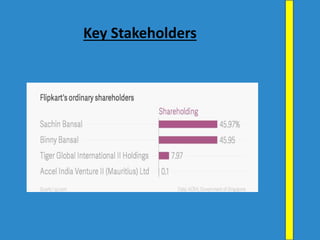
- Flipkart is India's largest e-commerce company that started as an online bookstore and has expanded into other product categories.
- It uses its own logistics network as well as third-party logistics to deliver products with a 30-day return policy.
- Flipkart targets urban Indian customers, especially young professionals, by offering low prices, payment options, and fast delivery compared to physical retailers.