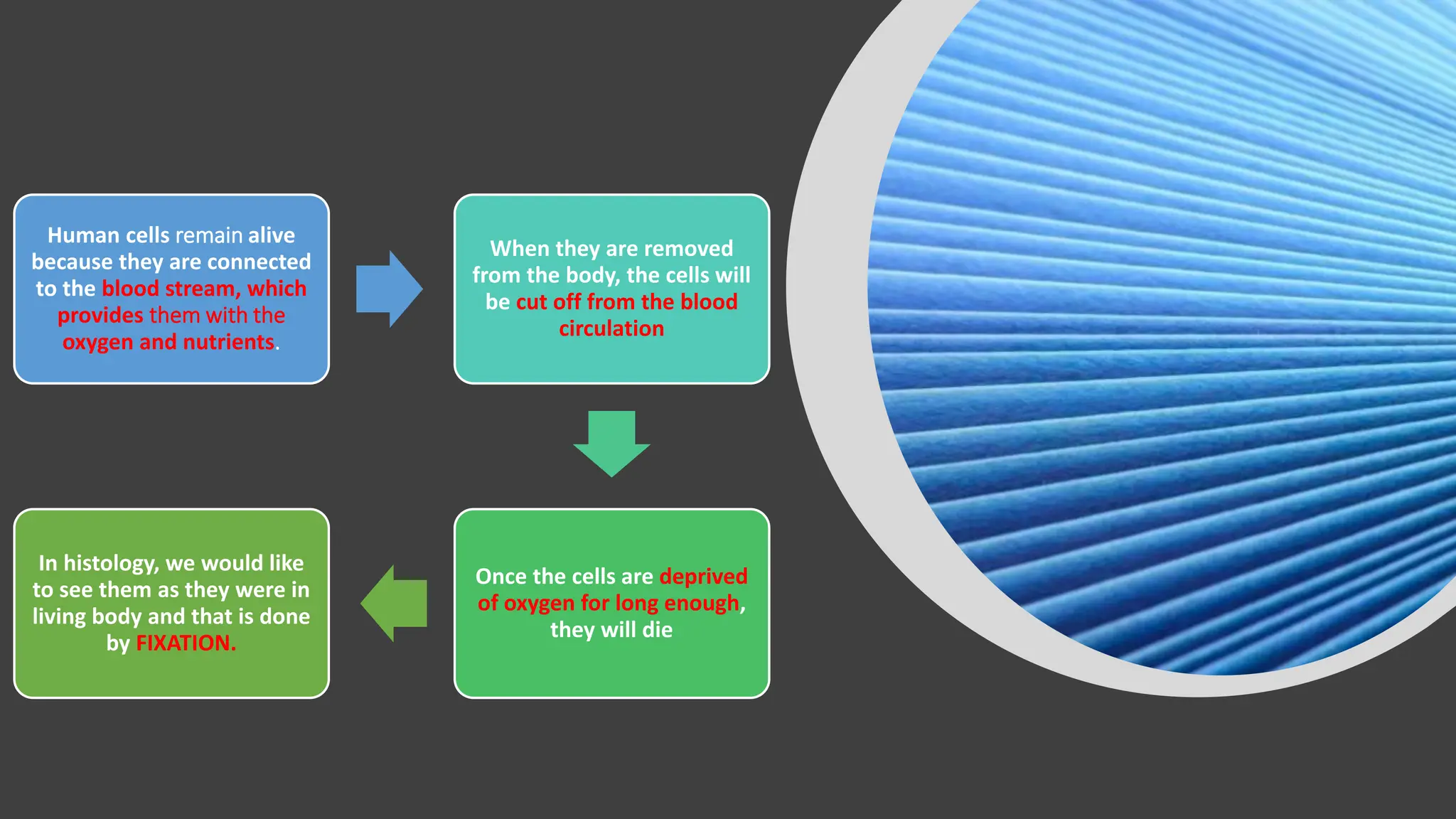
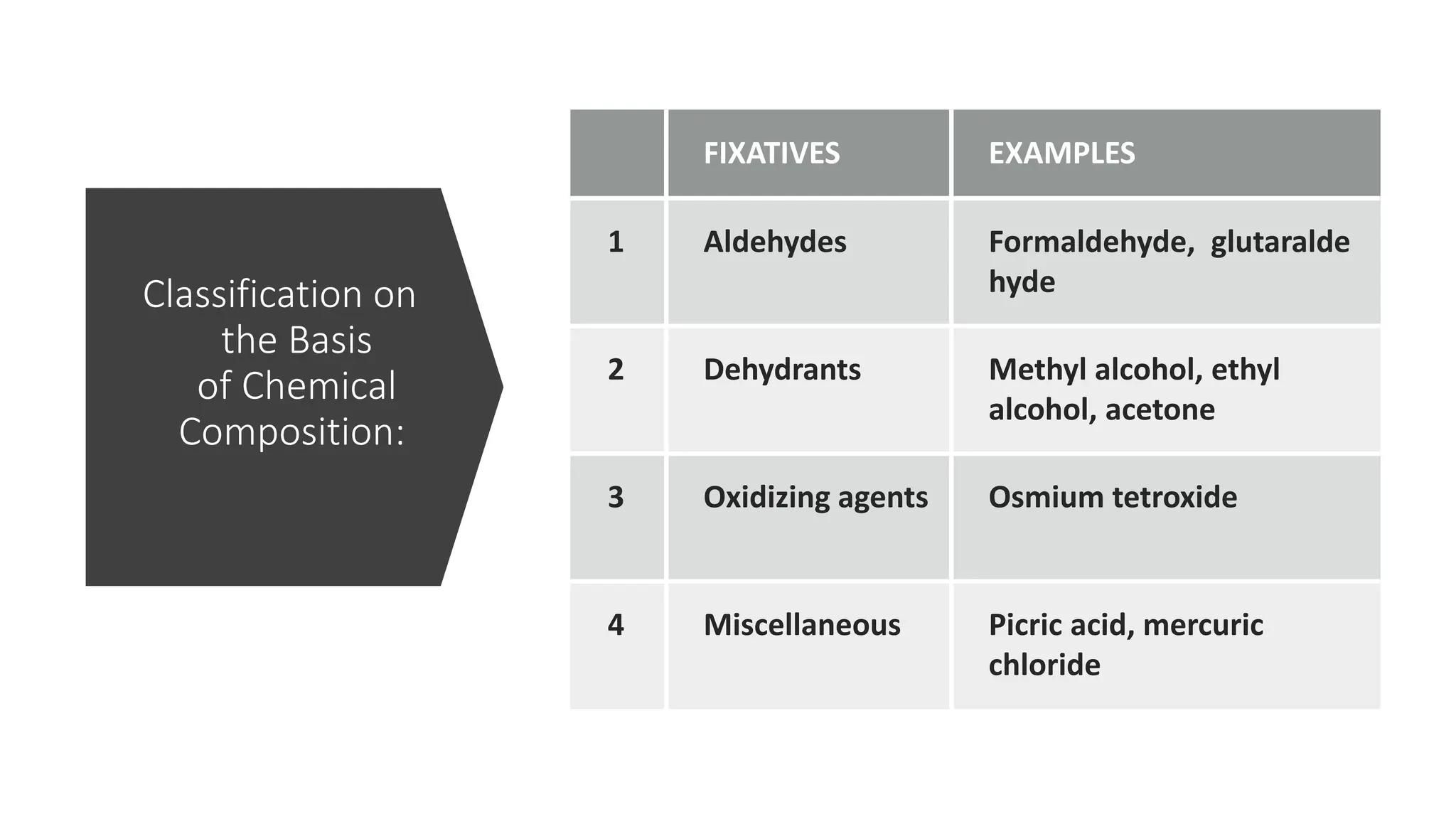
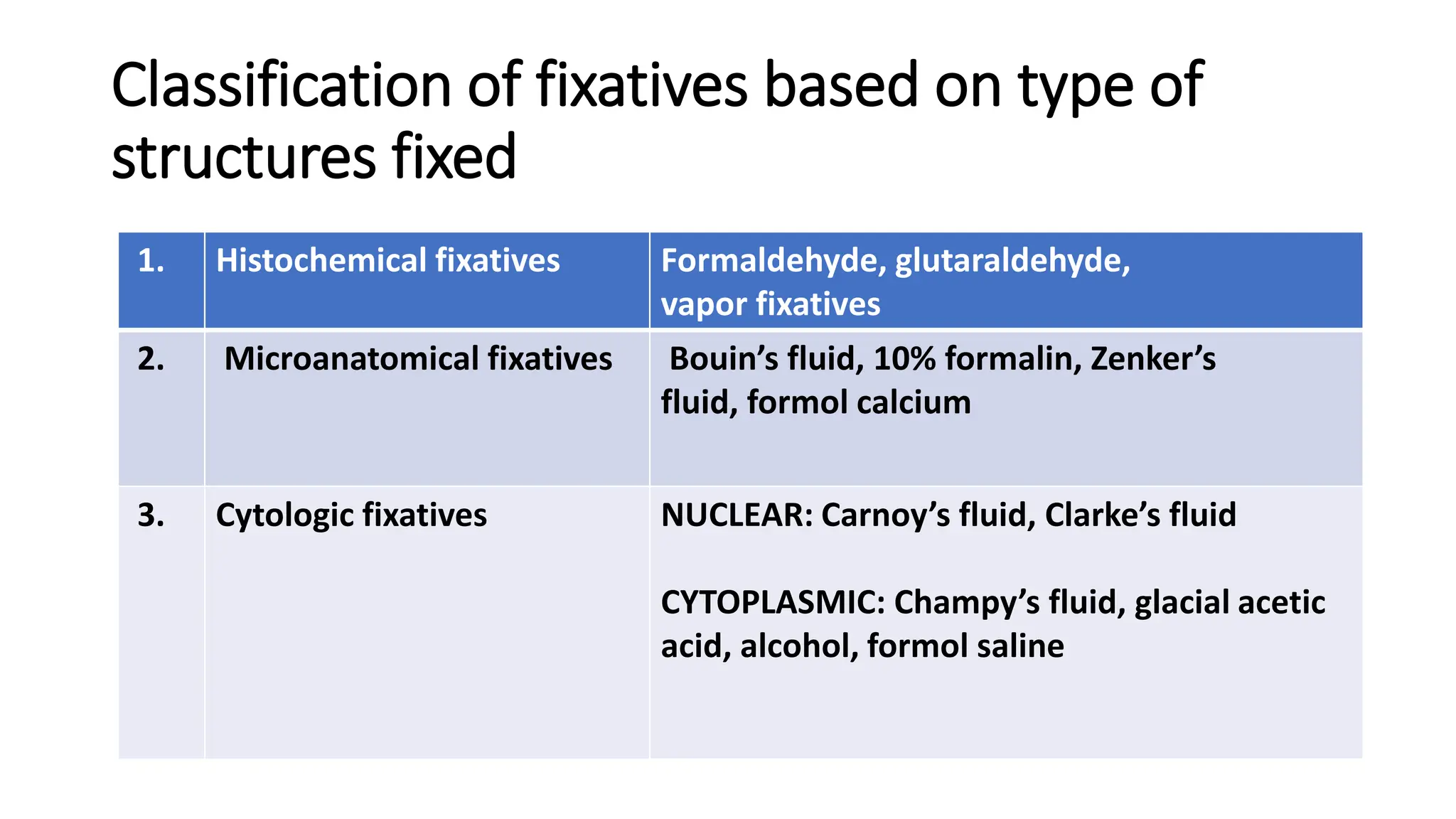
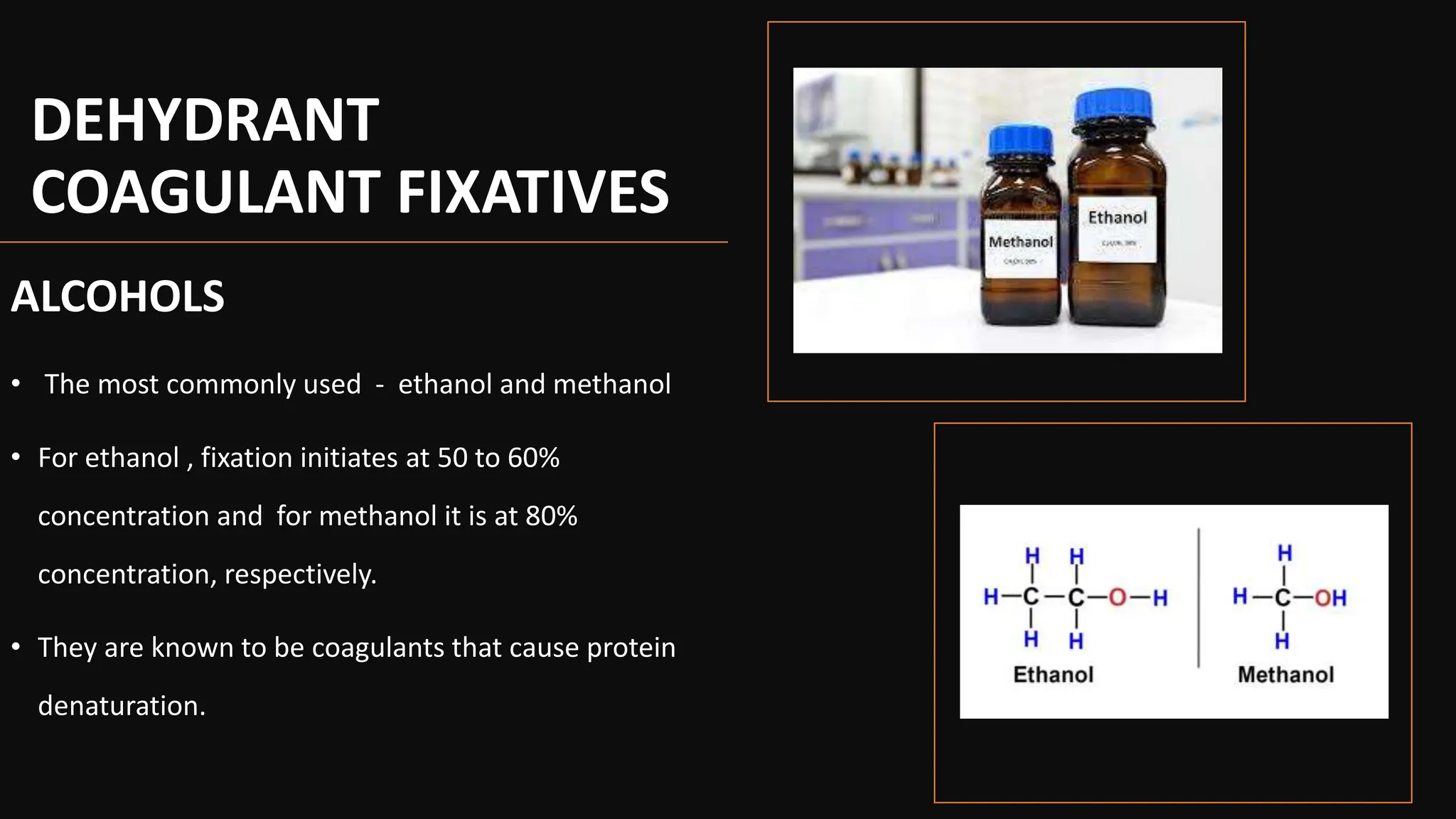
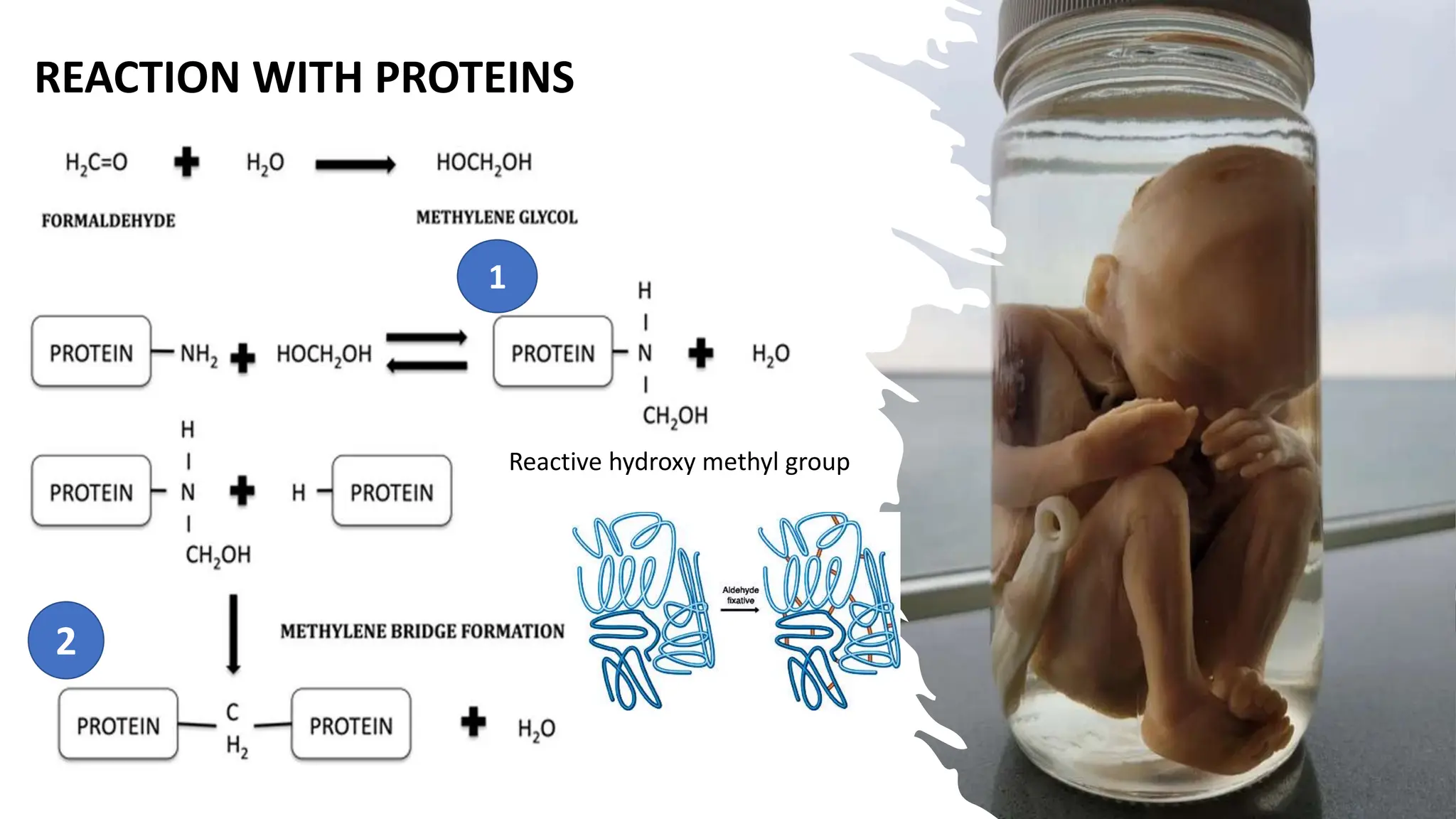
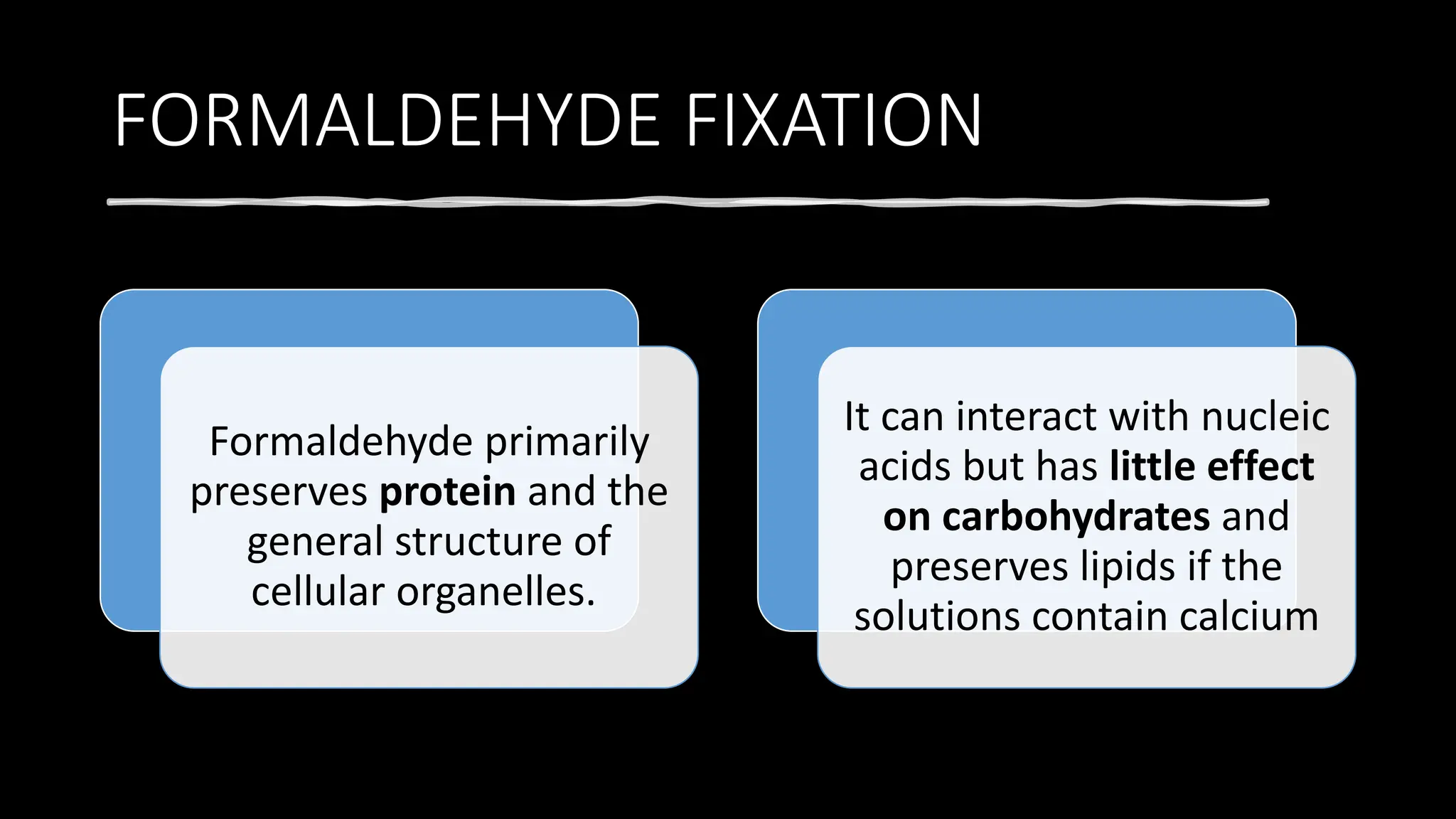
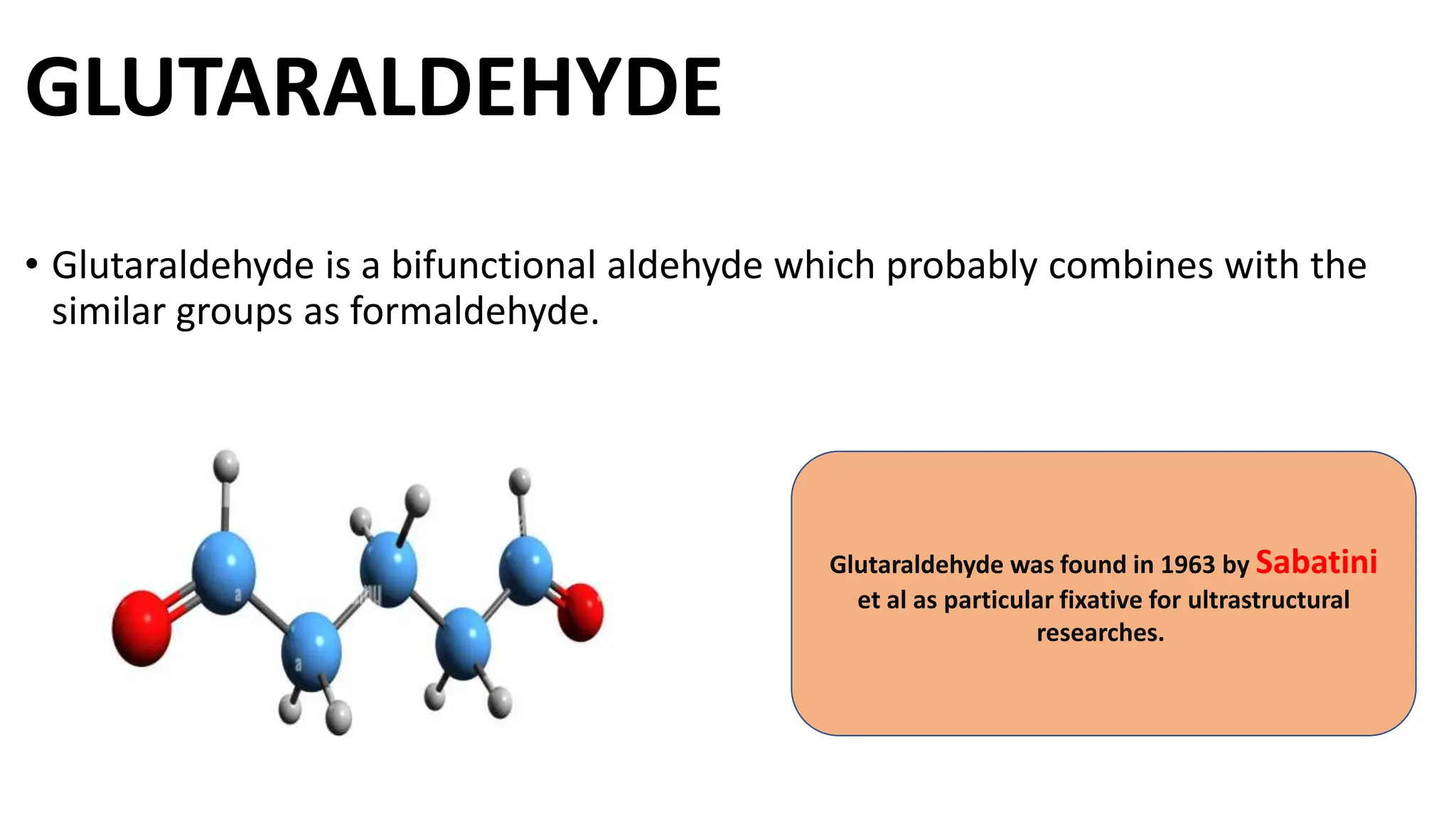
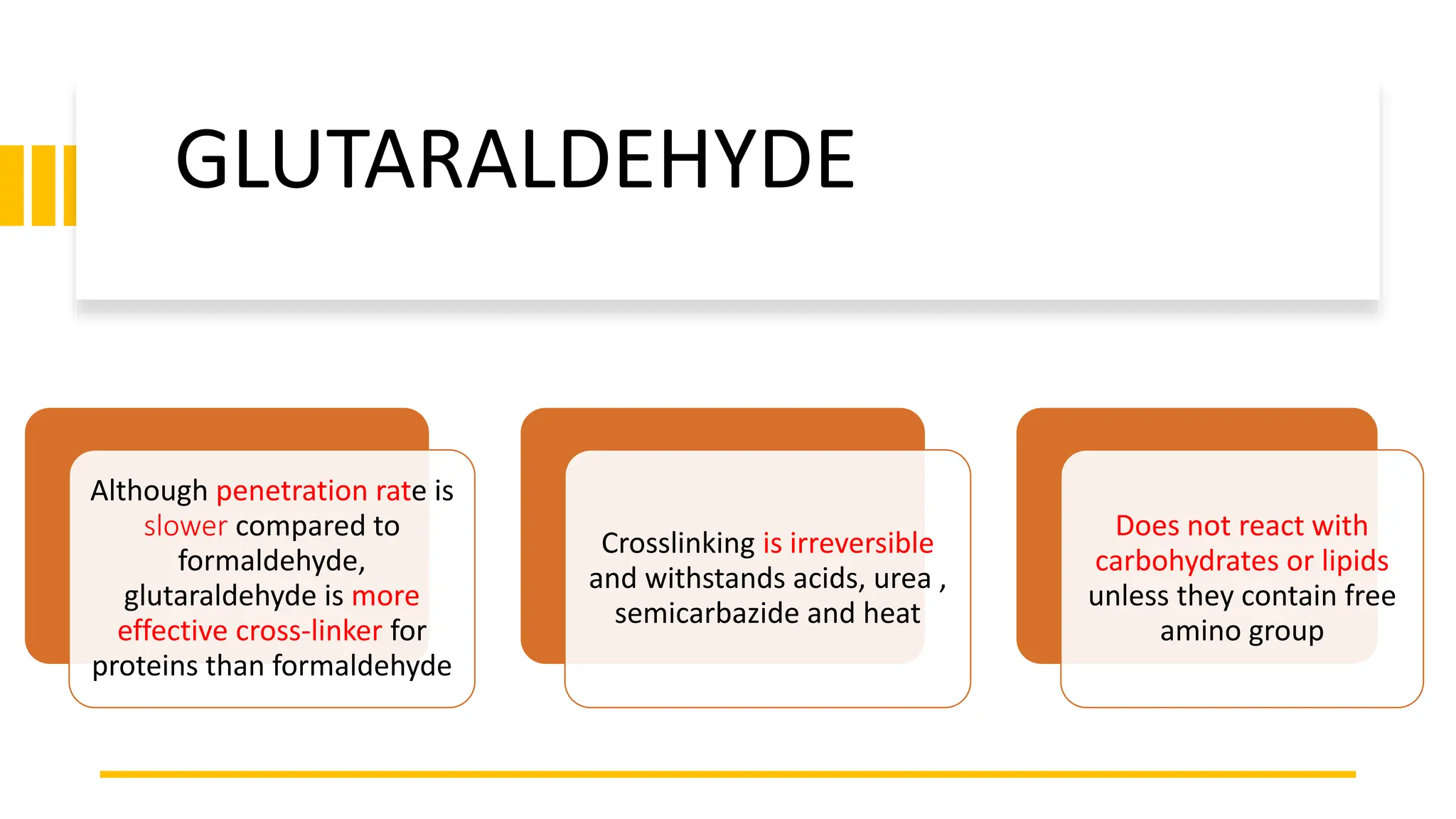
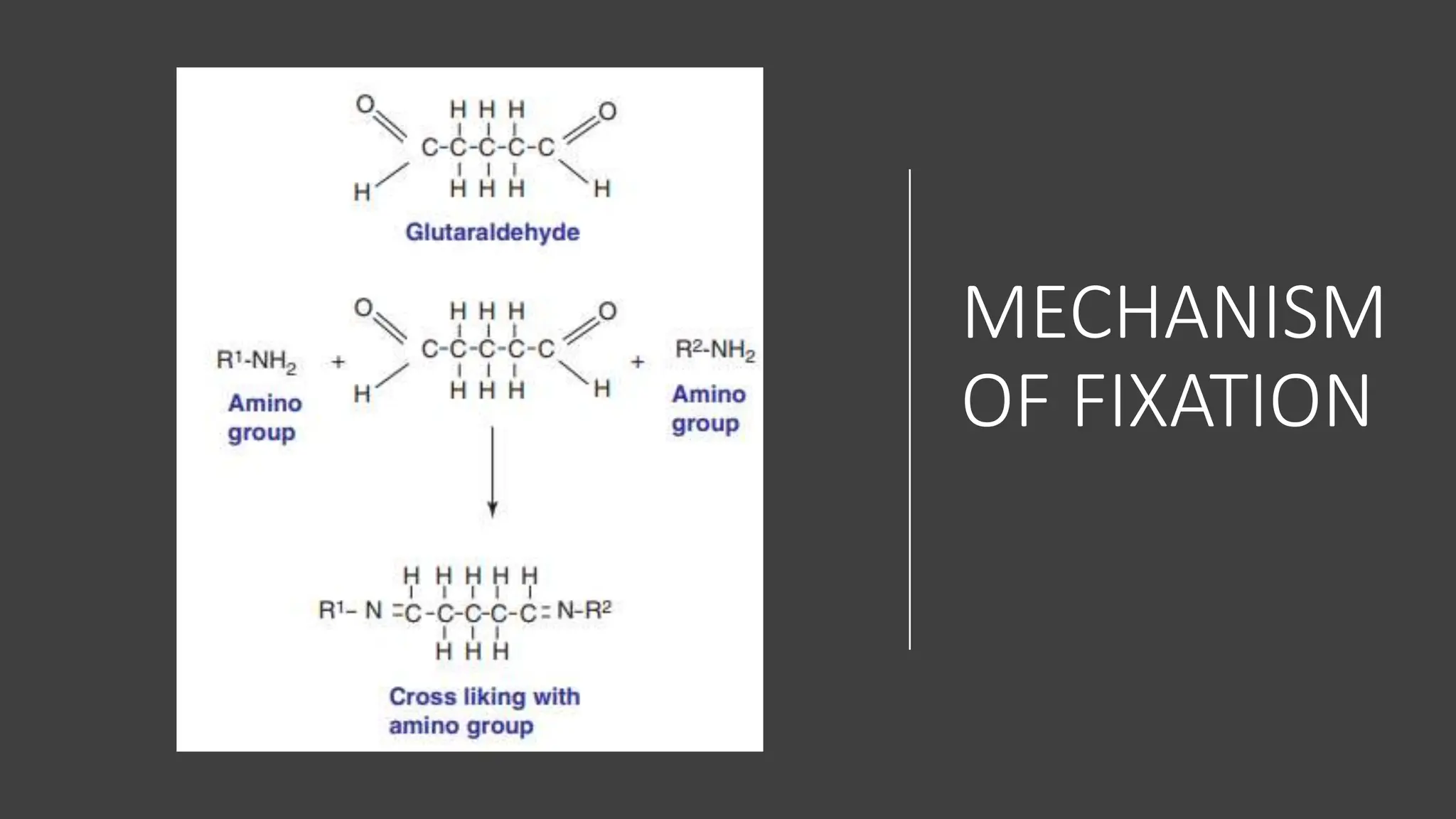
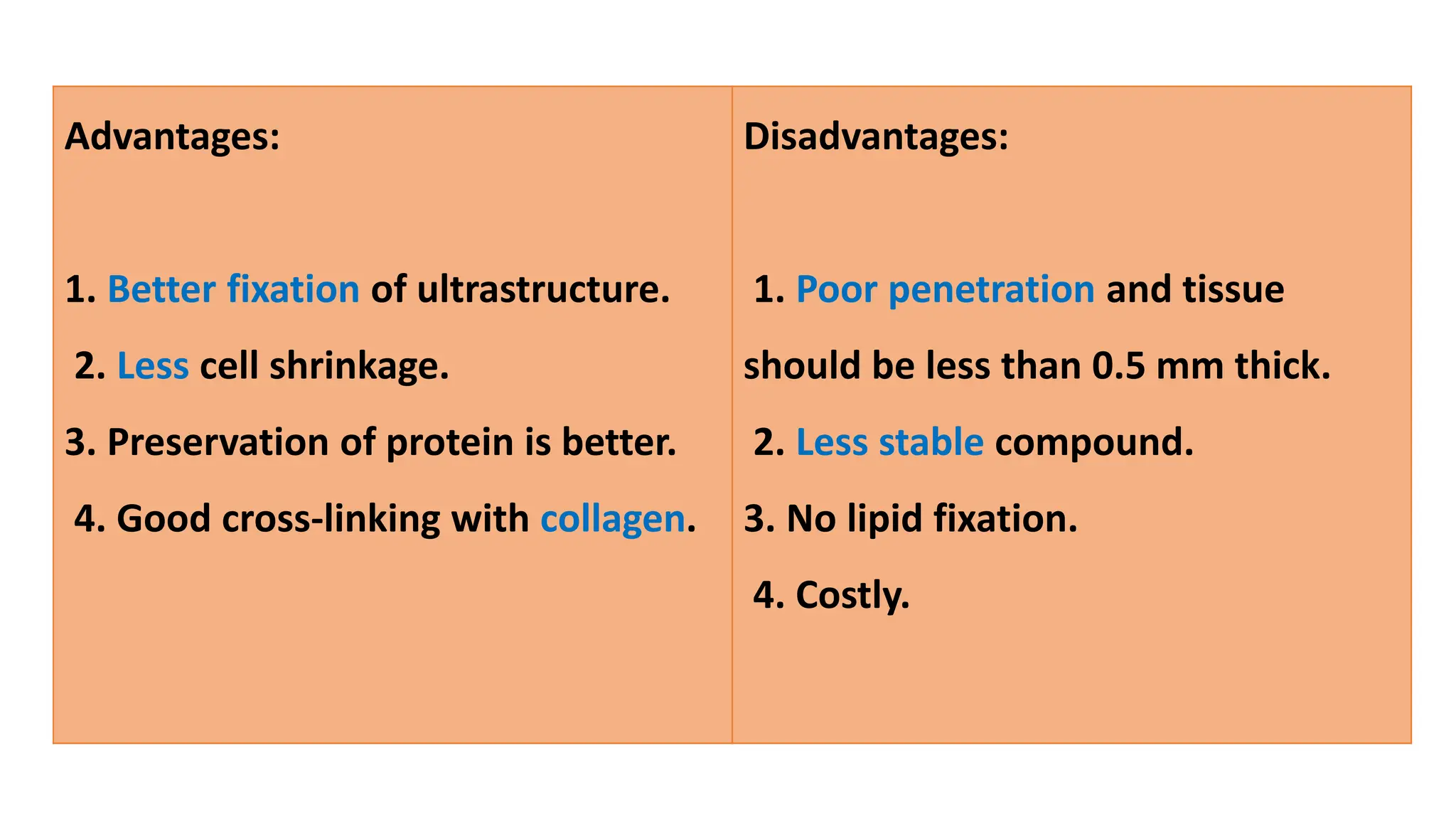
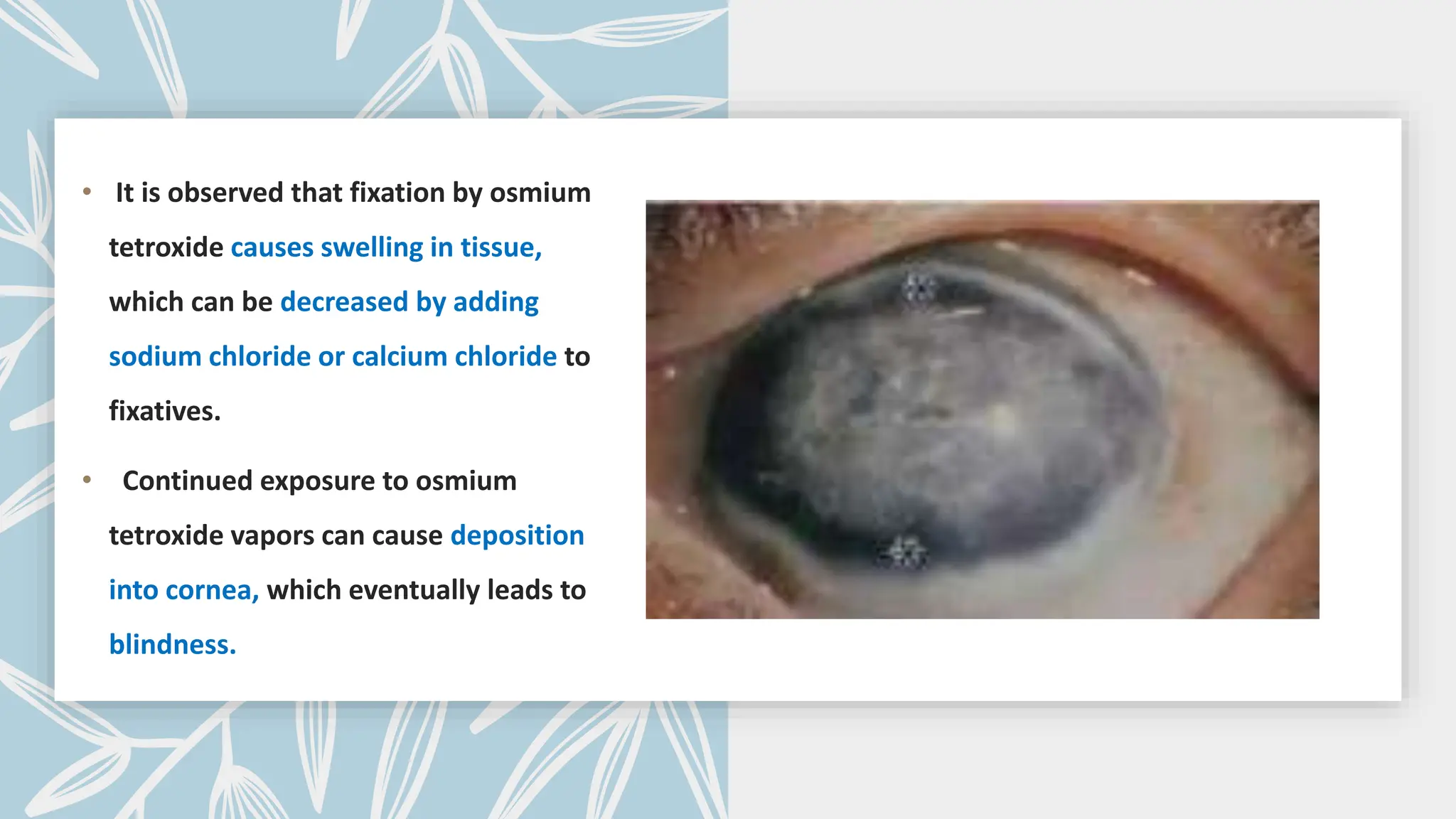
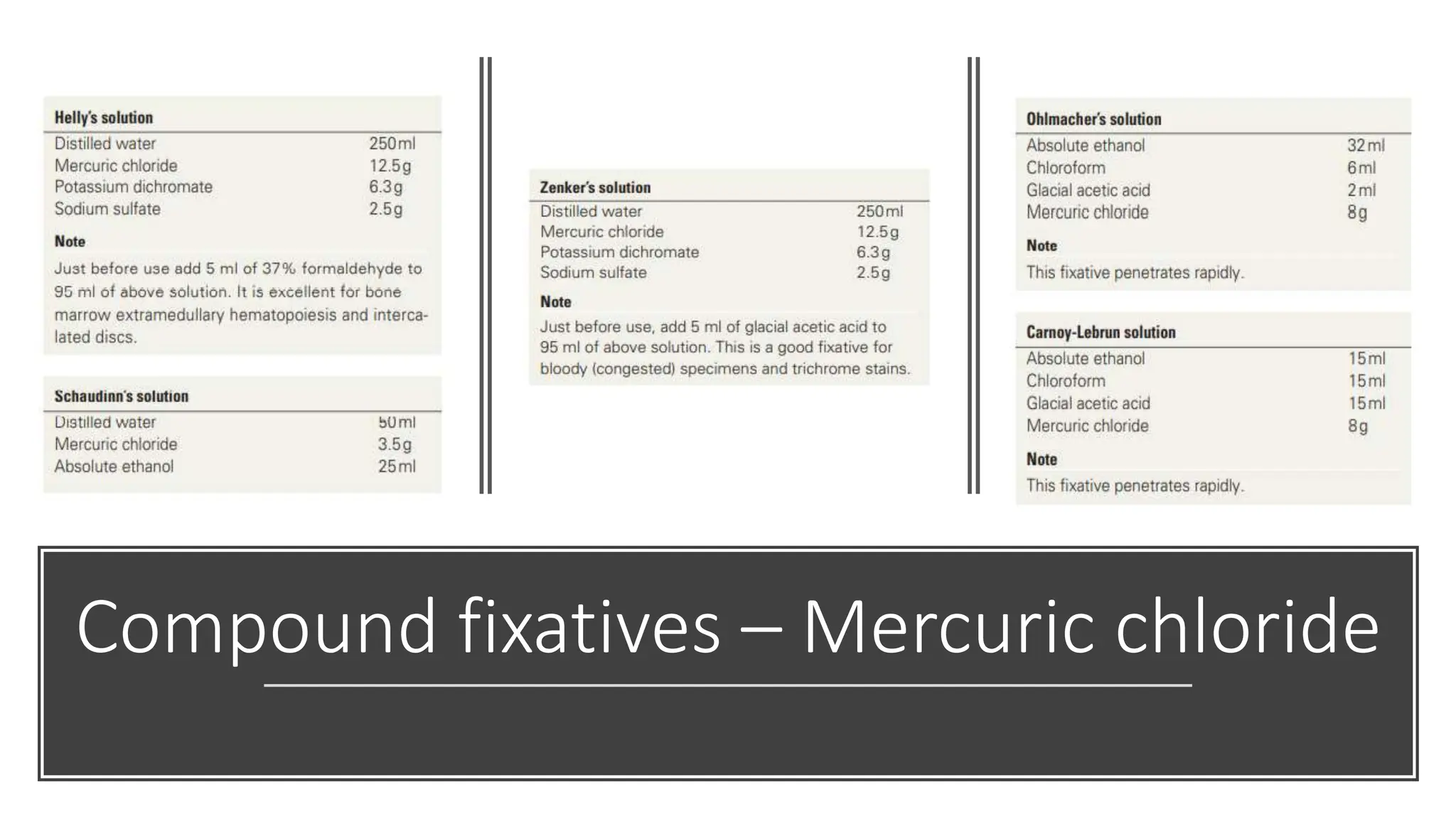
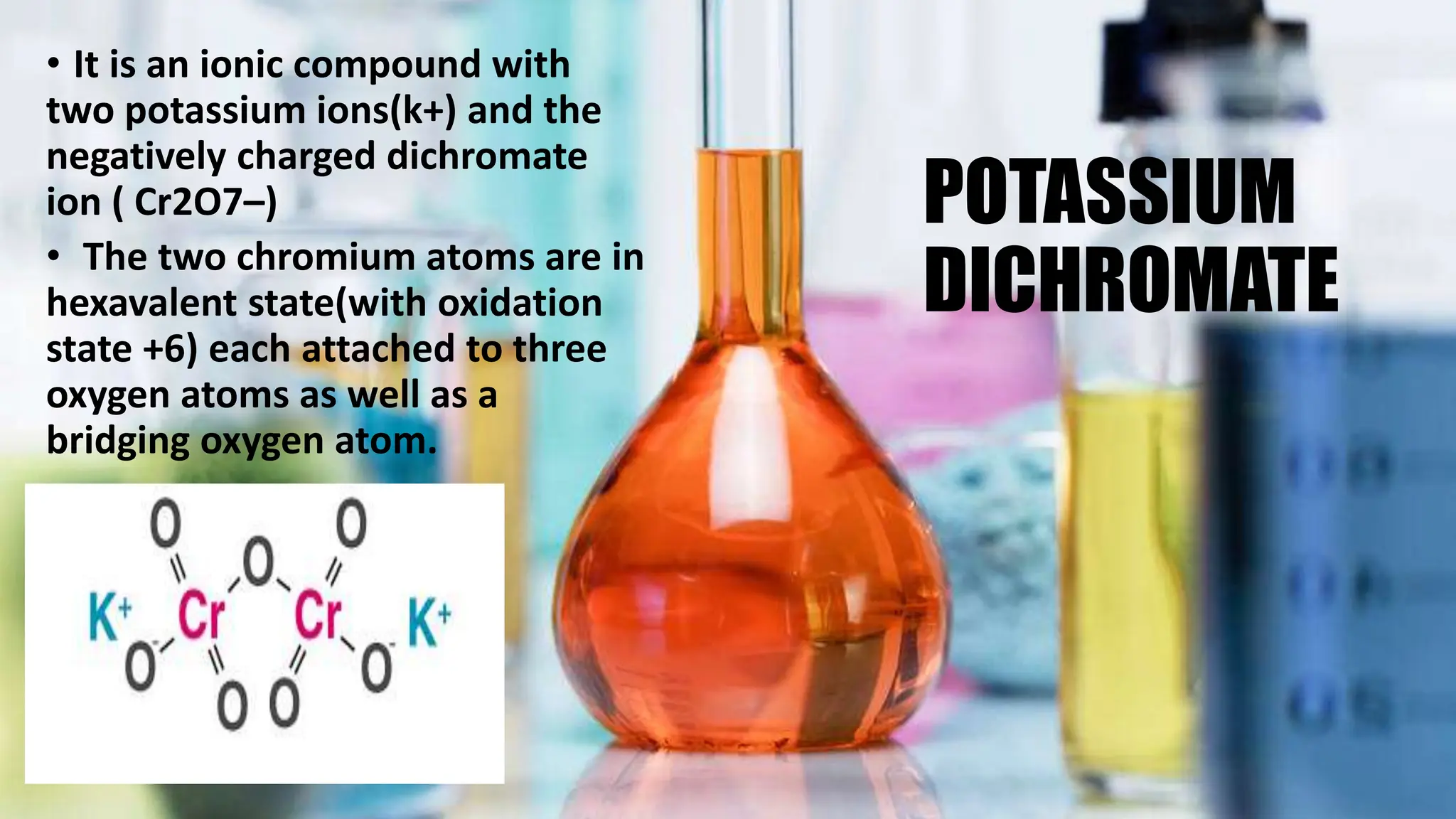
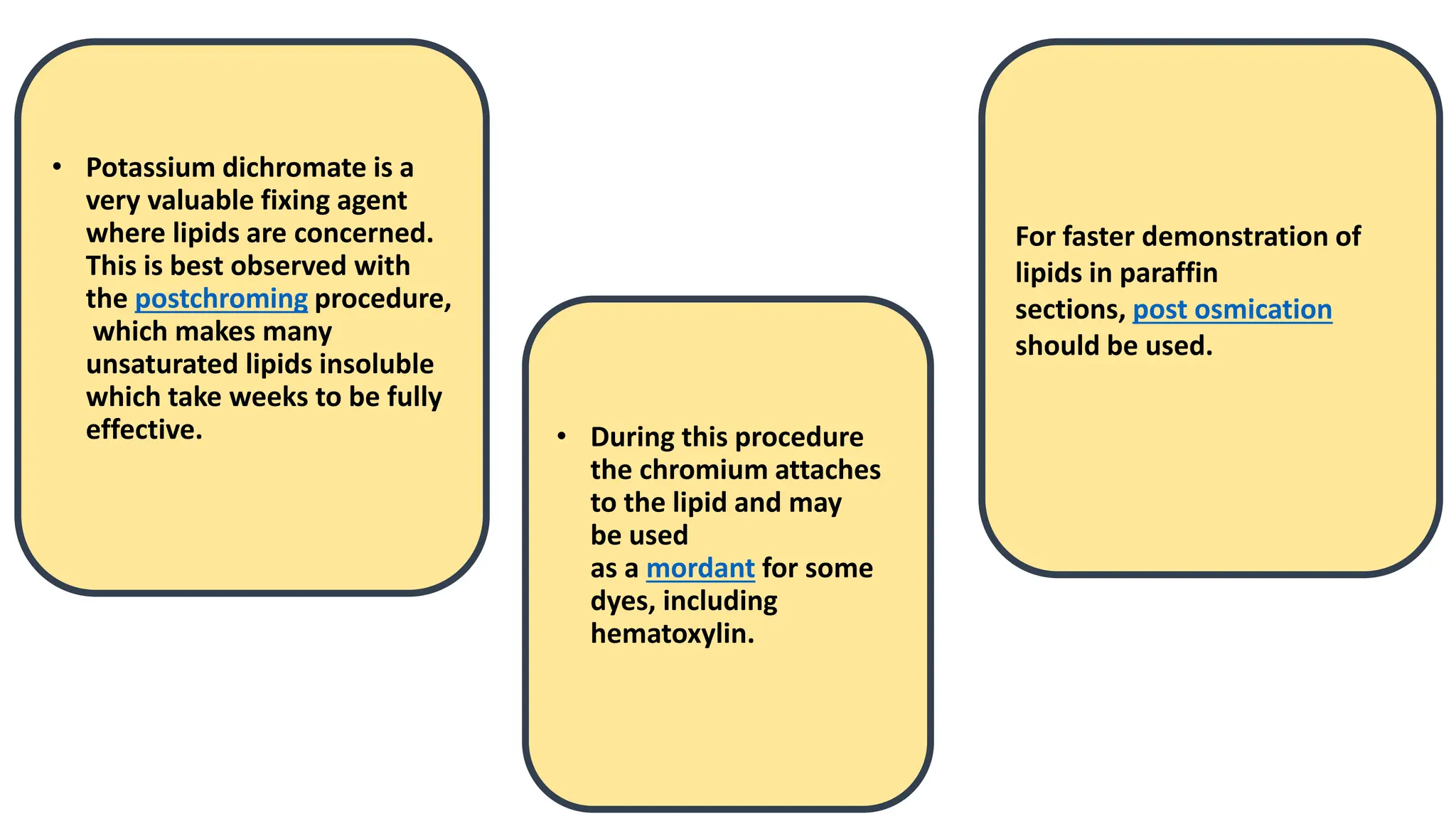
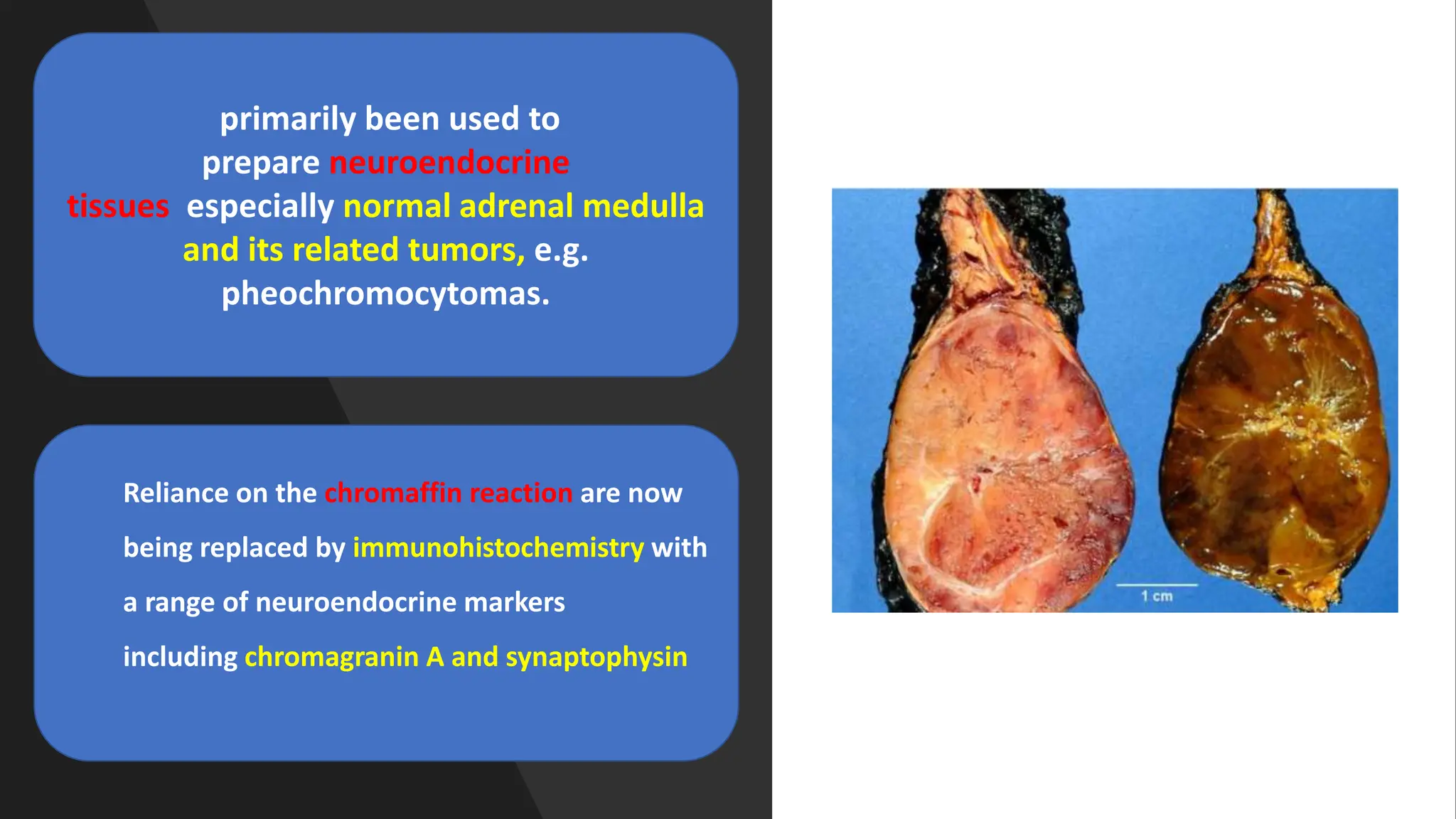
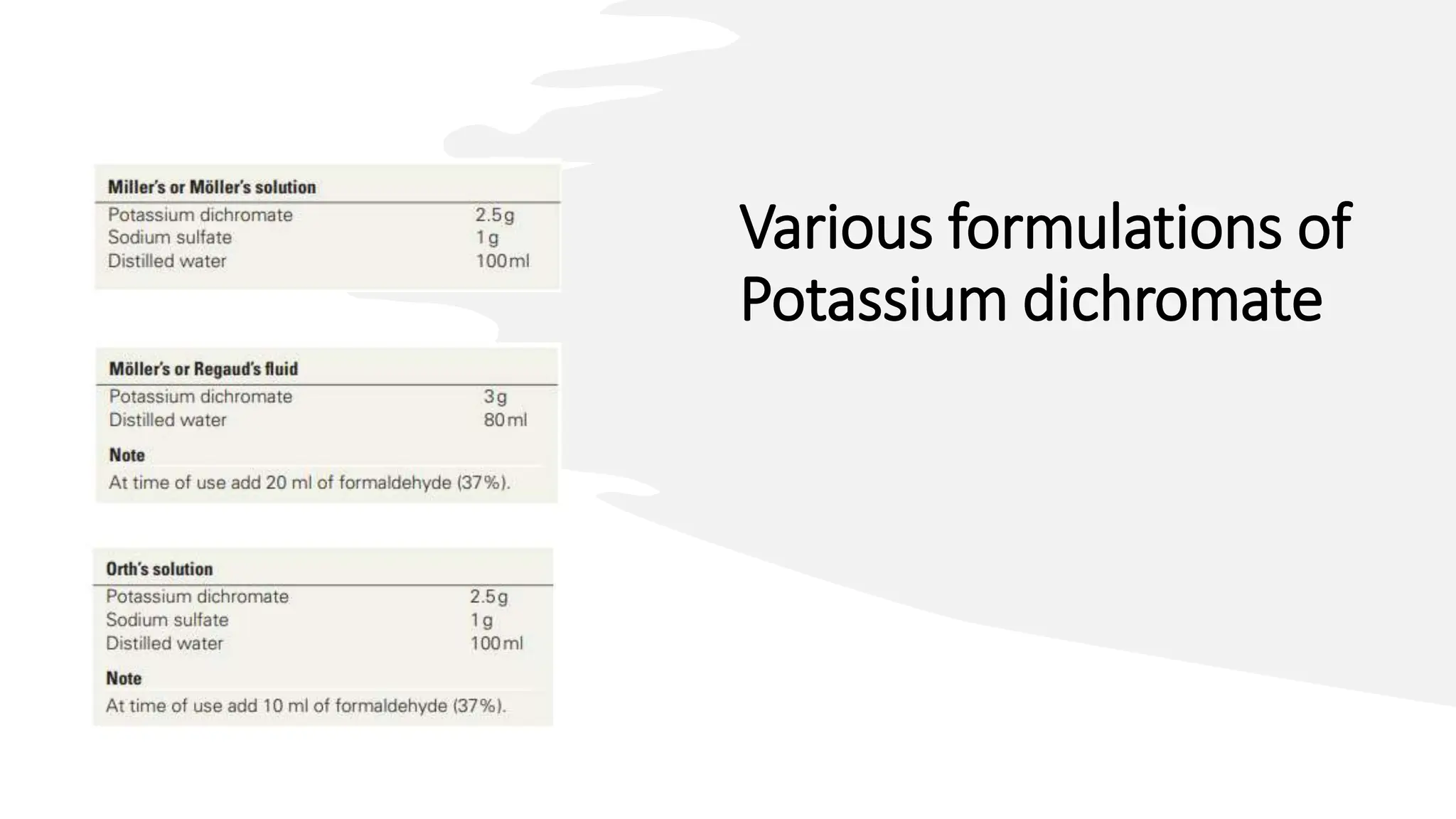
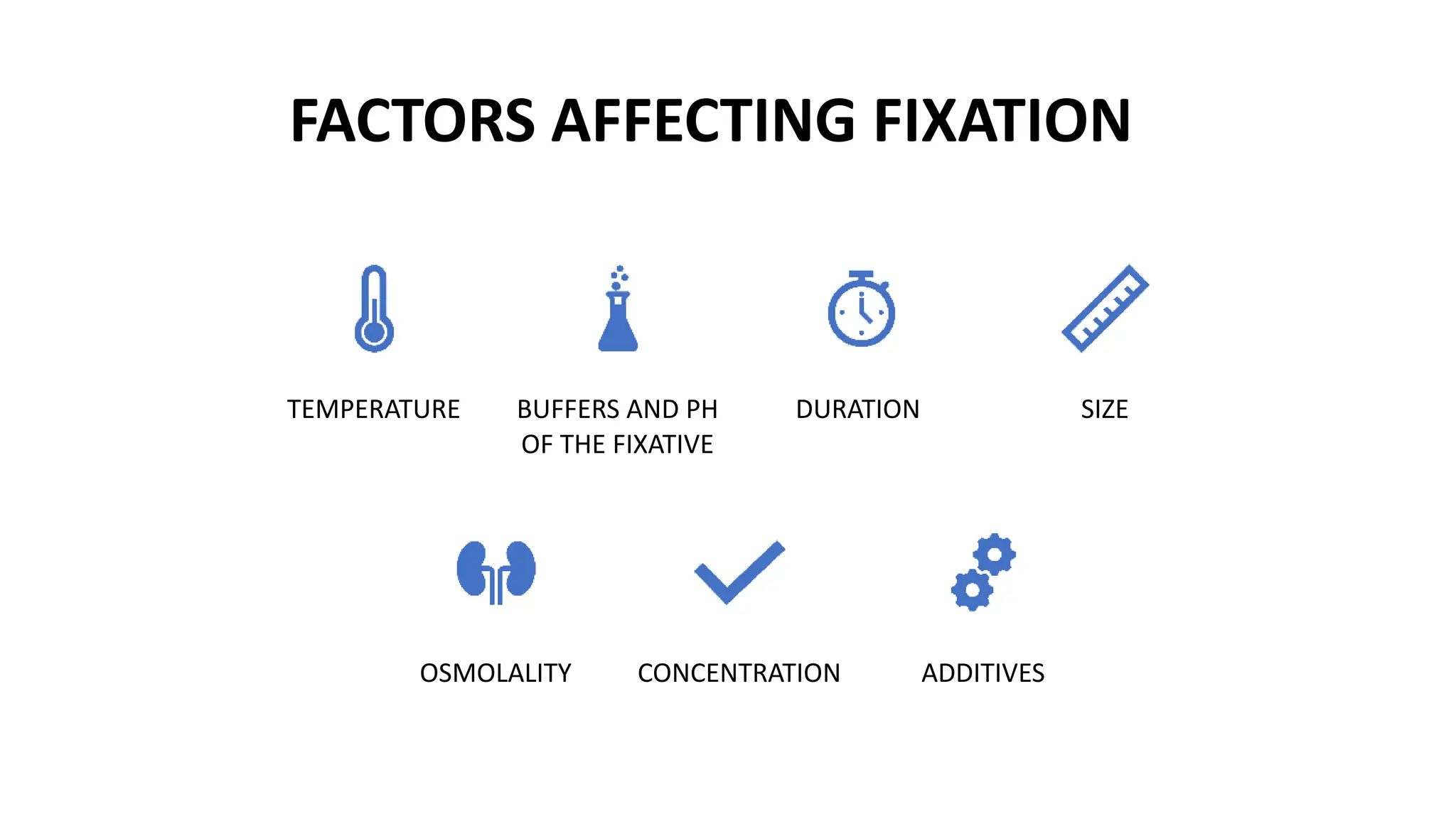
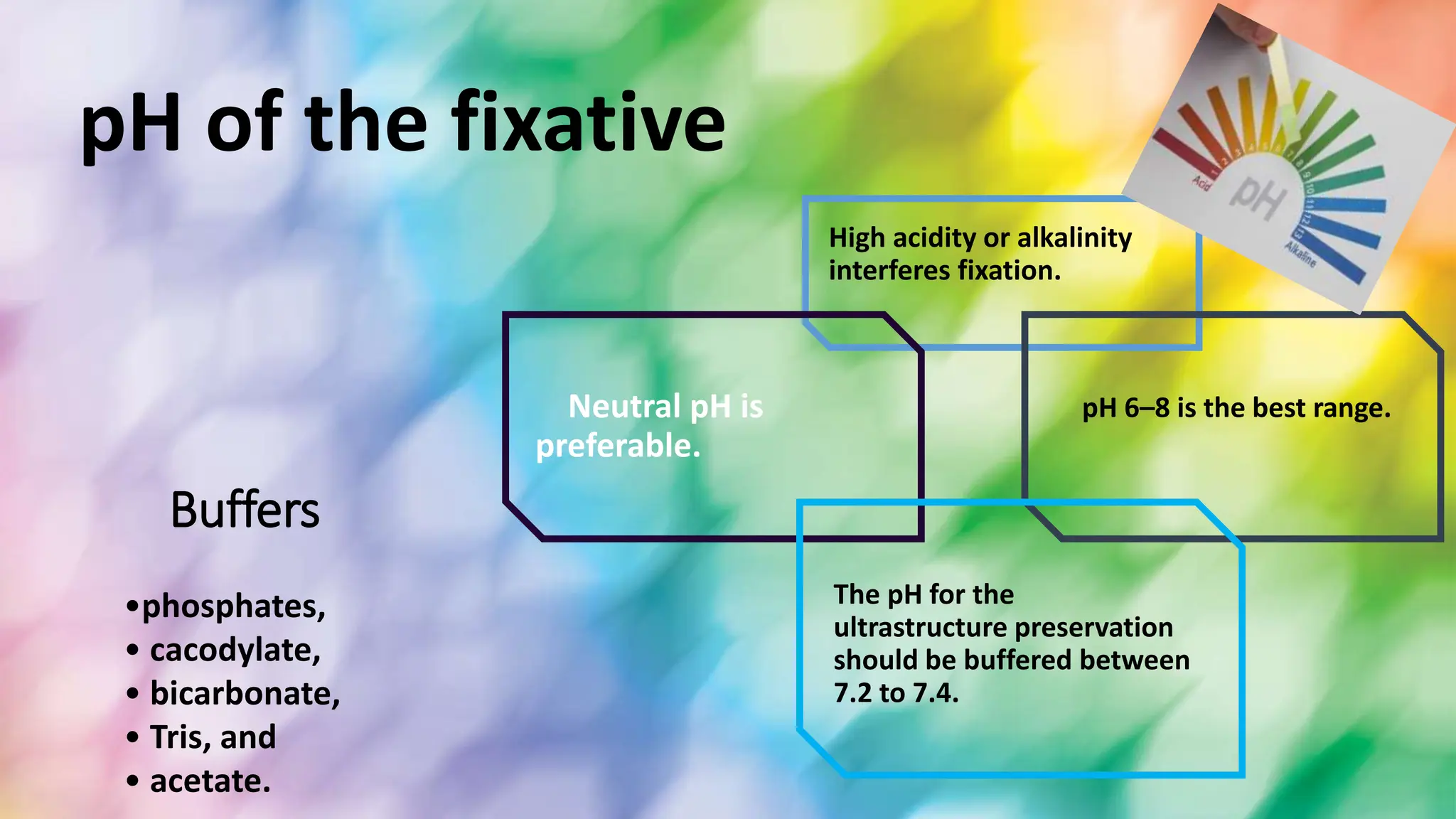
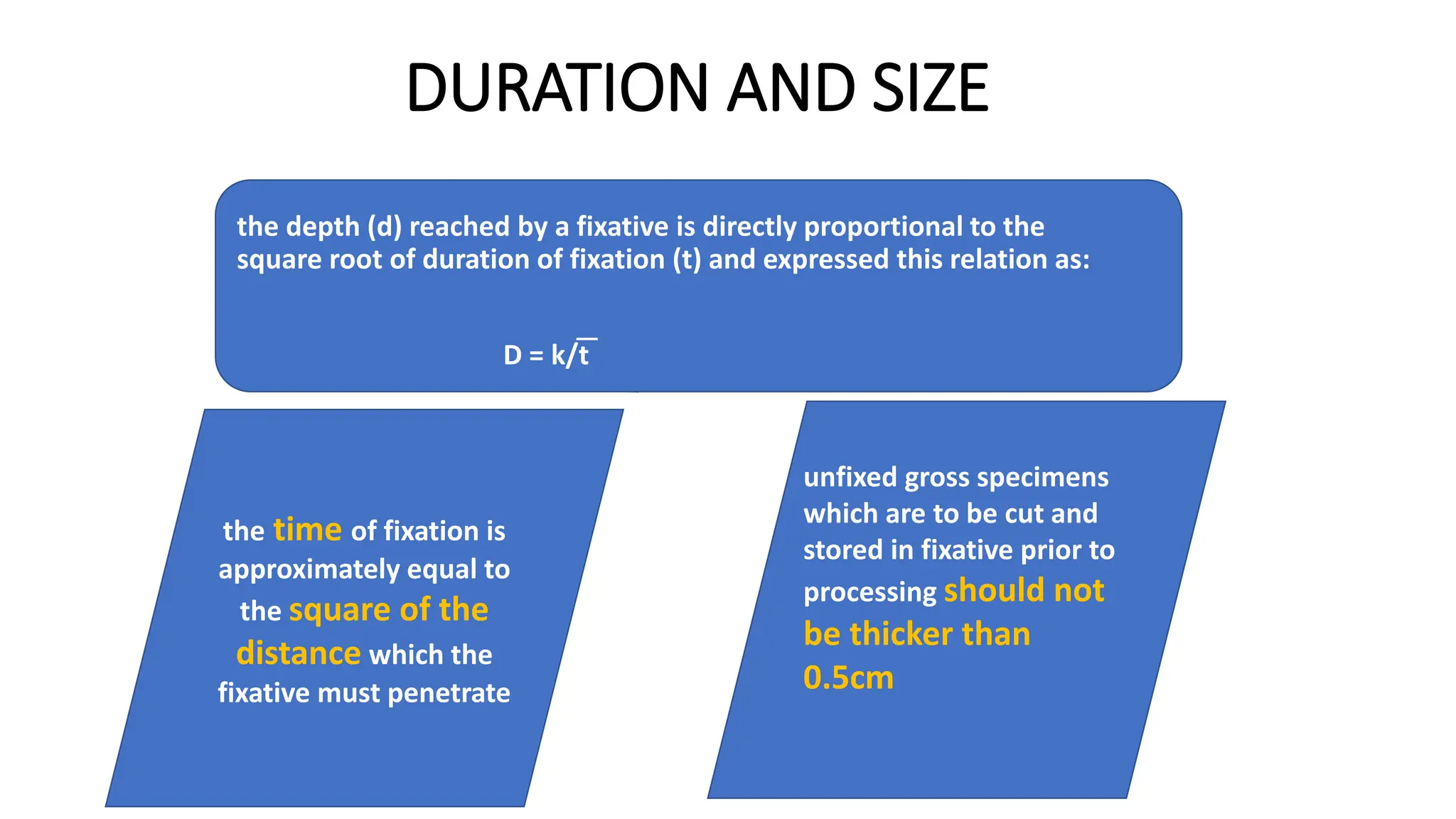
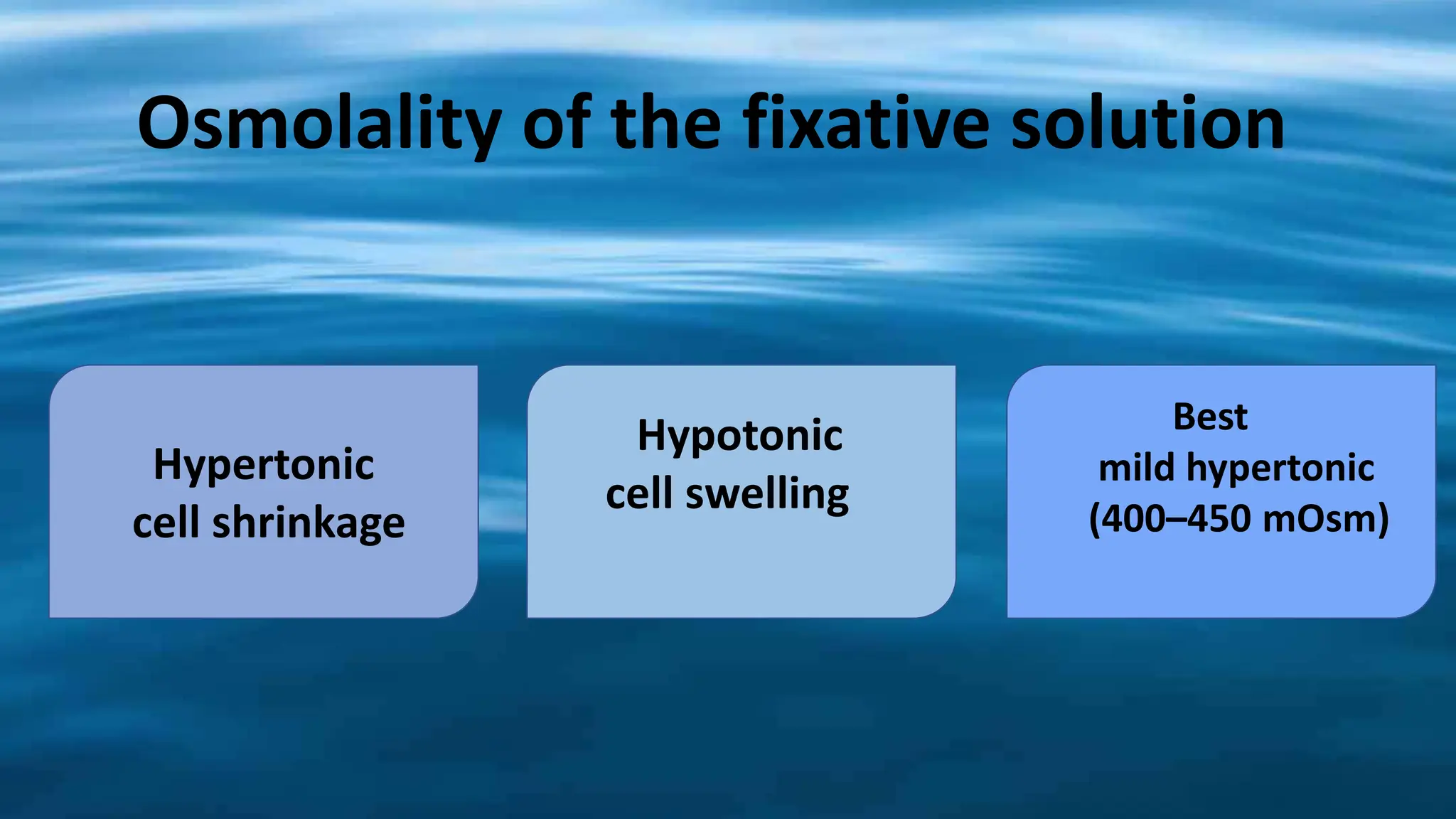
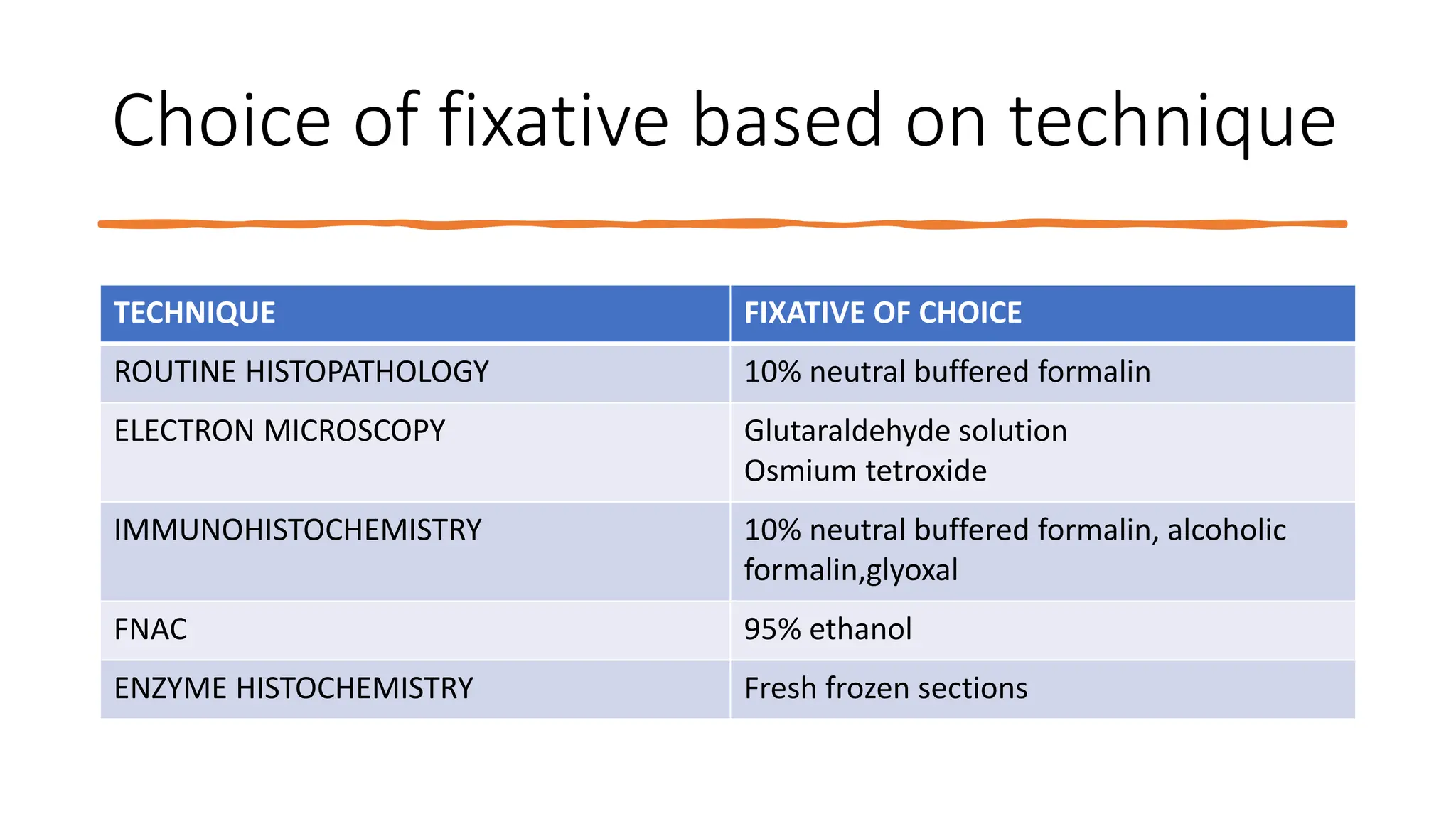
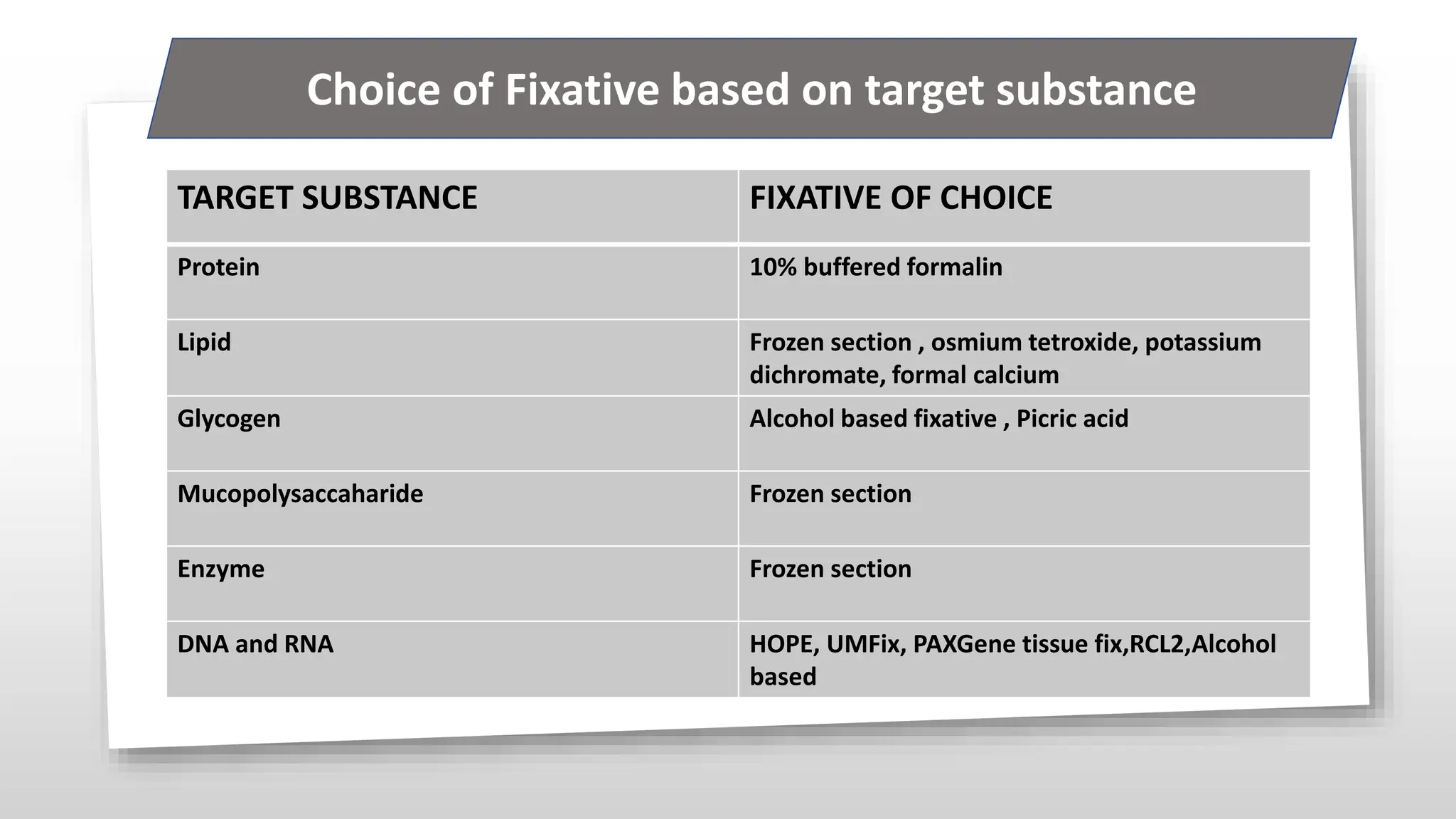
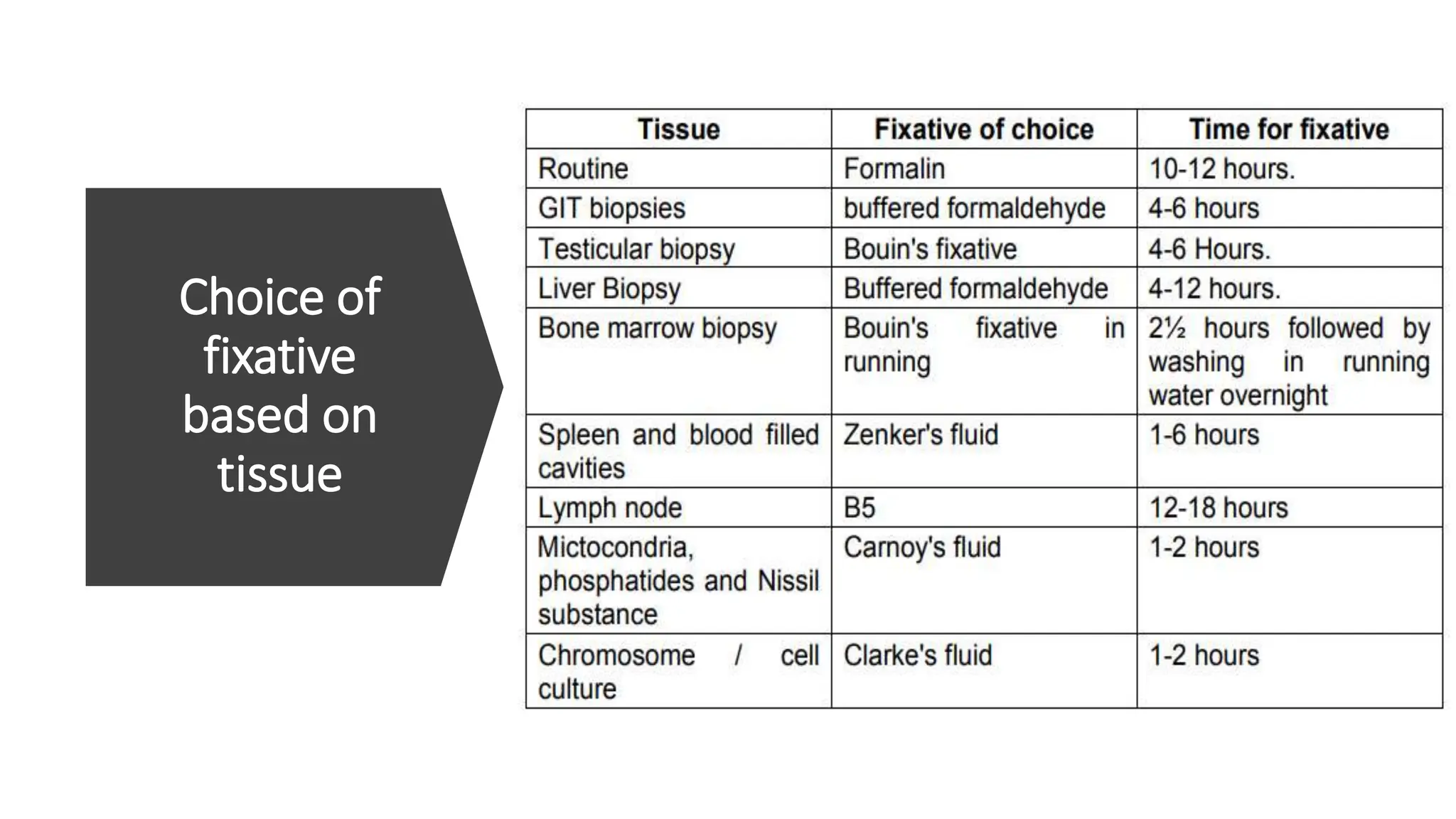
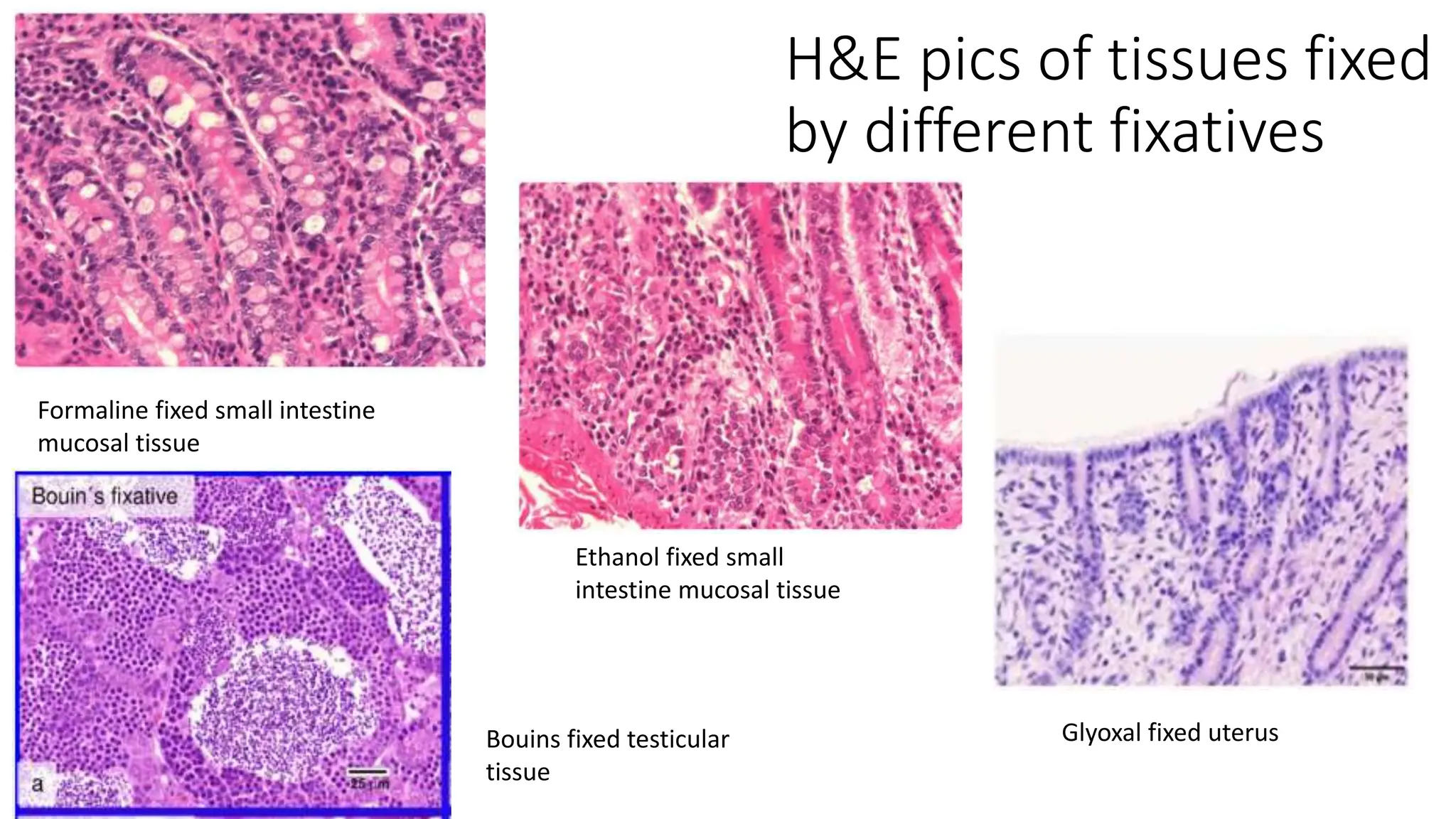
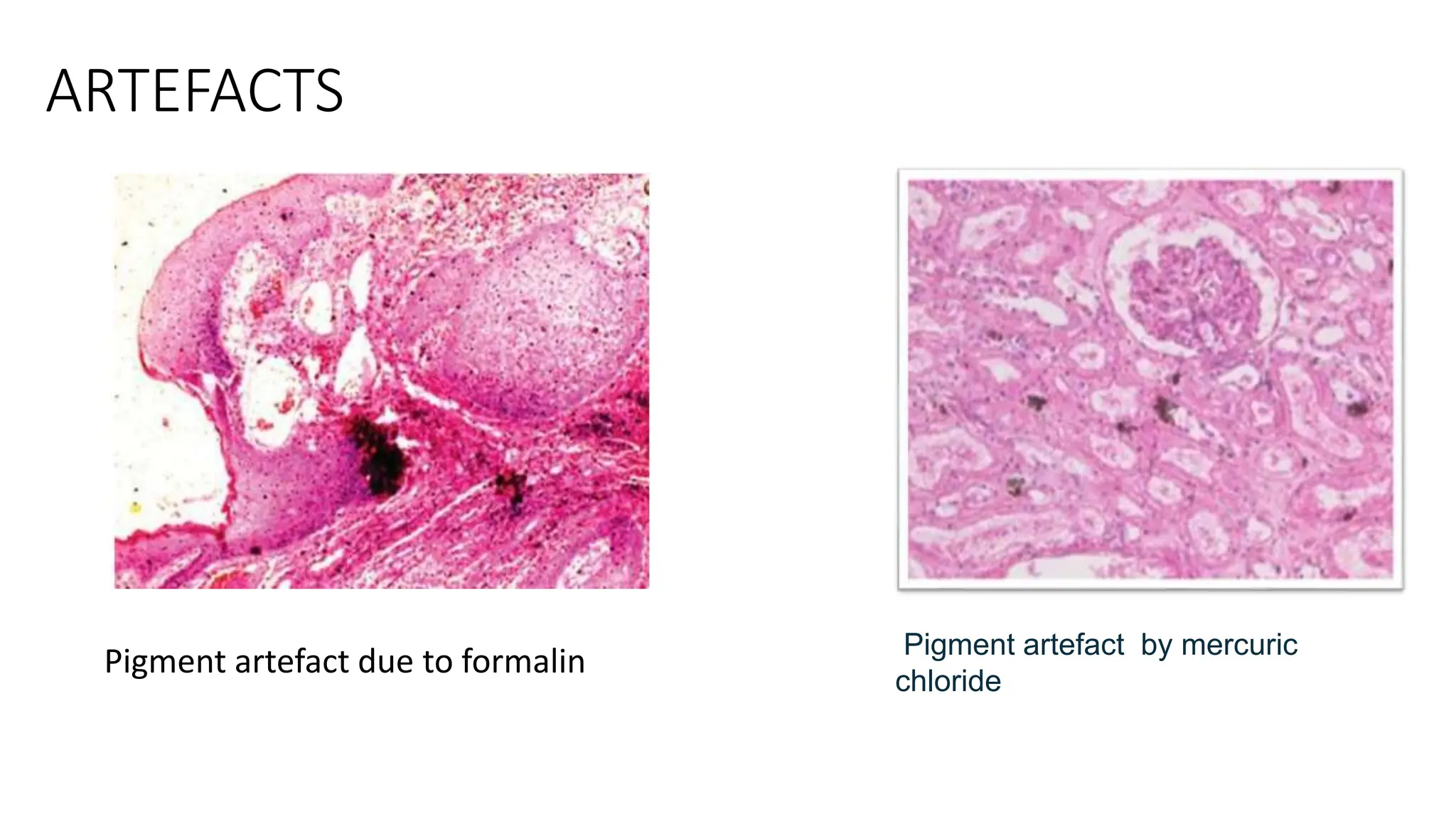
This document discusses various types of fixatives used to preserve cell and tissue structure. It begins by explaining how living cells require oxygen and nutrients from blood circulation, and will die when cut off from this supply. Fixation is needed to preserve tissues as they were in life for histological examination. Various fixatives are then described, including physical, chemical, simple, compound, dehydrant, coagulant, cross-linking, and osmium tetroxide fixatives. The ideal properties and mechanisms of several common fixatives like formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde, picric acid, acetic acid, and mercuric chloride are also summarized.