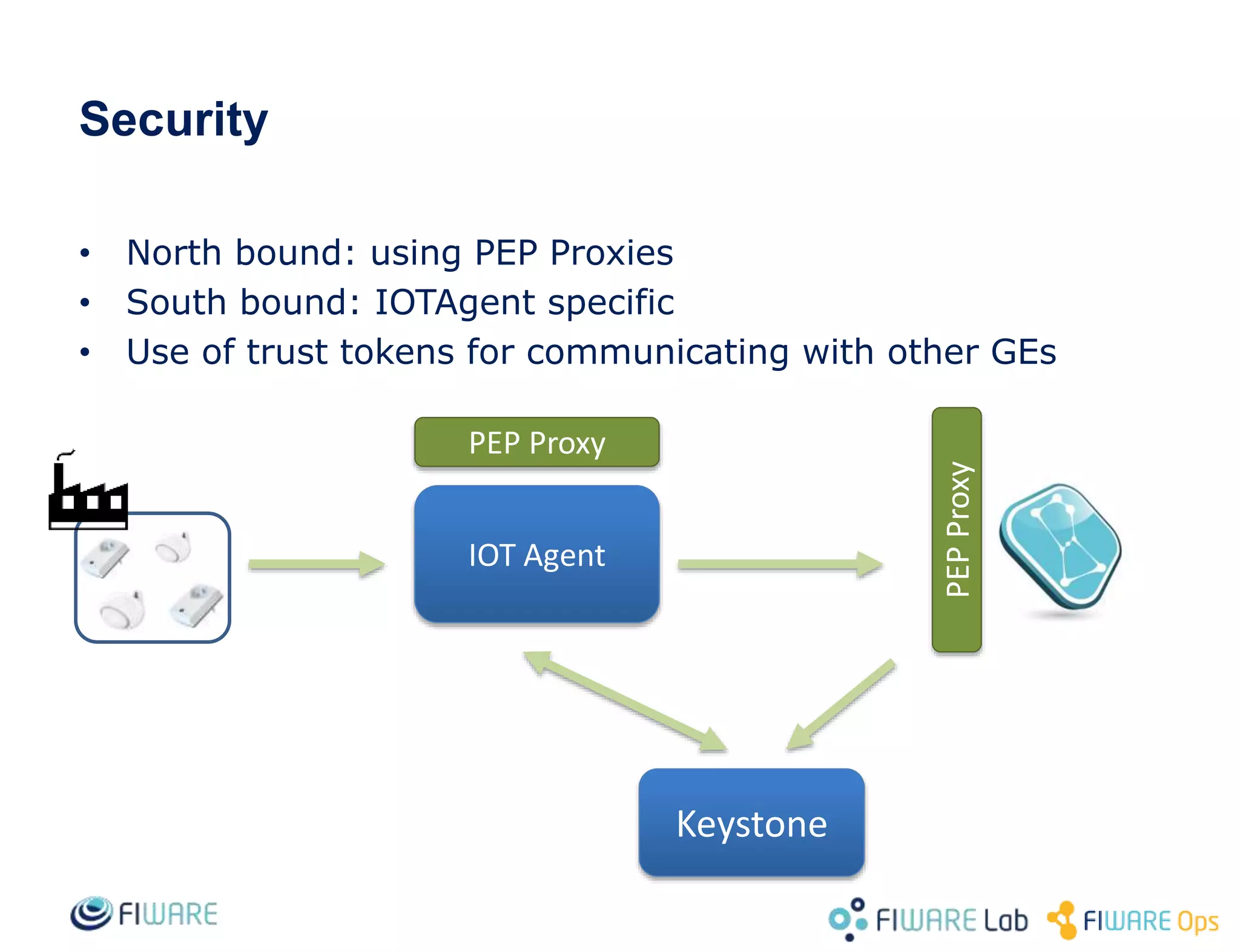
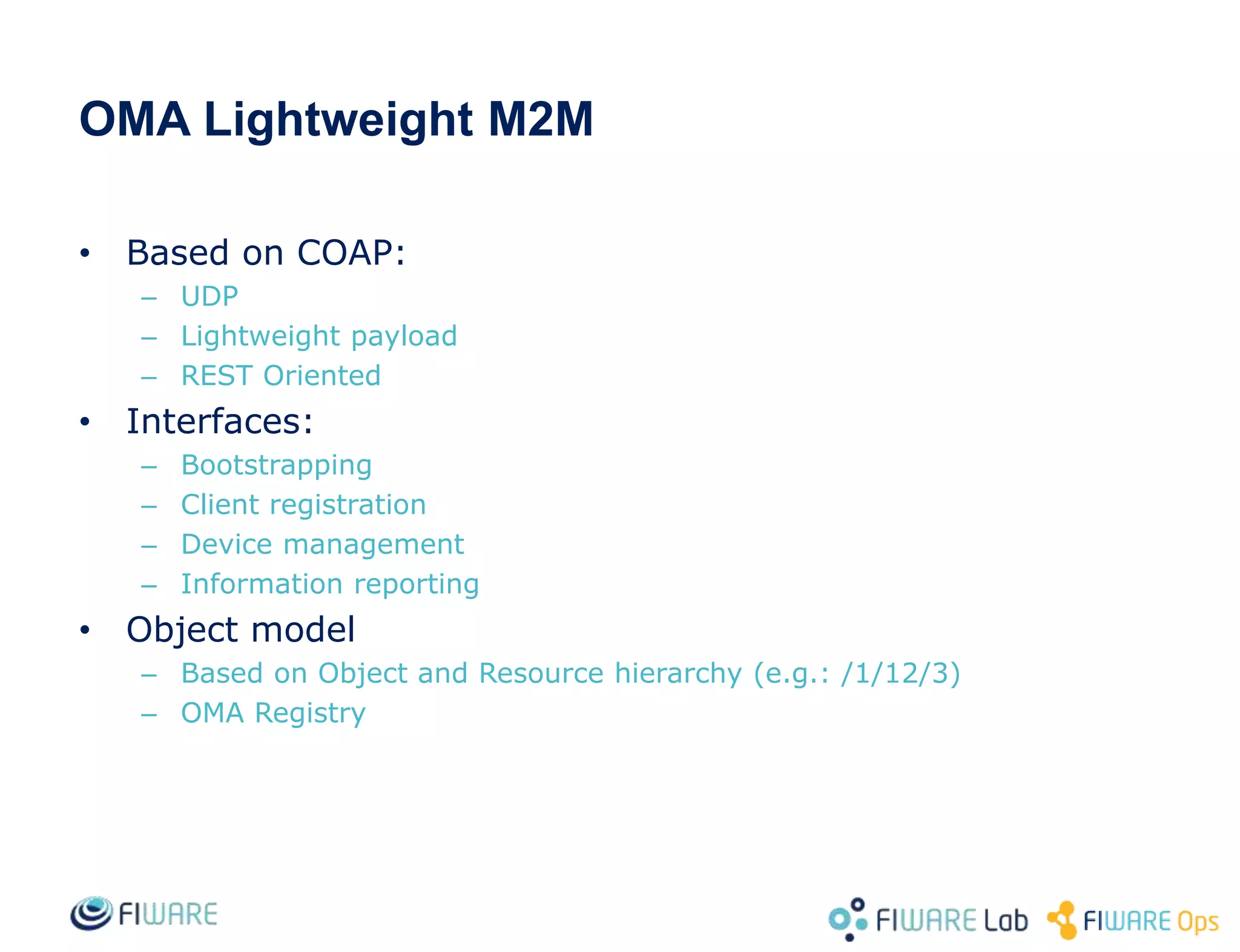
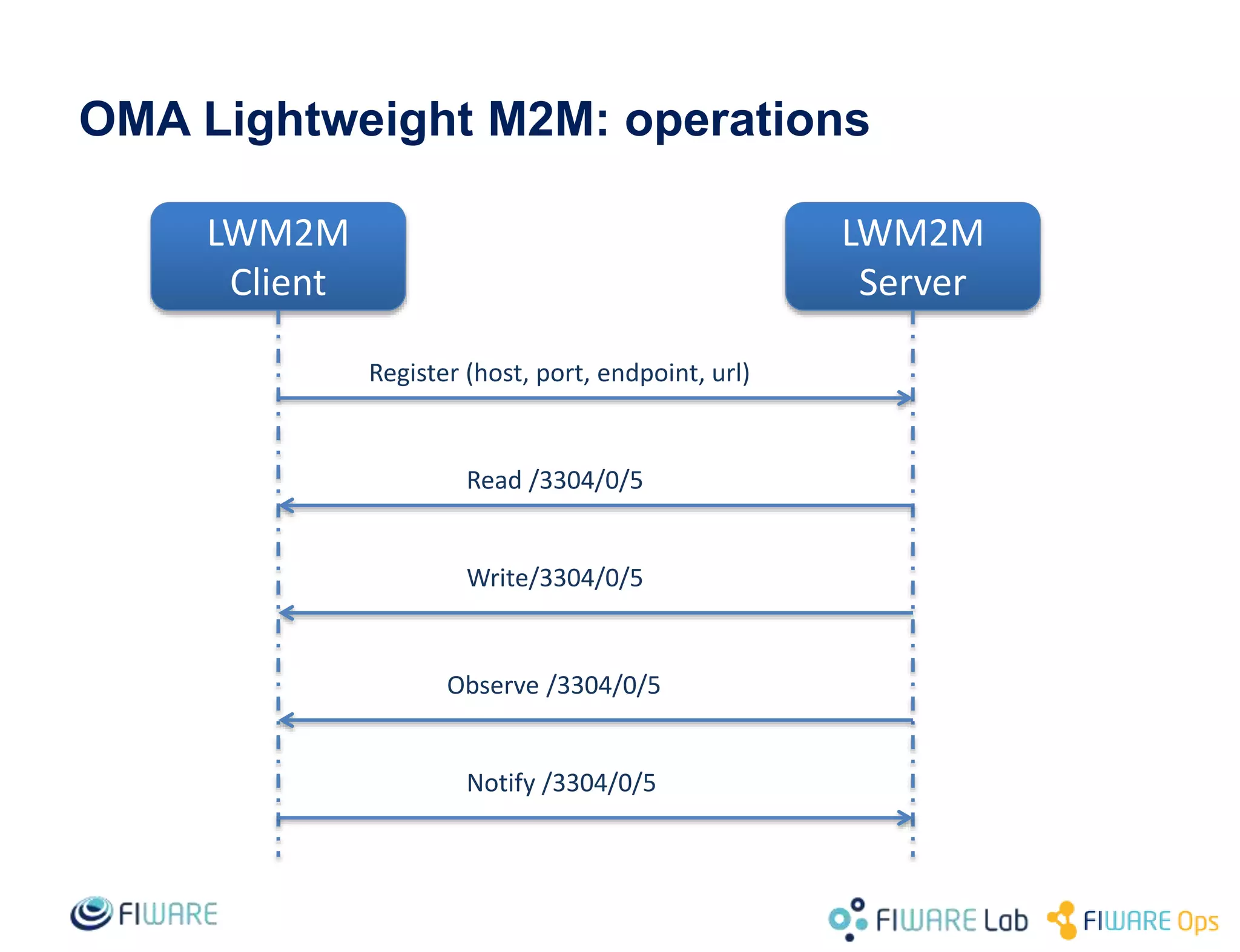
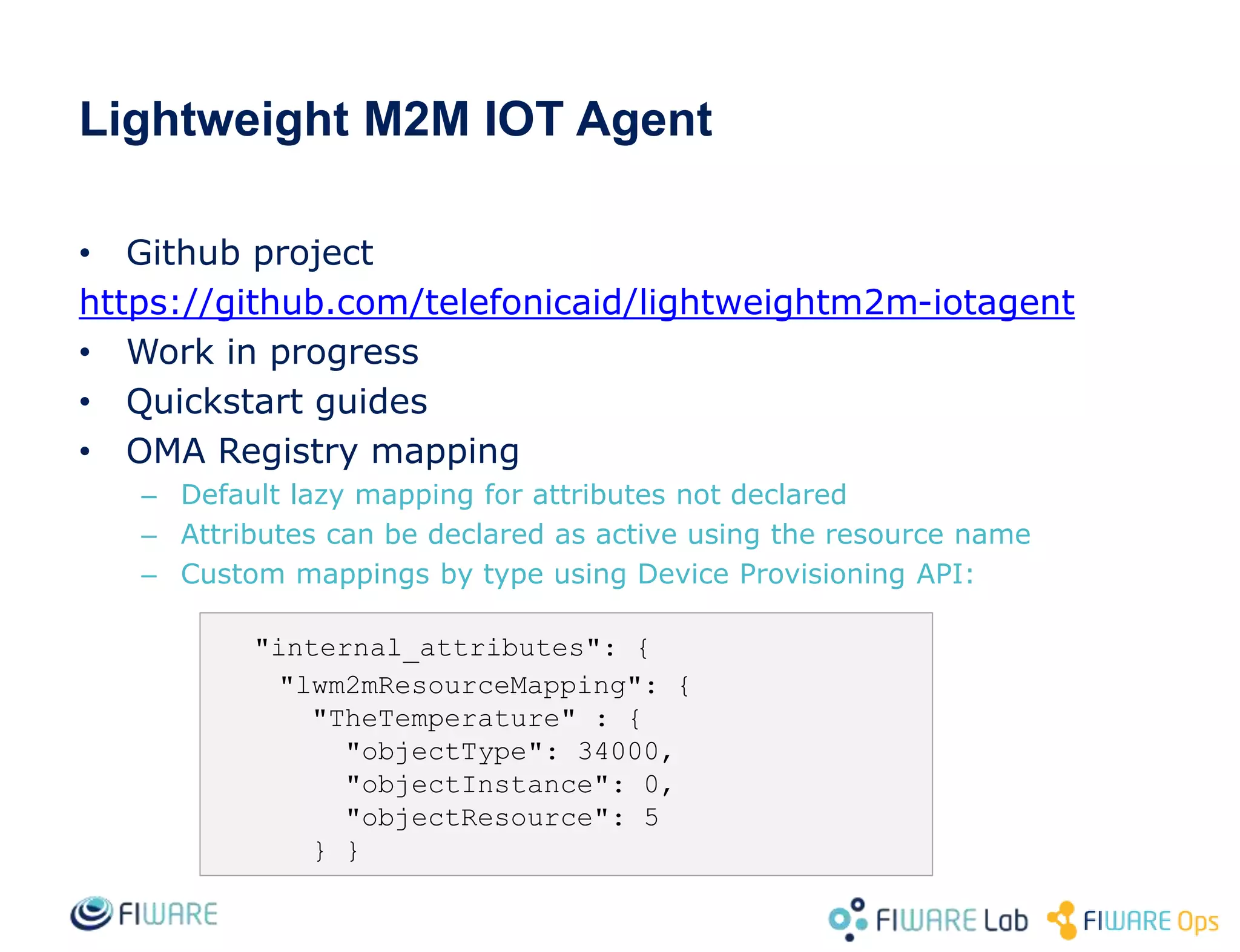
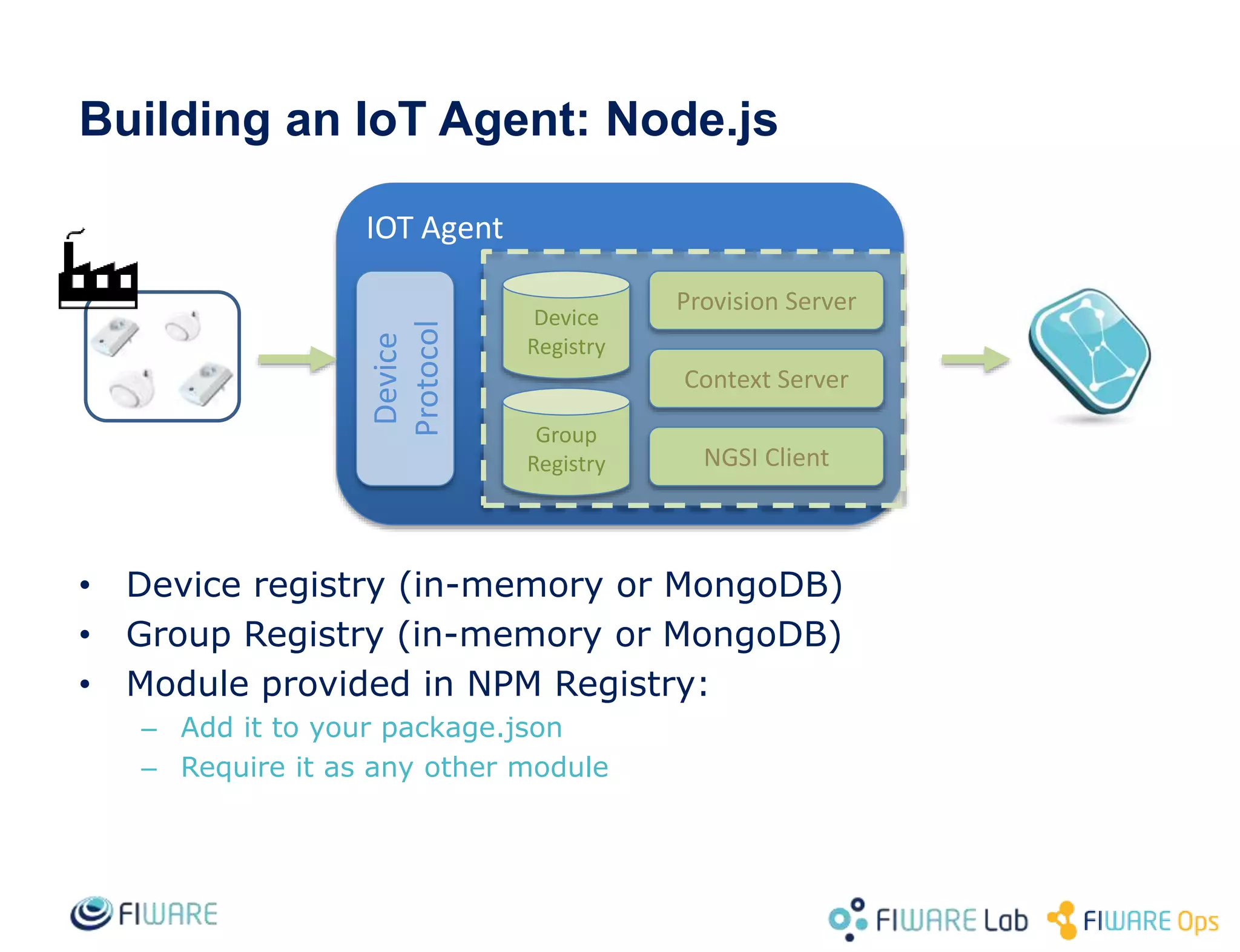
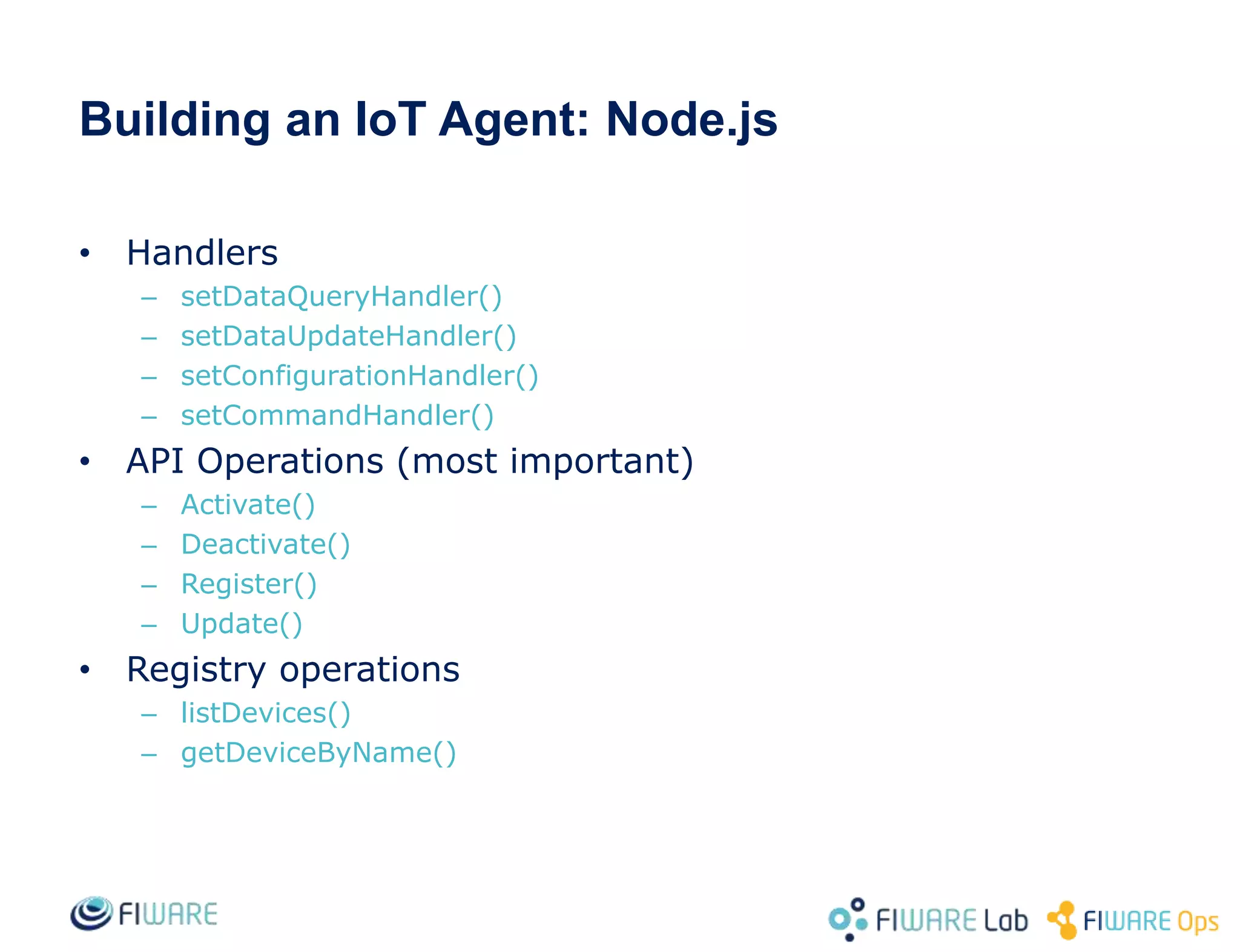
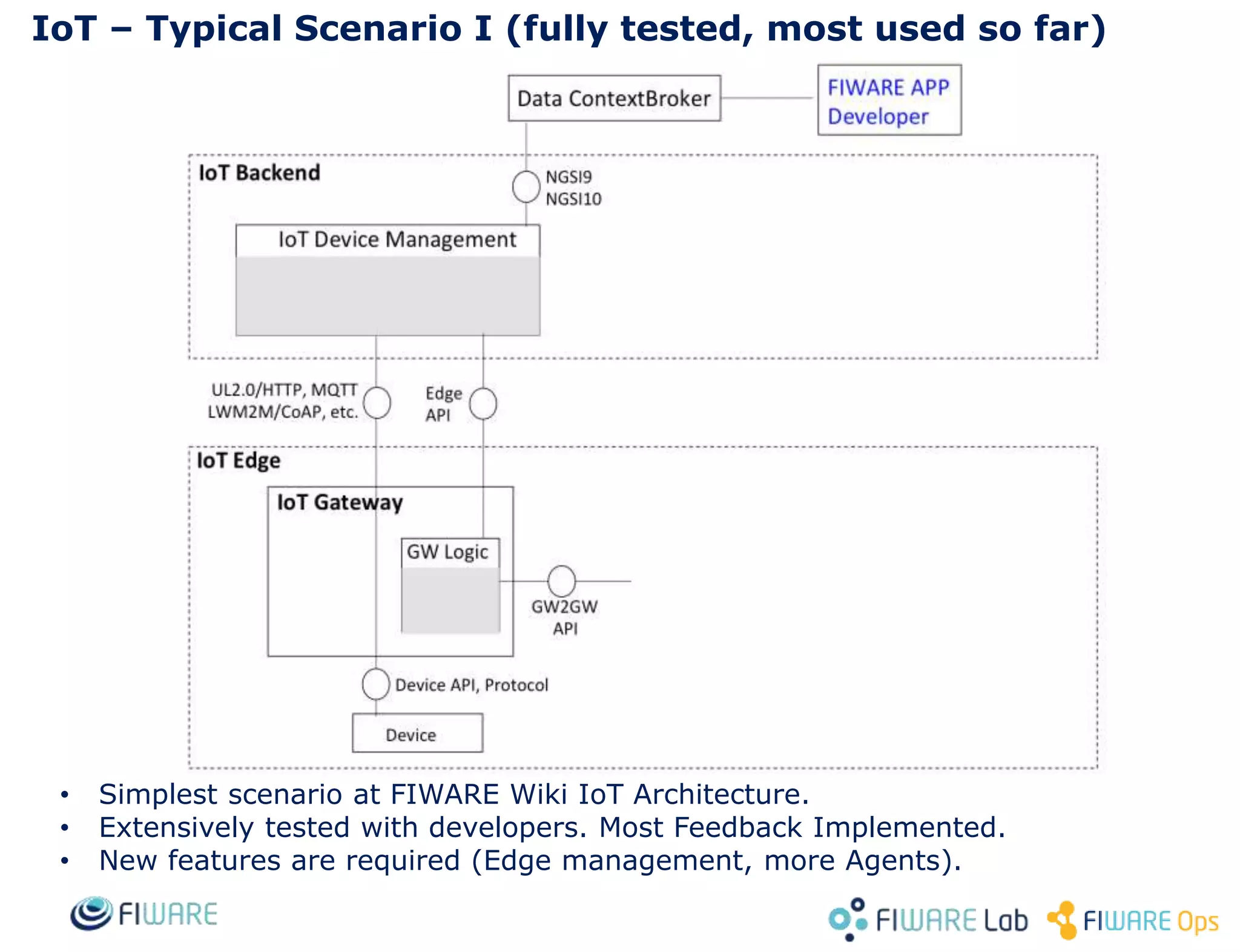
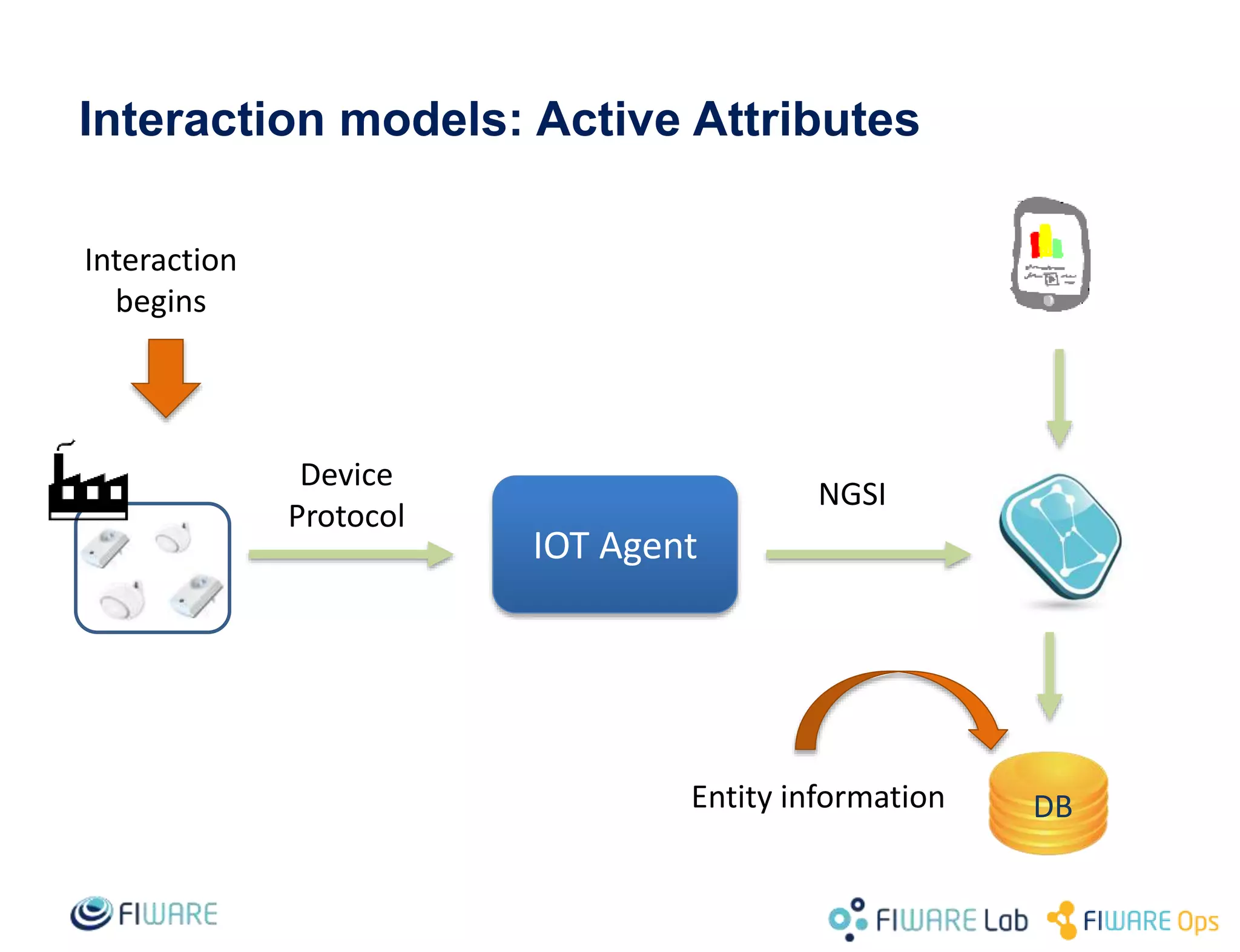
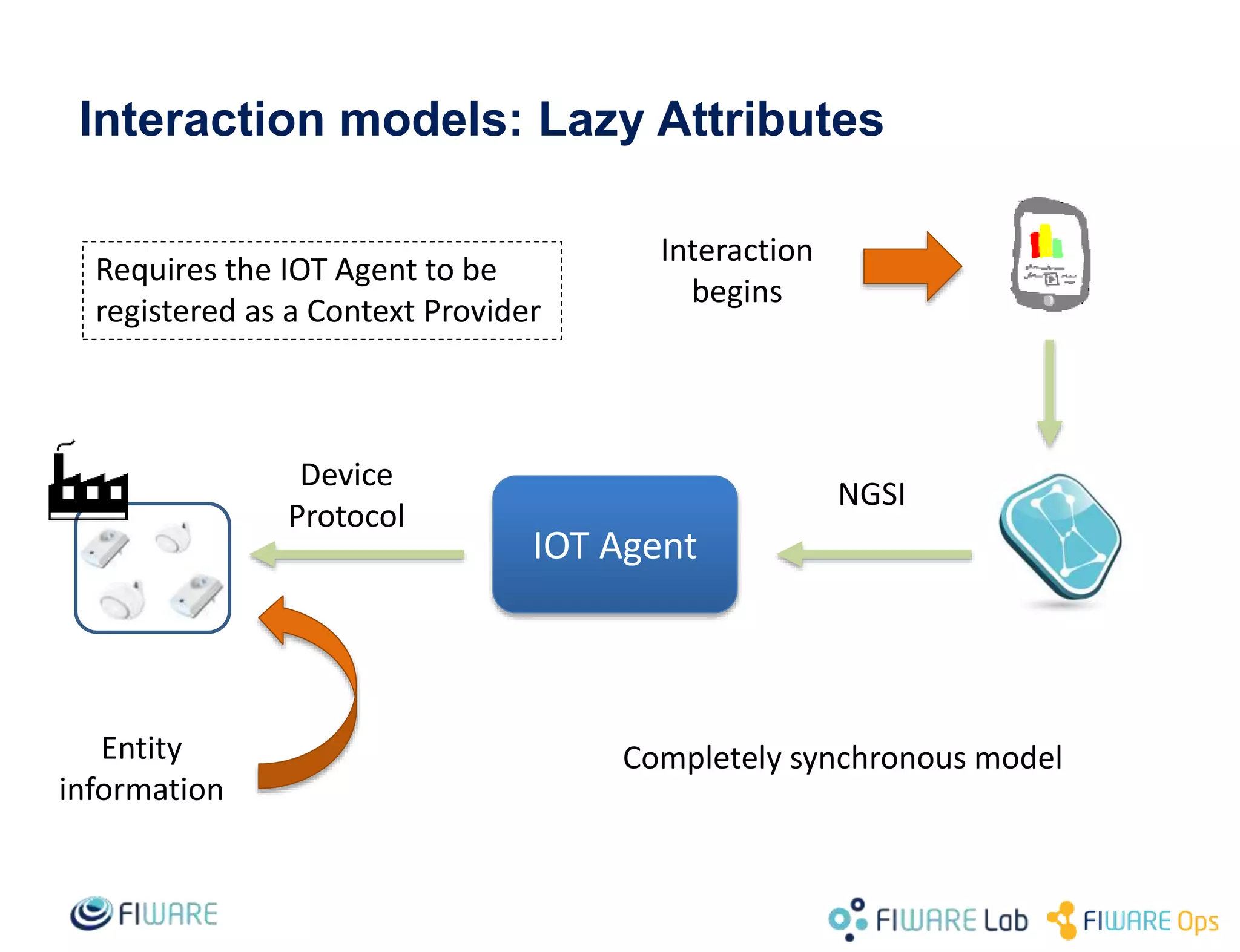
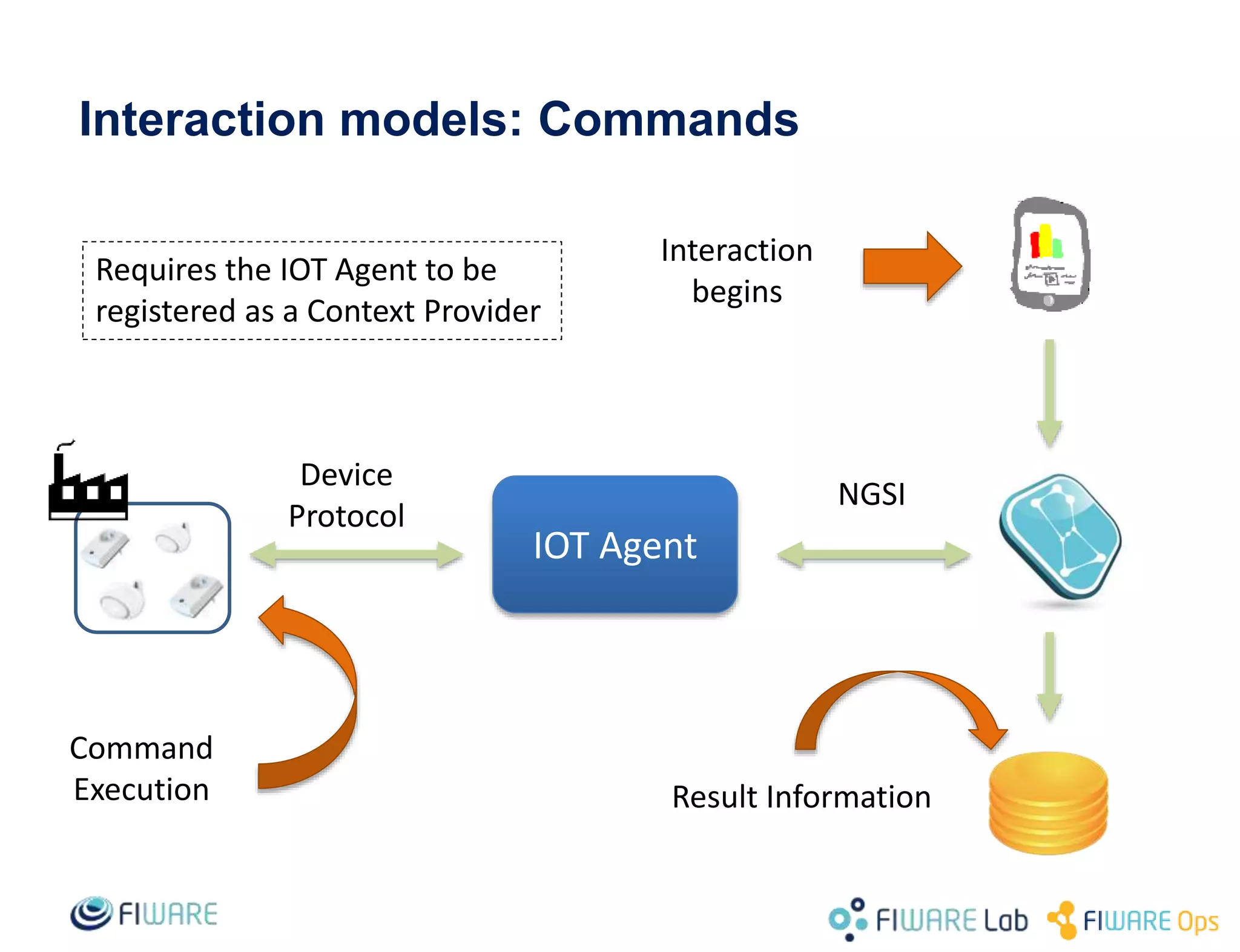
This document provides an overview of IoT Agents and the OMA Lightweight M2M IoT Agent. It discusses interaction models between IoT Agents and the Context Broker, including active attributes, lazy attributes, and commands. It covers device and service provisioning APIs. It also outlines typical IoT scenarios and describes building custom IoT Agents using Node.js or C++ frameworks. Resources listed include Github projects for IoT Agent libraries and the Lightweight M2M IoT Agent.



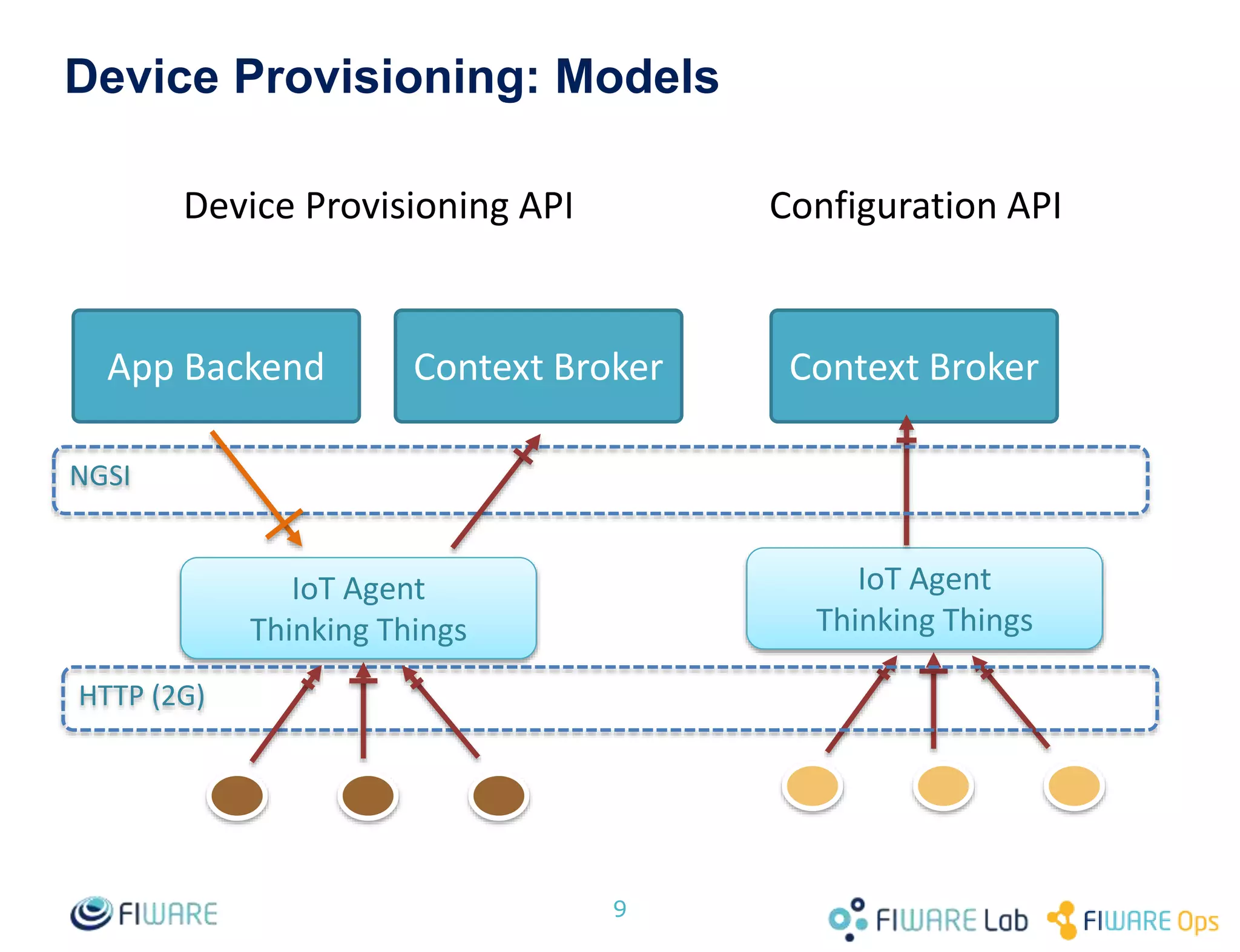
![Device Provisioning: Device Provisioning API
{
"name": "Light1",
"entity_name": "TheFirstLight",
"entity_type": "TheLightType",
"attributes": [
{
"name": "attr_name",
"type": "string"
}
],
"lazy": [
{
"name": "luminance",
"type": "lumens"
}
],
"commands": [
{
"name": "commandAttr",
"type": "commandType"
}
]
}
• /iot/devices/:deviceId
• REST CRUD:
– POST
– GET
– DELETE
– PUT
• Service headers:
– Fiware-service
– Fiware-servicepath
• Mandatory
– Name
– Entity_type
• Internal_attributes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancediot-150722162047-lva1-app6891/75/IoT-Agents-With-Lightweight-M2M-10-2048.jpg)
![Device Provisioning: Configuration API
{
services: [
{
resource: '/deviceTest',
apikey: '801230BJKL23Y24HV8732',
type: 'Light',
trust: '8970A9078A803HAMS’,
commands: [],
lazy: [
{
name: 'luminescence',
type: 'Lumens'
}
],
active: [
{
name: 'status',
type: 'Boolean'
}
]
}
]
}
• /iot/agents/default/servi
ces
• Not exactly REST (check
doc)
• Service headers:
– Fiware-service
– Fiware-servicepath
• Mandatory
– Resource
– Api_key
– Type](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancediot-150722162047-lva1-app6891/75/IoT-Agents-With-Lightweight-M2M-11-2048.jpg)