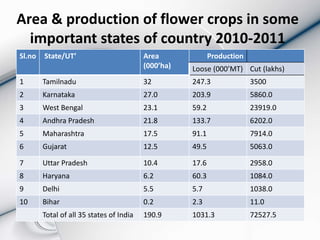
The floriculture industry has become a significant agricultural sector post-globalization, with potential for self-employment among small farmers and substantial foreign exchange earnings in developing countries like India. The global market is expanding at a rate of 15% annually, led by countries such as the Netherlands and Colombia, while India's floriculture sector is growing rapidly, projected to reach Rs. 8000 crore by 2015 with a focus on cut flowers for export. Key challenges include high costs of inputs and infrastructure issues, but opportunities in exports and product diversification remain promising.