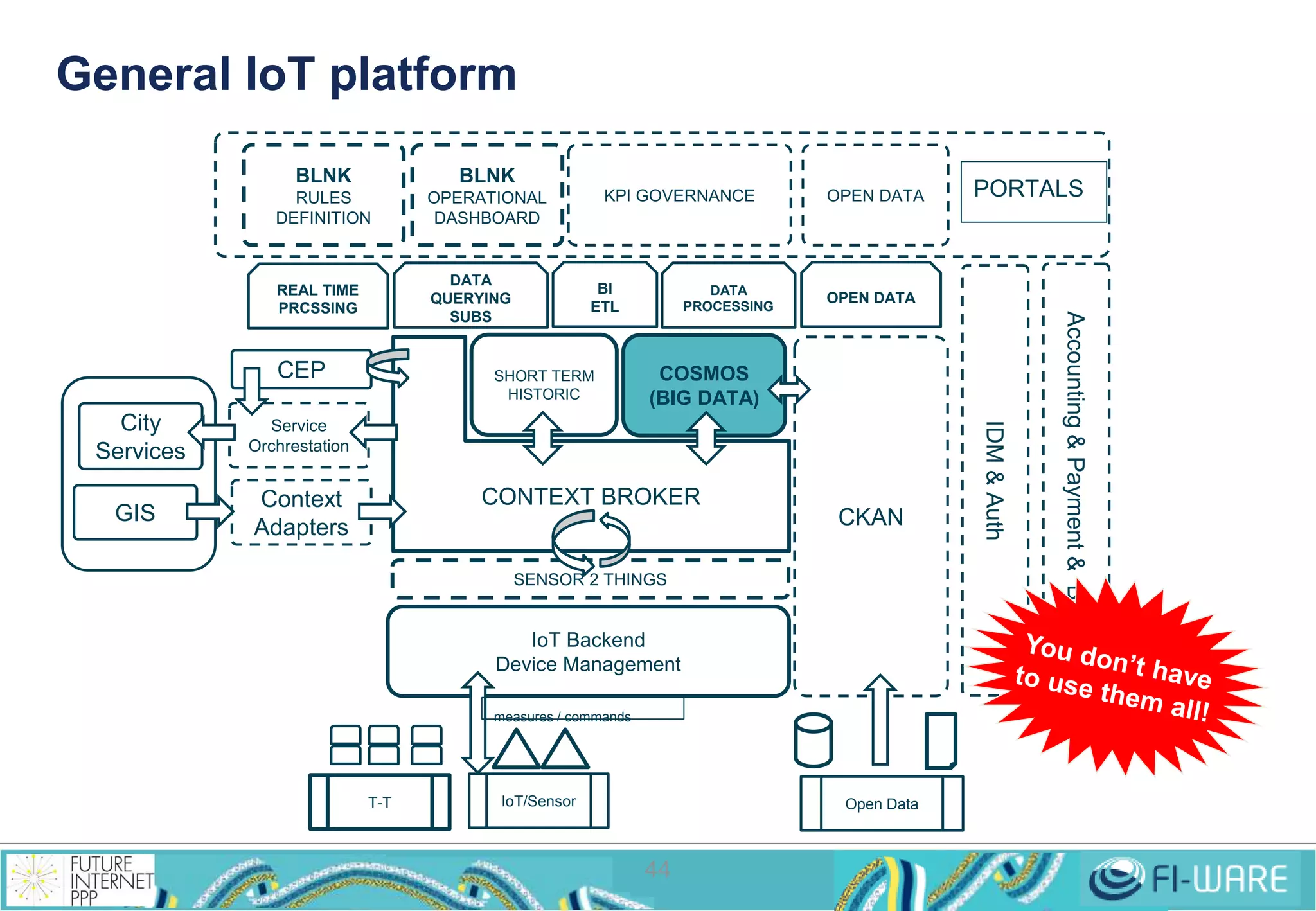
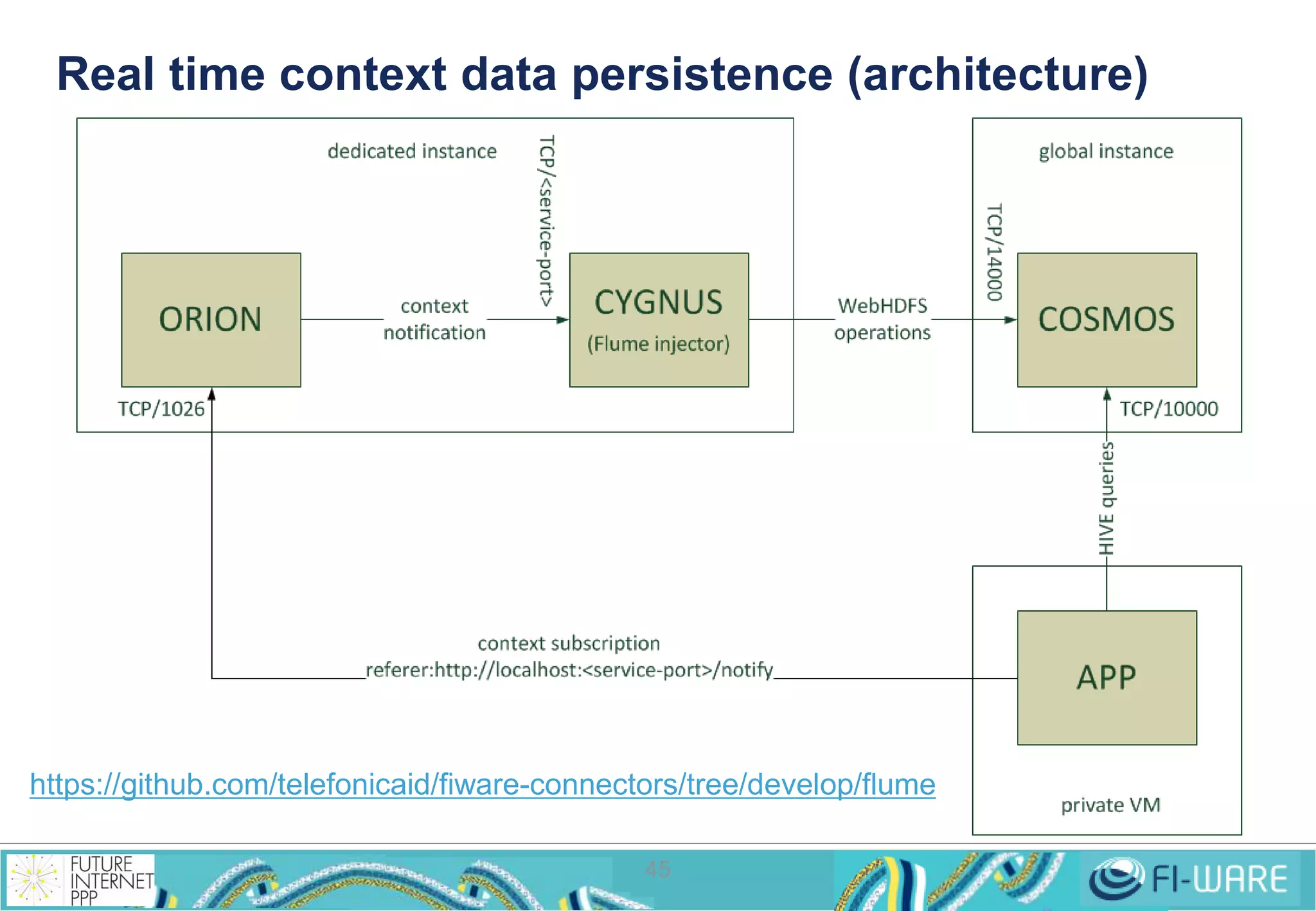
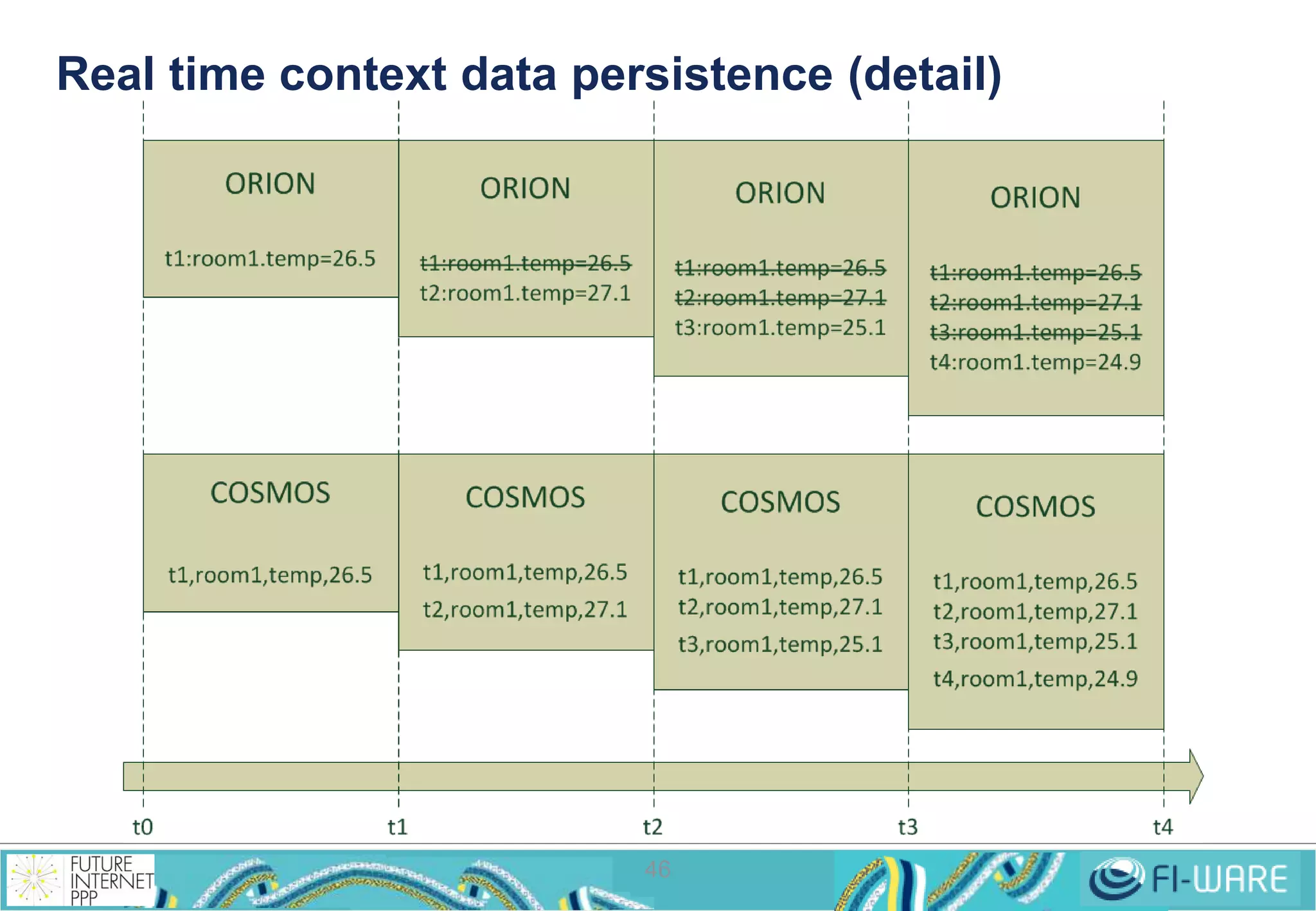
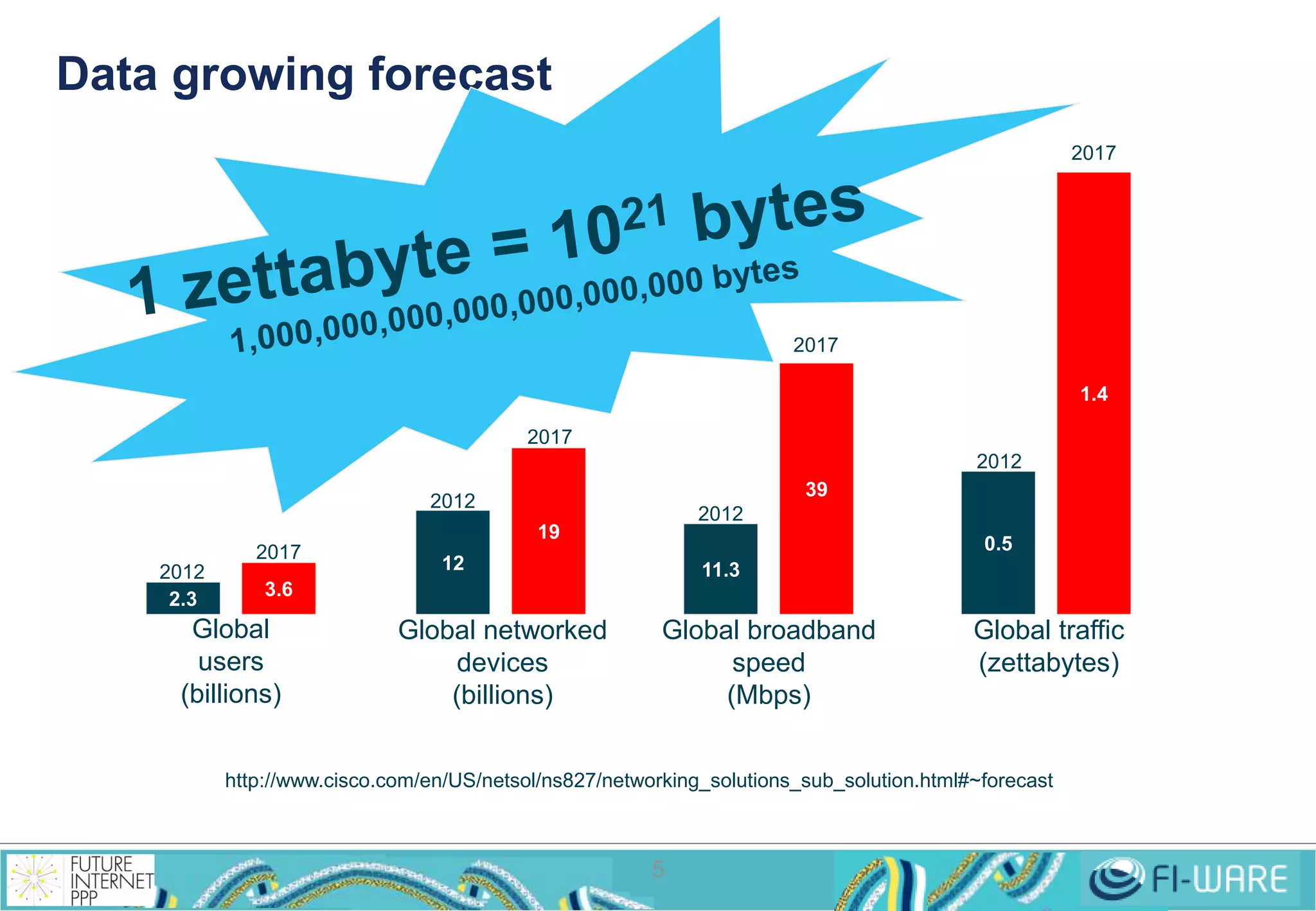
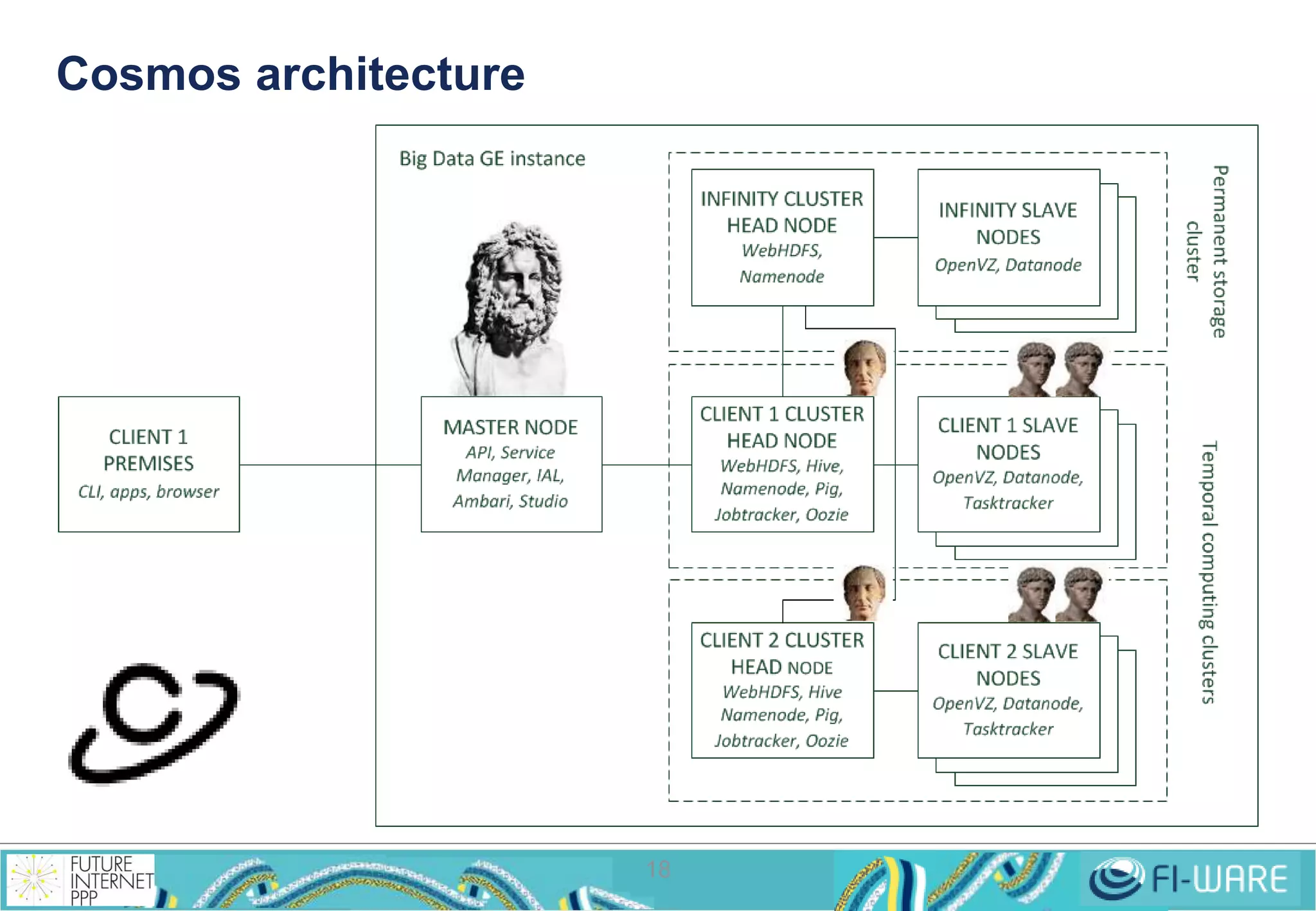
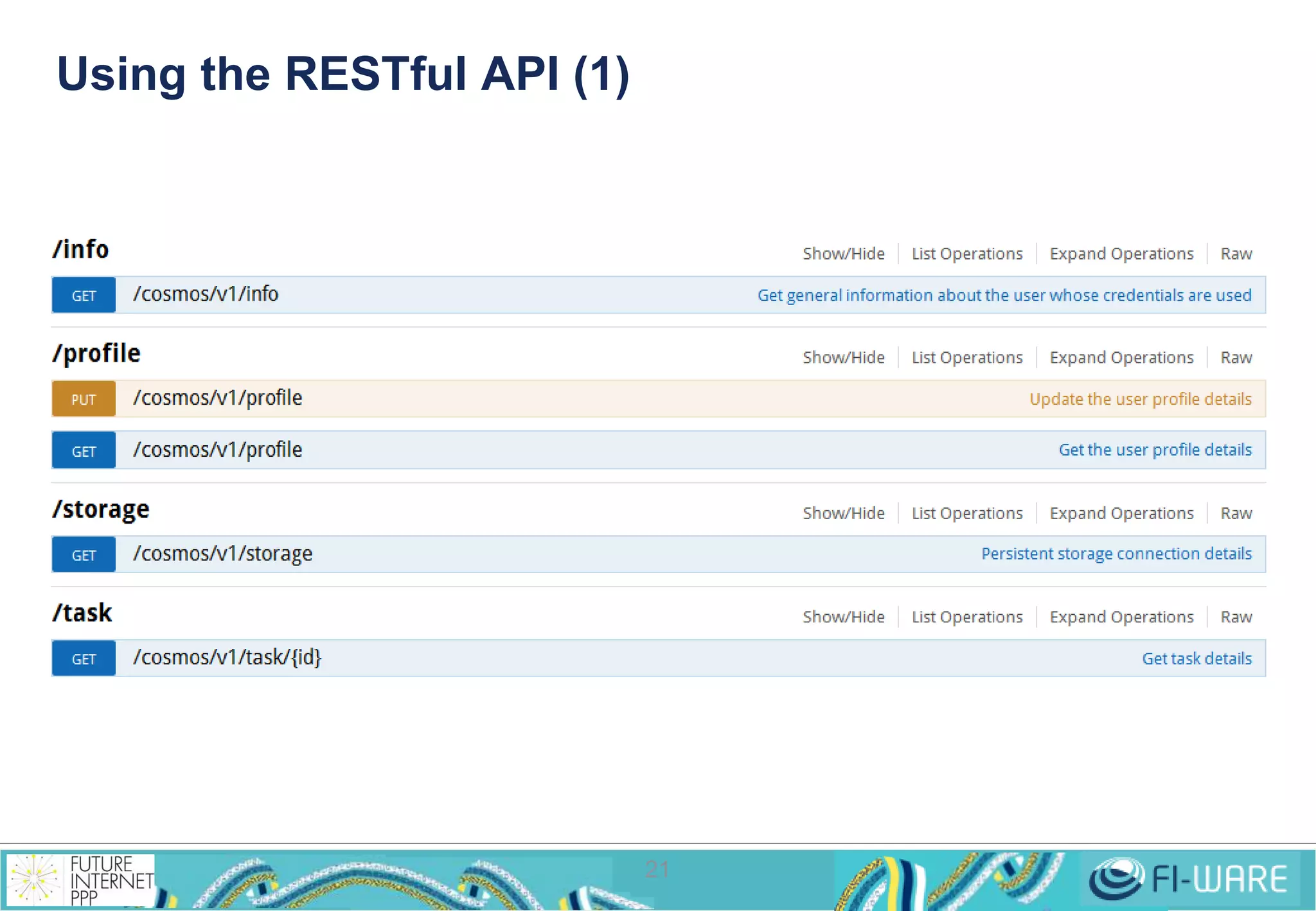
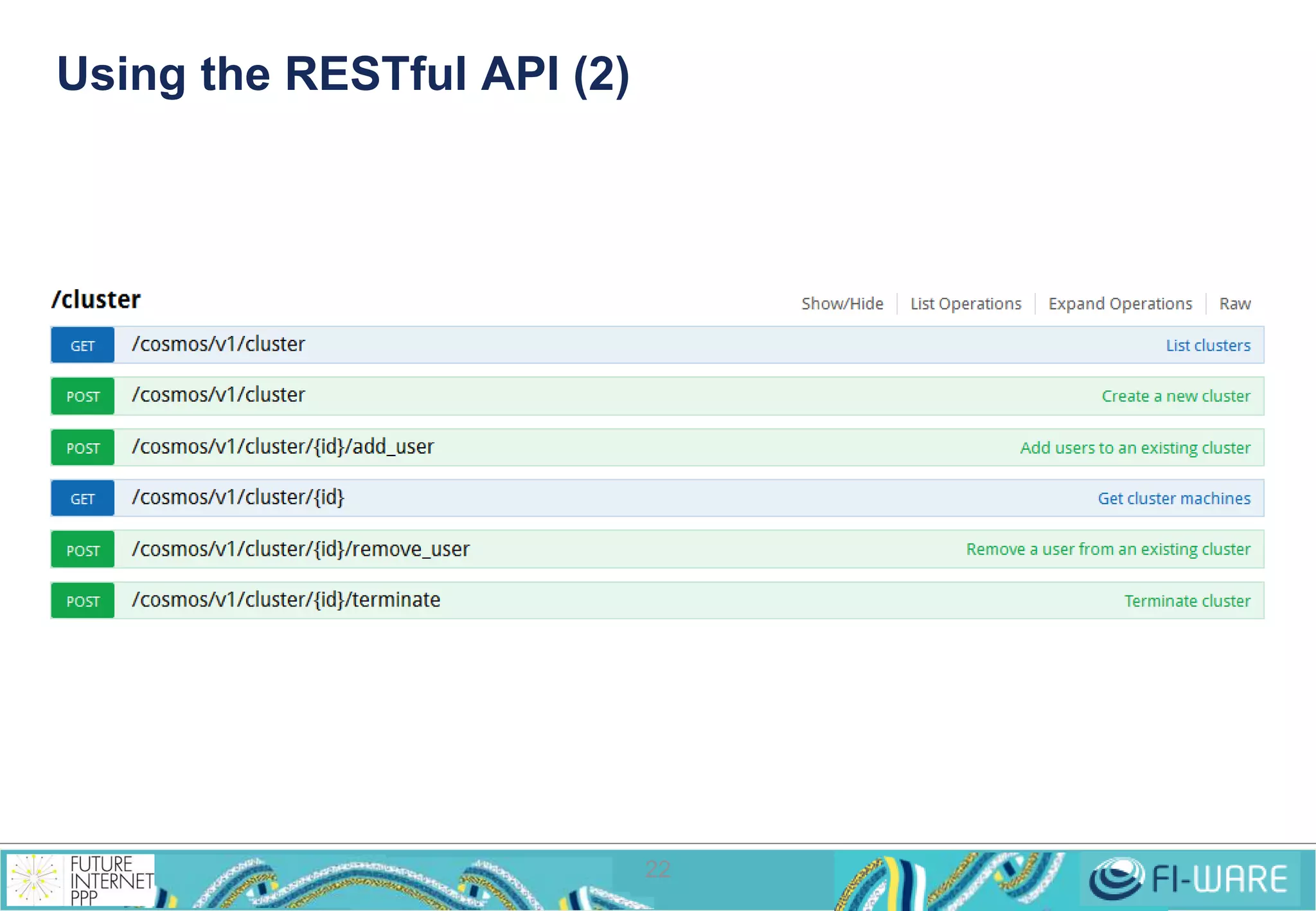
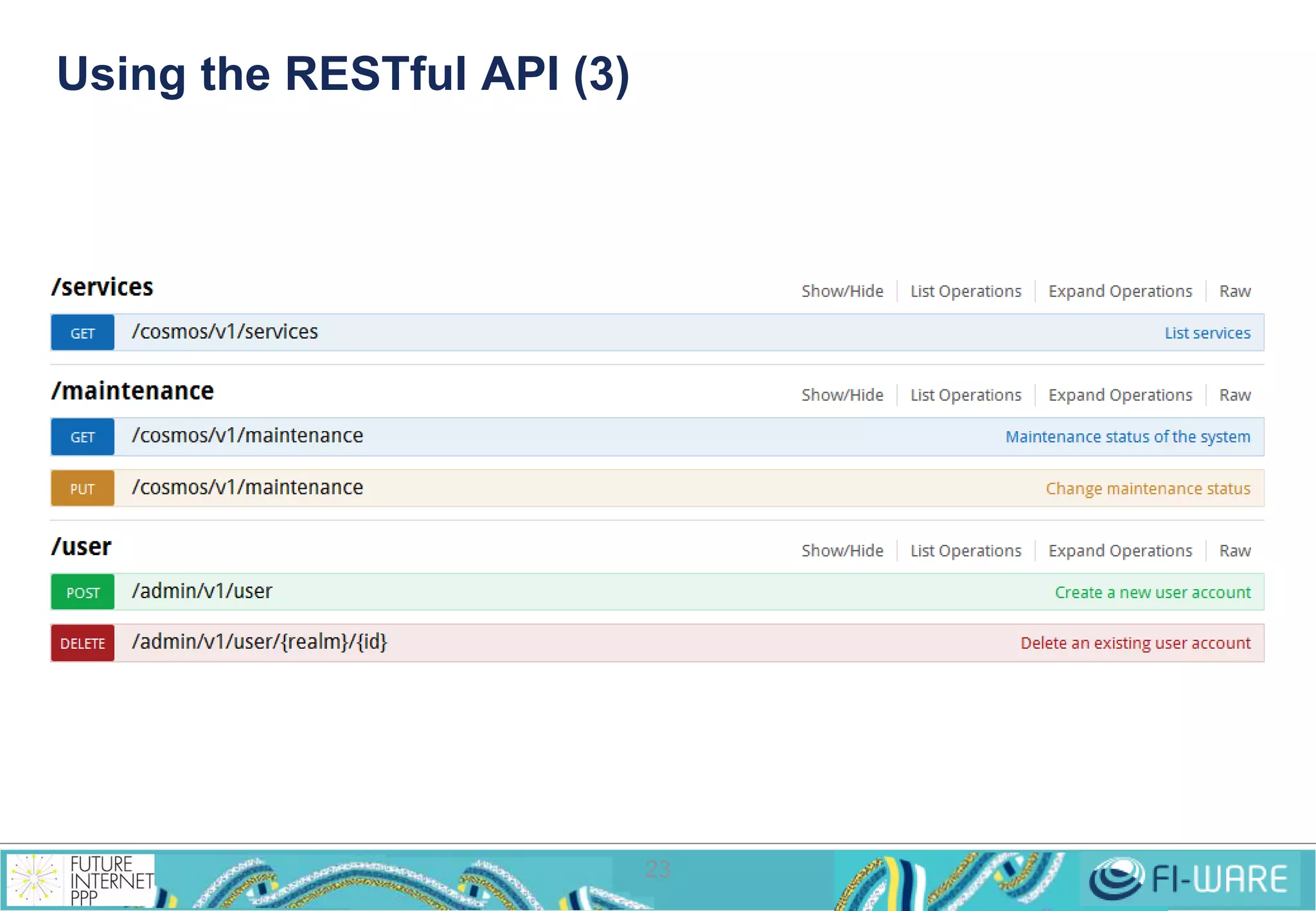
This document provides an overview of big data and the Cosmos big data platform from Telefonica. It discusses what big data is, how much data exists, and common tools for working with big data like Hadoop and MapReduce. It then describes the Cosmos platform, how to create clusters and access data using REST APIs or command line tools. Examples are given for querying data using Hive and writing MapReduce applications.
















![2. WebHDFS/HttpFS REST API
27
• List a directory
GET http://<HOST>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=LISTSTATUS
• Create a new directory
PUT http://<HOST>:<PORT>/<PATH>?op=MKDIRS[&permission=<OCTAL>]
• Delete a file or directory
DELETE http://<host>:<port>/webhdfs/v1/<path>?op=DELETE
[&recursive=<true|false>]
• Rename a file or directory
PUT
http://<HOST>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=RENAME&destination=<PATH>
• Concat files
POST
http://<HOST>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=CONCAT&sources=<PATHS>
• Set permission
PUT http://<HOST>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=SETPERMISSION
[&permission=<OCTAL>]
• Set owner
PUT http://<HOST>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=SETOWNER
[&owner=<USER>][&group=<GROUP>]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fi-warecosmosv7tech-141201032051-conversion-gate02/75/Cosmos-Big-Data-GE-Implementation-28-2048.jpg)
![2. WebHDFS/HttpFS REST API (cont.)
• Create a new file with initial content (2 steps operation)
PUT http://<HOST>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=CREATE
[&overwrite=<true|false>][&blocksize=<LONG>][&replication=<SHORT>]
[&permission=<OCTAL>][&buffersize=<INT>]
HTTP/1.1 307 TEMPORARY_REDIRECT
Location: http://<DATANODE>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=CREATE...
Content-Length: 0
PUT -T <LOCAL_FILE>
http://<DATANODE>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=CREATE...
28
• Append to a file (2 steps operation)
POST
http://<HOST>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=APPEND[&buffersize=<INT>]
HTTP/1.1 307 TEMPORARY_REDIRECT
Location: http://<DATANODE>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=APPEND...
Content-Length: 0
POST -T <LOCAL_FILE>
http://<DATANODE>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=APPEND...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fi-warecosmosv7tech-141201032051-conversion-gate02/75/Cosmos-Big-Data-GE-Implementation-29-2048.jpg)
![2. WebHDFS/HttpFS REST API (cont.)
• Open and read a file (2 steps operation)
GET http://<HOST>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=OPEN
[&offset=<LONG>][&length=<LONG>][&buffersize=<INT>]
HTTP/1.1 307 TEMPORARY_REDIRECT
Location: http://<DATANODE>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=OPEN...
Content-Length: 0
GET http://<DATANODE>:<PORT>/webhdfs/v1/<PATH>?op=OPEN...
• http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-project-dist/
hadoop-hdfs/WebHDFS.html
• HttpFS does not redirect to the Datanode but to the HttpFS
server, hidding the Datanodes (and saving tens of public IP
addresses)
• The API is the same
• http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-hdfs-httpfs/
29
index.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fi-warecosmosv7tech-141201032051-conversion-gate02/75/Cosmos-Big-Data-GE-Implementation-30-2048.jpg)




![5. MapReduce applications
• MapReduce applications are commonly written in Java
• Can be written in other languages through Hadoop Streaming
• They are executed in the command line
$ hadoop jar <jar-file> <main-class> <input-dir> <output-dir>
• A MapReduce job consists of:
• A driver, a piece of software where to define inputs, outputs, formats,
etc. and the entry point for launching the job
• A set of Mappers, given by a piece of software defining its behaviour
• A set of Reducers, given by a piece of software defining its behaviour
36
• There are 2 APIS
• org.apache.mapred old one
• org.apache.mapreduce new one
• Hadoop is distributed with MapReduce examples
• [HADOOP_HOME]/hadoop-examples.jar](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fi-warecosmosv7tech-141201032051-conversion-gate02/75/Cosmos-Big-Data-GE-Implementation-37-2048.jpg)


![5. MapReduce applications – Driver
39
/* org.apache.mapred example */
package my.org
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.*;
public class WordCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
JobConf conf = new JobConf(WordCount.class);
conf.setJobName("wordcount");
conf.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
conf.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
conf.setMapperClass(MapClass.class);
conf.setCombinerClass(ReduceClass.class);
conf.setReducerClass(ReduceClass.class);
conf.setInputFormat(TextInputFormat.class);
conf.setOutputFormat(TextOutputFormat.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(conf, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(conf, new Path(args[1]));
JobClient.runJob(conf);
} // main
} // WordCount](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fi-warecosmosv7tech-141201032051-conversion-gate02/75/Cosmos-Big-Data-GE-Implementation-40-2048.jpg)