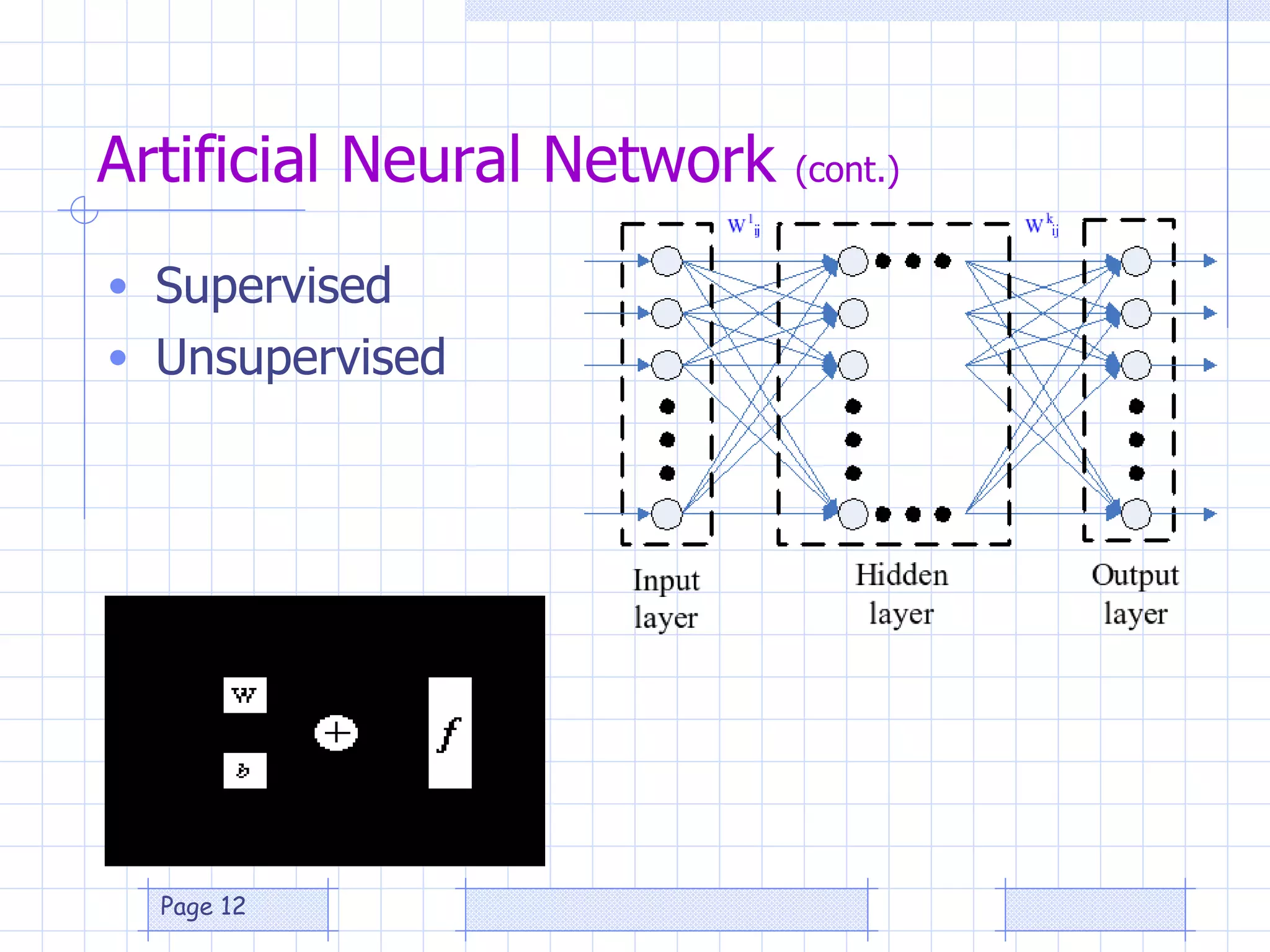
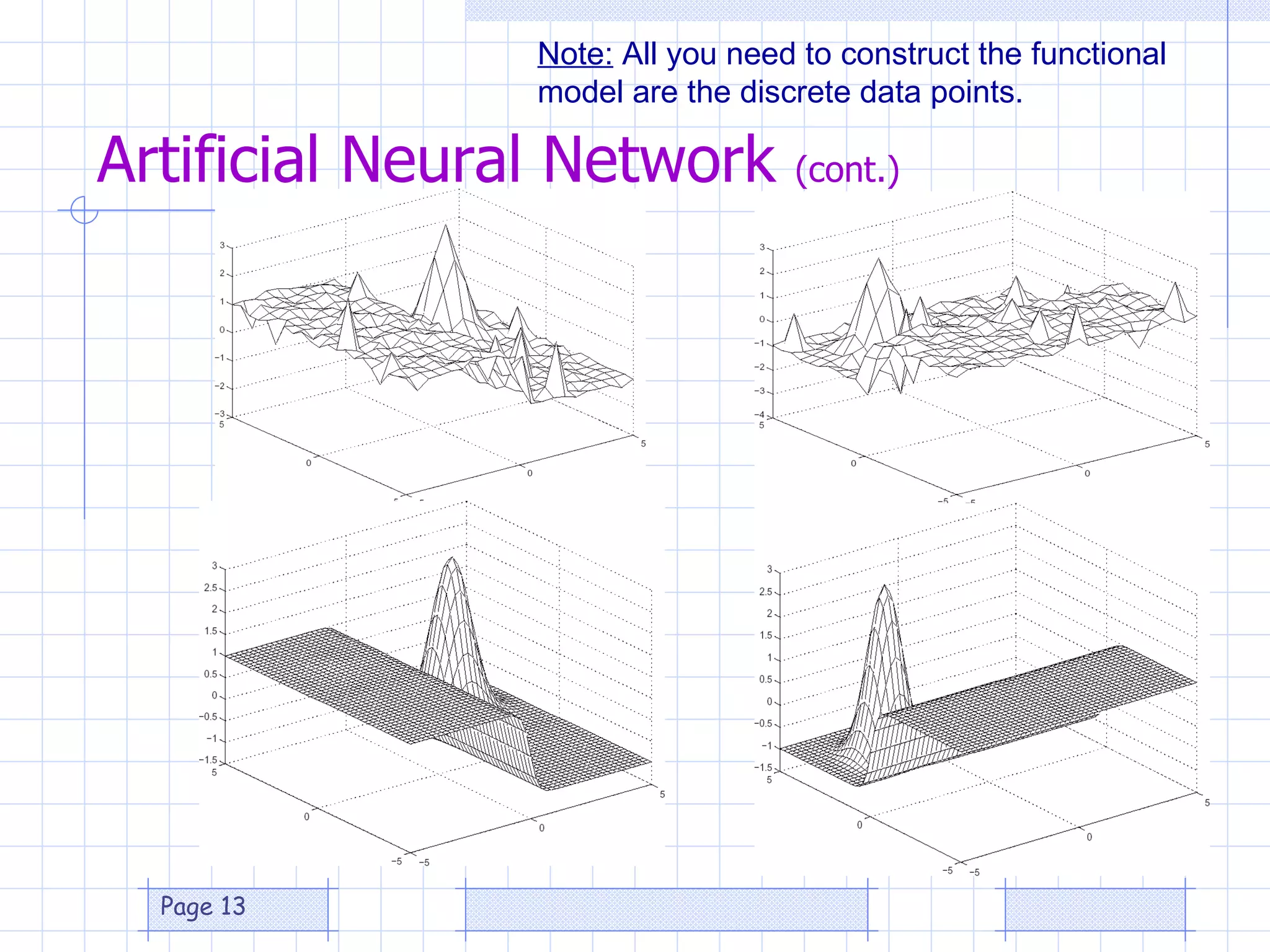
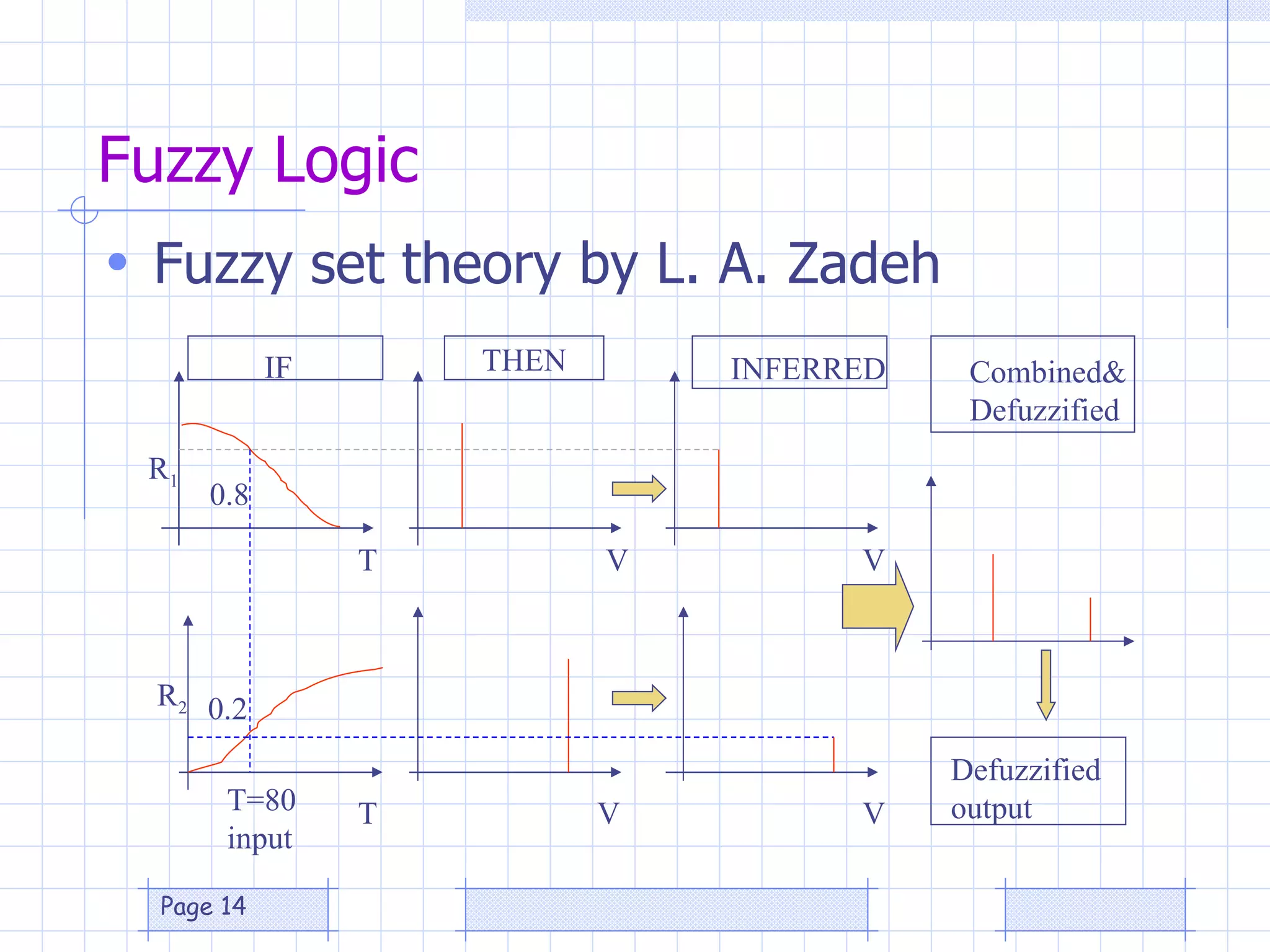
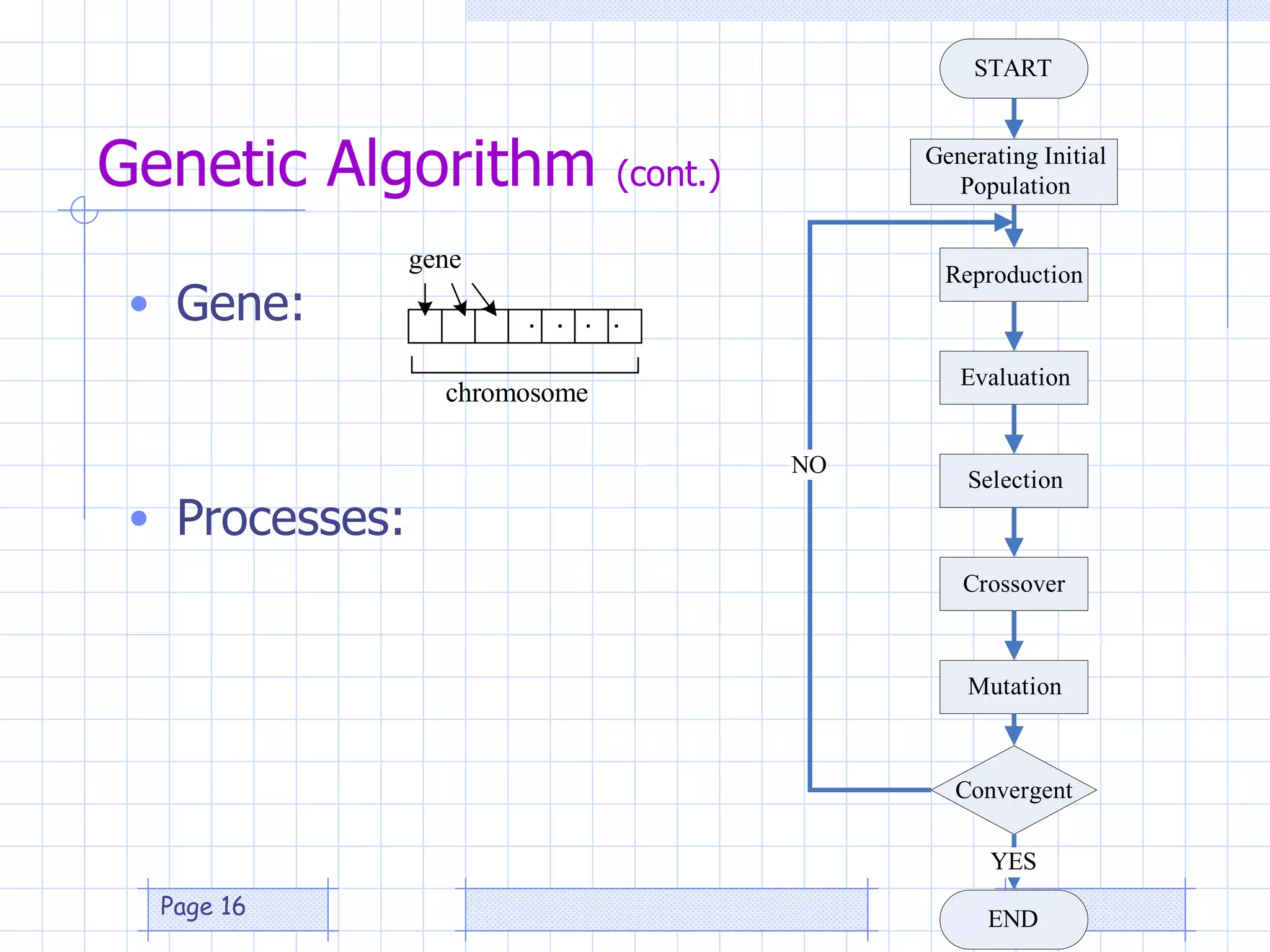
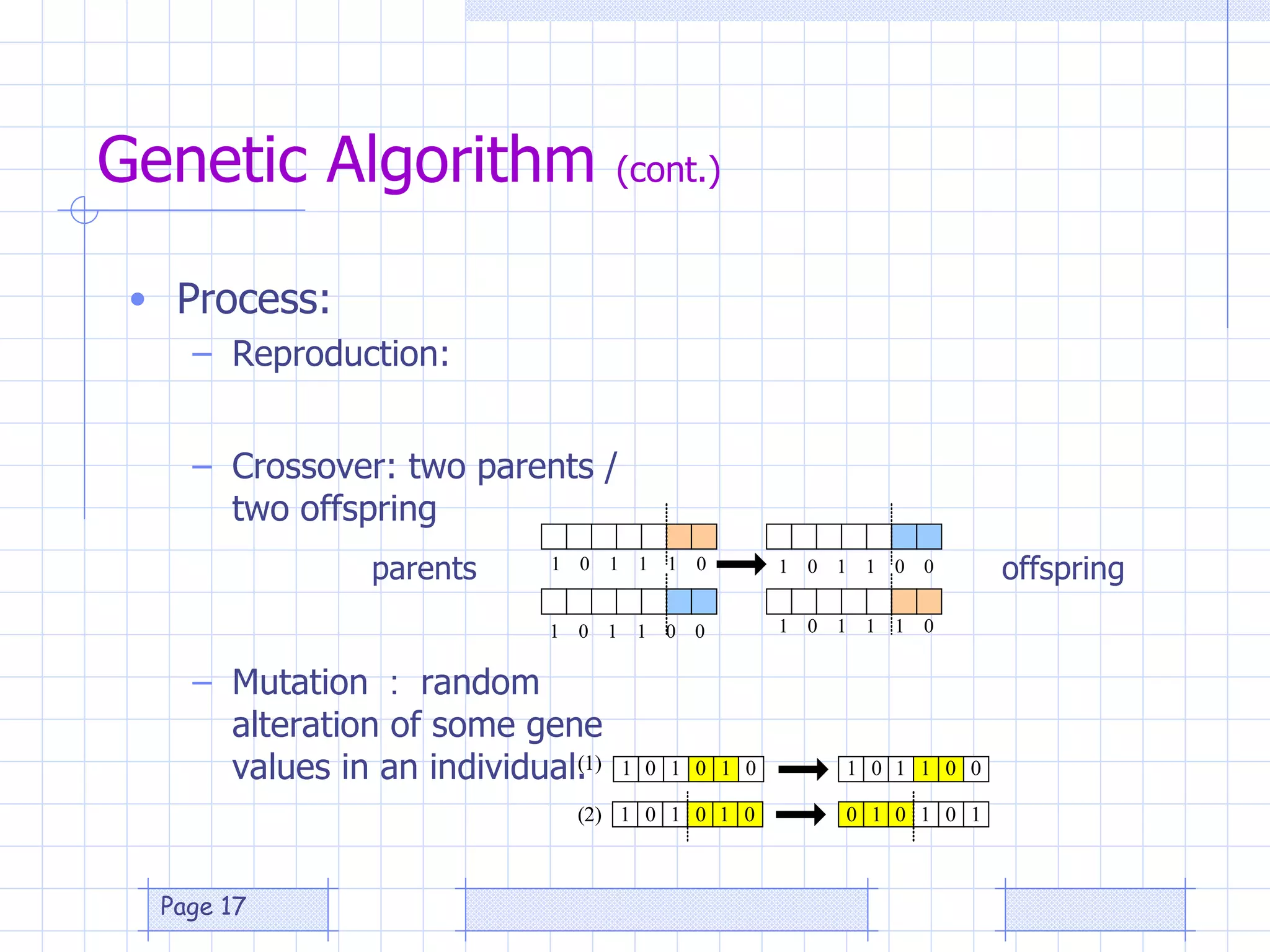
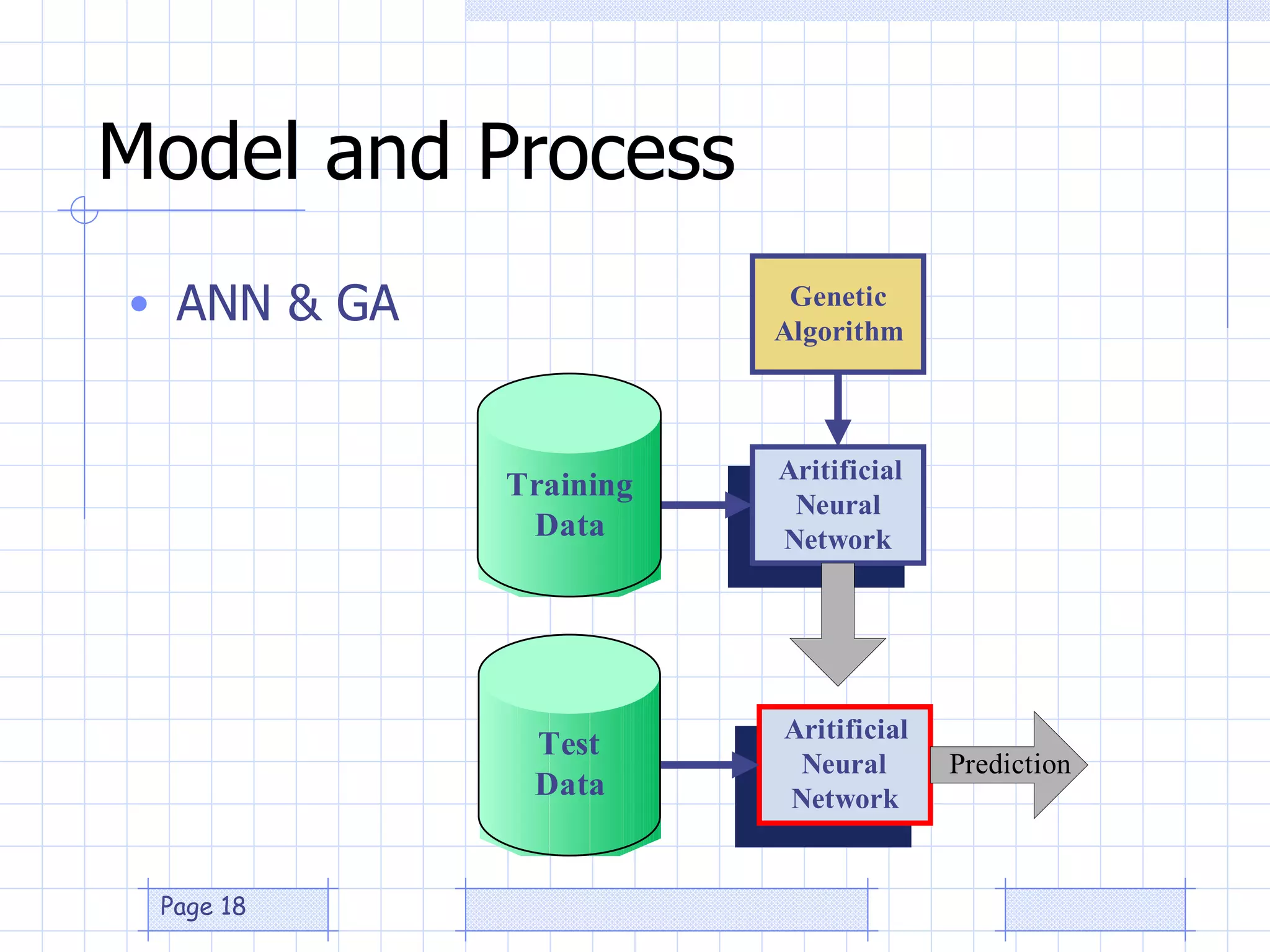
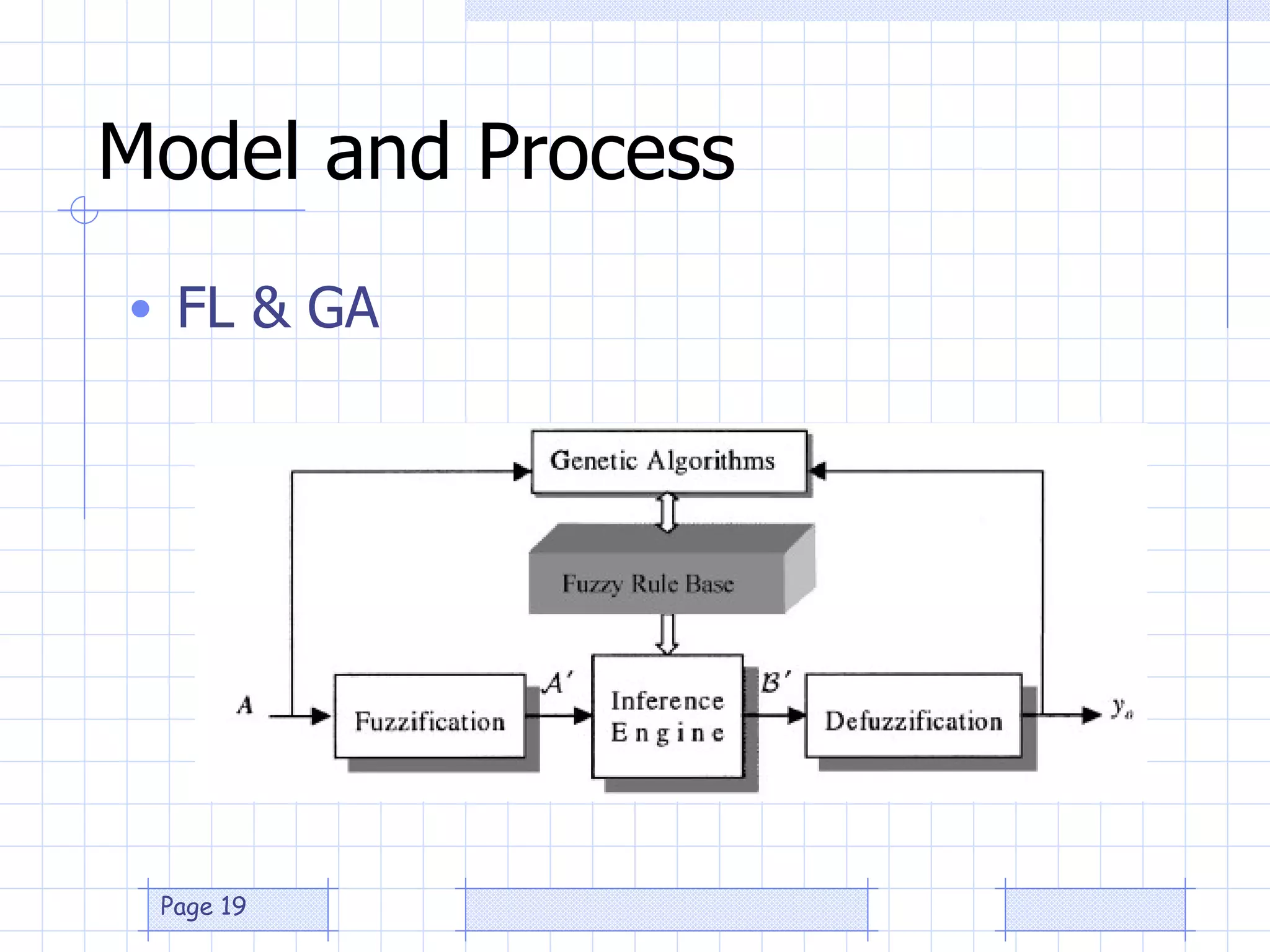
The document discusses the use of a genetic algorithm (GA) for forecasting renewable energy production, specifically focusing on optimizing hydrogen production potential through a hybrid system of wind and photovoltaic (PV) energy. It highlights the application of artificial neural networks and fuzzy logic in accurate forecasting as well as the efficiency of different forecasting models. The conclusions suggest that integrating GA with neural networks enhances accuracy, benefiting the sizing of hybrid renewable energy systems.


![Accuracy Comparison Mean square error of ANN prediction in [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forecasting-of-renewable-energy-production-by-using-genetic-algorithm-ga-for-determininghydrogen-production-potential-18912/75/FORECASTING-OF-RENEWABLE-ENERGY-PRODUCTION-BY-USING-GENETIC-ALGORITHM-GA-FOR-DETERMINING-HYDROGEN-PRODUCTION-POTENTIAL-20-2048.jpg)
![Table 1. Comparison results of RMSE of various forecasting models [4] Efficiency Comparison (cont.) 0.007 500 ANFIS 0.06 500 Cascade Correlation NN 0.55 500 Linear Predictive Method 0.0907 500 Product operator 0.09 500 Min operator 0.19 500 Auto Regressive Model 0.04 500 6th-order Polynomial 0.02 500 BP ANN 0.038011 (9 partition) 500 FL&GA Prediction Error (RMSE) Training Method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forecasting-of-renewable-energy-production-by-using-genetic-algorithm-ga-for-determininghydrogen-production-potential-18912/75/FORECASTING-OF-RENEWABLE-ENERGY-PRODUCTION-BY-USING-GENETIC-ALGORITHM-GA-FOR-DETERMINING-HYDROGEN-PRODUCTION-POTENTIAL-21-2048.jpg)