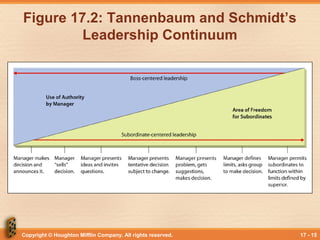
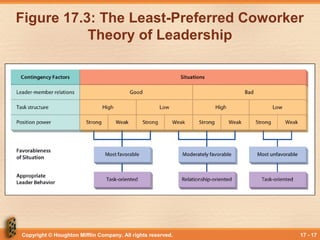
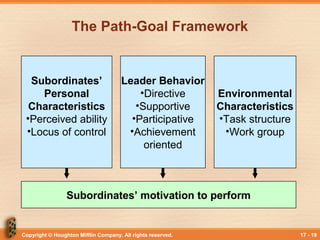
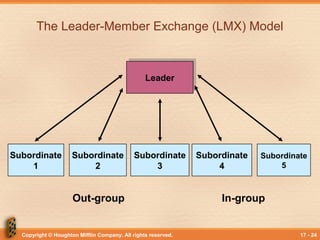
This document discusses various theories and models of leadership. It describes leadership as a process of non-coercive influence used to shape organizational goals and motivate behavior. Several leadership styles and theories are examined, including trait-based approaches, situational leadership theories, and those focused on leader-member relationships like LMX. Transformational leadership is defined as going beyond expectations to inspire new ways of thinking. Political behavior in organizations and impression management are also briefly covered.