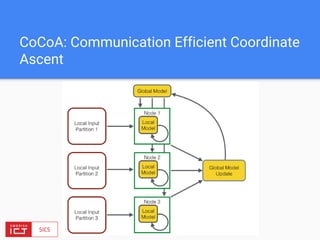
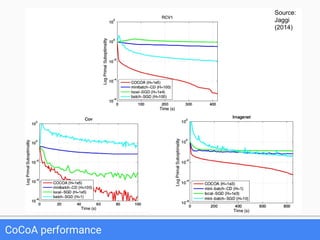
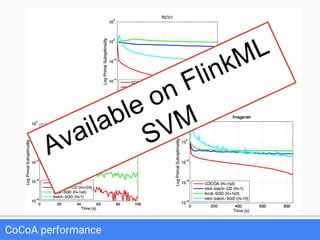
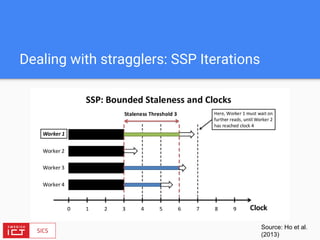
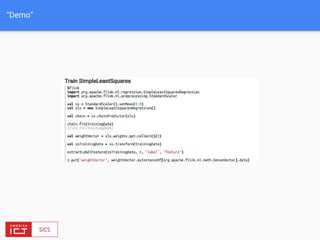
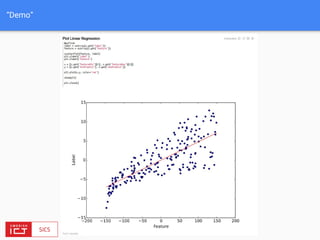
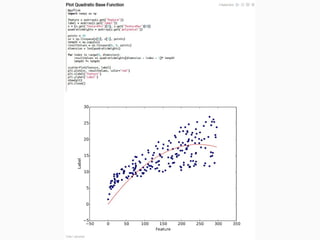
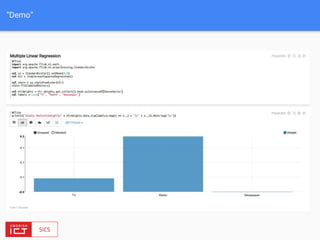
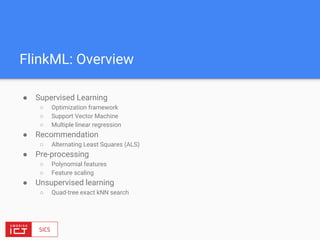
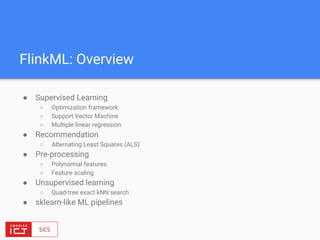
The document discusses FlinkML, an effort to enhance Apache Flink with large-scale machine learning capabilities, emphasizing scalable implementations and ease of use. It covers various aspects such as supervised and unsupervised learning, optimization frameworks, recommendation systems, and techniques for managing stragglers in distributed machine learning. Additionally, the document outlines current tools and algorithms being developed for FlinkML, including streaming machine learning techniques.




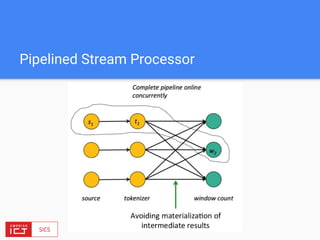
![Expressive APIs
● Main bounded data abstraction: DataSet
● Program using functional-style transformations, creating a dataflow.
case class Word(word: String, frequency: Int)
val lines: DataSet[String] = env.readTextFile(...)
lines.flatMap(line => line.split(“ “).map(word => Word(word, 1))
.groupBy(“word”).sum(“frequency”)
.print()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataapplicationsmeetup-160727175922/85/FlinkML-Big-data-application-meetup-11-320.jpg)
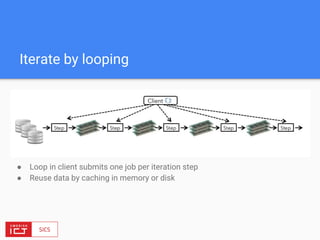
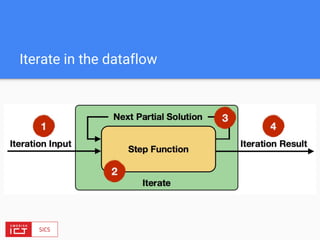
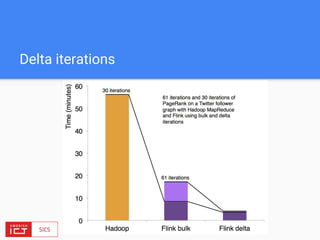
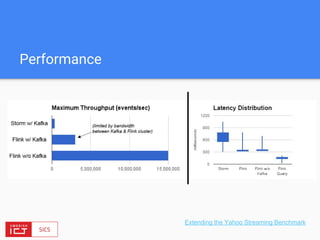



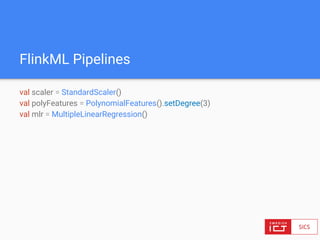
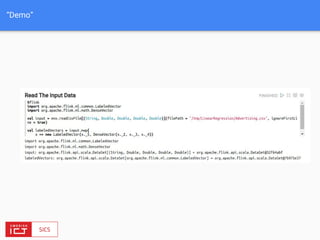
![FlinkML API
// LabeledVector is a feature vector with a label (class or real value)
val trainingData: DataSet[LabeledVector] = ...
val testingData: DataSet[Vector] = ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataapplicationsmeetup-160727175922/85/FlinkML-Big-data-application-meetup-27-320.jpg)
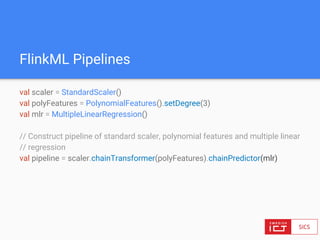
![FlinkML API
// LabeledVector is a feature vector with a label (class or real value)
val trainingData: DataSet[LabeledVector] = ...
val testingData: DataSet[Vector] = ...
val mlr = MultipleLinearRegression()
.setStepsize(0.01)
.setIterations(100)
.setConvergenceThreshold(0.001)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataapplicationsmeetup-160727175922/85/FlinkML-Big-data-application-meetup-28-320.jpg)
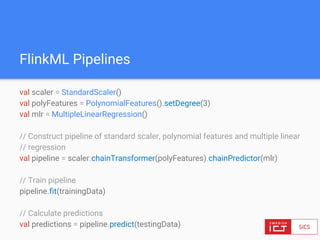
![FlinkML API
// LabeledVector is a feature vector with a label (class or real value)
val trainingData: DataSet[LabeledVector] = ...
val testingData: DataSet[Vector] = ...
val mlr = MultipleLinearRegression()
.setStepsize(0.01)
.setIterations(100)
.setConvergenceThreshold(0.001)
mlr.fit(trainingData)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataapplicationsmeetup-160727175922/85/FlinkML-Big-data-application-meetup-29-320.jpg)
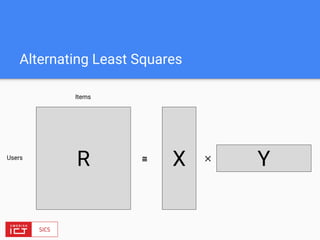
![FlinkML API
// LabeledVector is a feature vector with a label (class or real value)
val trainingData: DataSet[LabeledVector] = ...
val testingData: DataSet[Vector] = ...
val mlr = MultipleLinearRegression()
.setStepsize(0.01)
.setIterations(100)
.setConvergenceThreshold(0.001)
mlr.fit(trainingData)
// The fitted model can now be used to make predictions
val predictions: DataSet[LabeledVector] = mlr.predict(testingData)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataapplicationsmeetup-160727175922/85/FlinkML-Big-data-application-meetup-30-320.jpg)