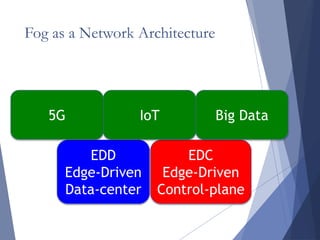
The document discusses fog networking, which uses edge devices and clients to perform computing tasks rather than routing all information through data centers. It defines fog networking as using end-user devices for storage, communication, and management. Edge devices are becoming more powerful but still have limitations. The document argues fog networking can enable real-time processing at the local level along with pooling local resources. It presents client resource pooling as a case study and identifies research challenges in areas like trustworthiness, incentives for client participation, and managing interactions between fog and cloud systems.