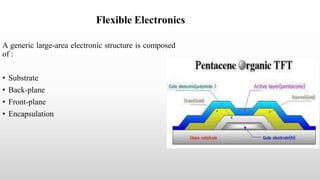
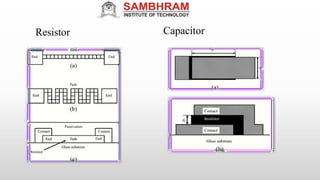
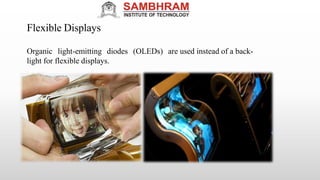
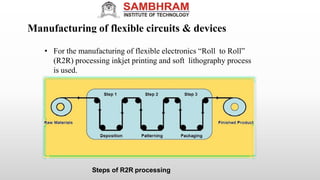
This document summarizes a technical seminar on flexible electronics presented by Ginnam Mahalaxmi. The seminar covered an introduction to flexible electronics, fabrication technologies, flexible circuit boards and components, manufacturing processes, materials and thickness used, market growth and applications. Flexible electronics uses flexible plastic substrates to assemble electronic circuits. Key fabrication methods discussed were roll-to-roll processing and inkjet printing. Applications mentioned include wearables, displays, solar cells and medical devices. Advantages of flexible electronics are lighter weight, smaller size and bendable form factors.
![Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
A Technical Seminar
on
“Flexible Electronics”
Presentation By
GINNAM MAHALAXMI
[1ST15EC134]
Dept. of ECE, SaIT.
Under the guidance of
Prof. S.SOWNDESWARI
Professor,
Dept. of ECE,
SaIT, Bengaluru - 560097
Technical Seminar Coordinators
Prof. YOGANADINI P
Prof. SUDHA J.
Dept. of ECE,
SaIT ,Bengaluru - 560097](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mahalaxmitechnicalseminarpresentation-copy-221128144358-89cc88c3/75/Mahalaxmi-technical-seminar-presentation-Copy-pptx-1-2048.jpg)
















![References
• [1] www.wikkipedia.org.in/flexibleelectronics
• [2] "Printed Circuit Techniques" by Cledo Brunetti and Roger W. Curtis
(National Bureau of Standards Circular 468 first issued 15 November
1947)
• [3] Gleskova, H., Wagner, S., Gasˇpar k, V. & Kova´cˇ, P. 150uC
Amorphous Silicon thin-Film Transistor technology for Polyimide
Substrates. J.Electrochem. Soc.148, G370-G374 (2001)
• [4] Cotema, coating machinery GmbH www.cotema.de
• [5]https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/printed-
electronics-market-197.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mahalaxmitechnicalseminarpresentation-copy-221128144358-89cc88c3/85/Mahalaxmi-technical-seminar-presentation-Copy-pptx-24-320.jpg)
