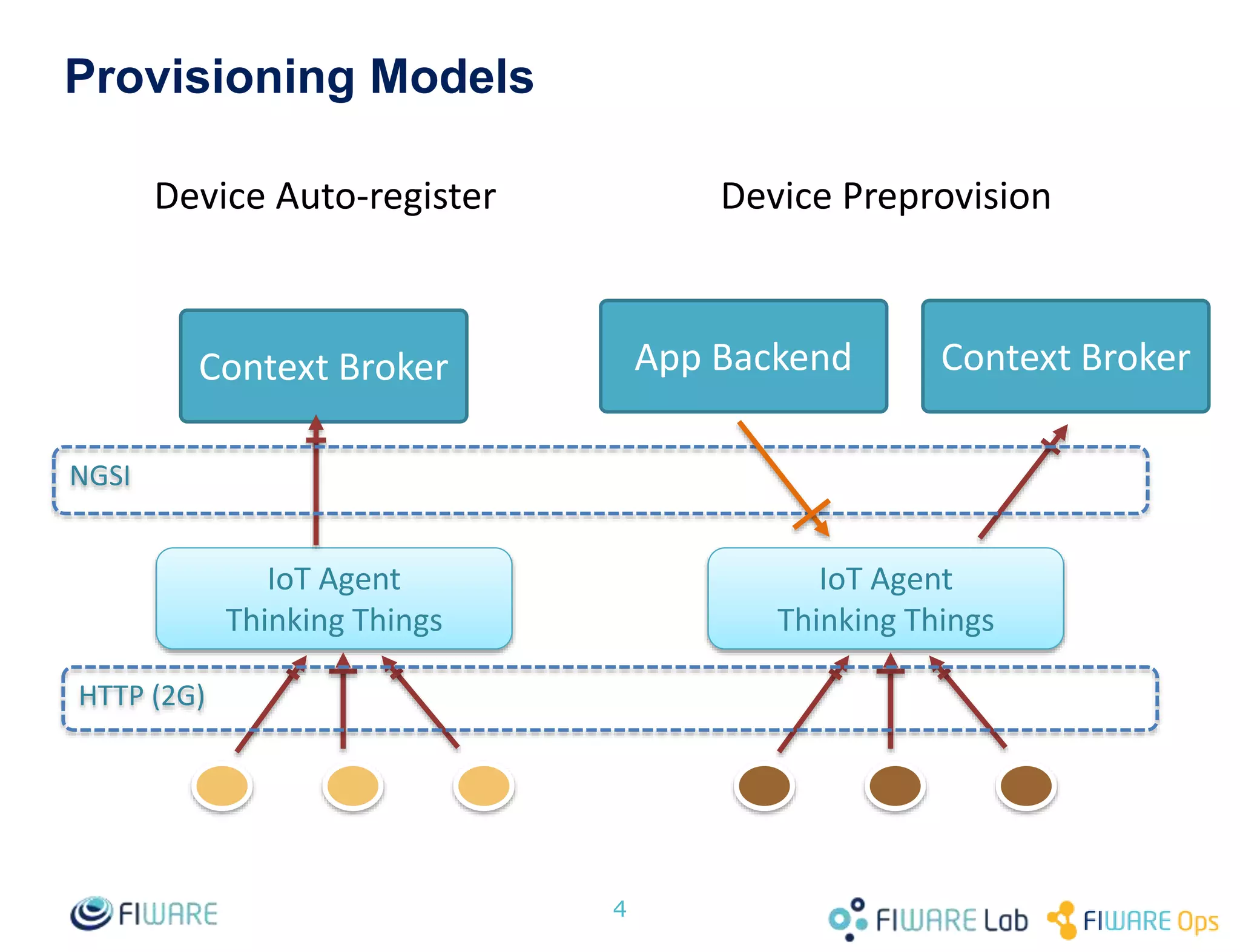
The document details a workshop on IoT agents, focusing on the use of Thinking Things and OMA Lightweight M2M protocols. It covers the setup, connection, and querying of real devices, as well as preprovisioning and simulation exercises for device management using context brokers. Key resources, requirements, and communication protocols are provided to facilitate participant engagement with the technology.










![OMA Lightweight Device Provisioning
{
"name": "EndpointId",
"service" : "campusPart",
"service_path": "/workshop",
"entity_name": "AnotherDevice",
"entity_type": "AnotherType",
"attributes": [ {
"name": "luminance",
"type": "Lumens"
}],
"lazy": [ {
"name": "temperature",
"type": "degrees"
}],
"commands": [],
"internal_attributes": {
"lwm2mResourceMapping": {
"luminance" : {
"objectType": 17,
"objectInstance": 0,
"objectResource": 1
},
"temperature" : {
"objectType": 5,
"objectInstance": 0,
"objectResource": 2
}}}}
• Lazy vs active attributes
• Service information
• URI Mapping](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fiwareiottt-omalwm2mcpbr8-150204115524-conversion-gate02/75/FIWARE-Developers-Week_IoT-Agents-with-Thinking-Things-and-OMA-lightweight-M2M_conference-13-2048.jpg)

