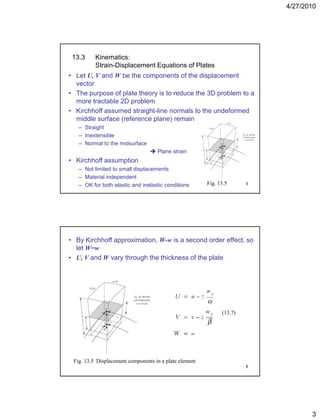
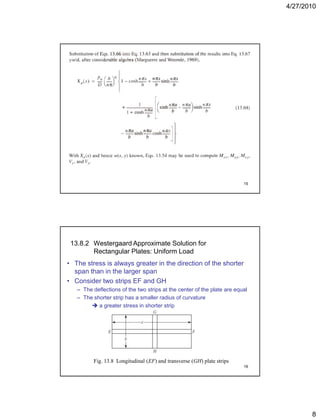
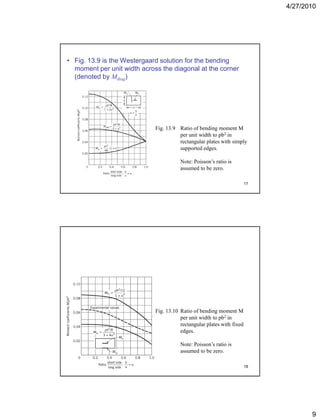
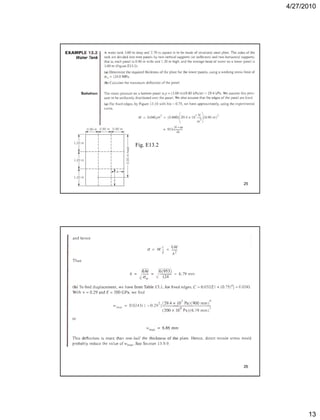
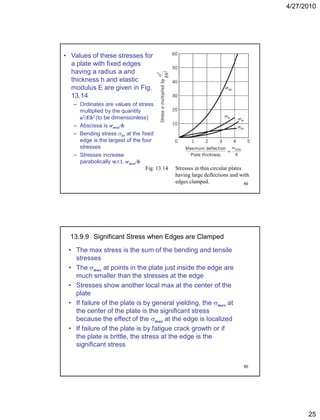
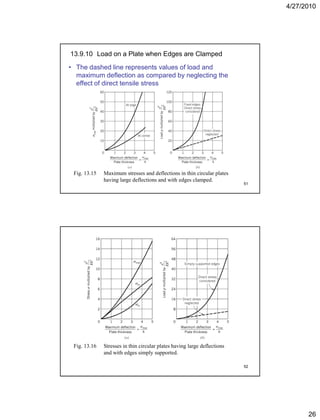
This document summarizes key concepts in plate theory from Chapter 13. Some key points:
- Flat plates are structural members where the thickness is small relative to length and width, with the middle surface lying in a plane. Plate theory reduces the 3D problem to 2D.
- Stress resultants in plates include in-plane forces (Nxx, Nyy, Nxy), bending moments (Mxx, Myy), and shears (Qx, Qy). Boundary conditions for plates include no displacement, no slope, no moment, and no shear.
- Closed-form solutions exist for rectangular and circular plates with various edge conditions (simply supported, fixed) subjected to uniform loads

![4/27/2010
2
3
• Special notation for
– In-plane forces (tractions), Nxx, Nyy, Nxy [force per unit length]
– Bending moments, Mxx, Myy [moment per unit length]
– Twisting moments, Mxy [moment per unit length]
– Shears, Qx, Qy, [force per unit length]
13.2 Stress Resultants in a Flat Plate
Fig. 13.2 Infinitesimal element of a flat plate
Fig. 13.3 Resultant tractions on a reference surface
4Fig. 13.4 Resultant moments and shears on a reference surface](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flatplatedeflection-chapter131-180920005738/85/Flat-plate-deflection-chapter13-1-2-320.jpg)