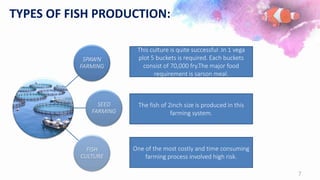
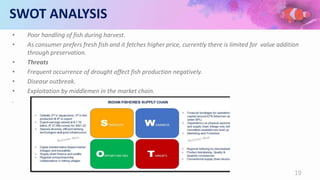
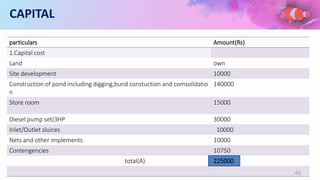
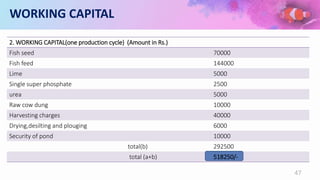
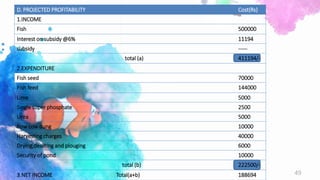
This document provides a summary of a fishery project report presented by 6 students. It discusses the introduction to fisheries and its importance in India. It then covers various aspects of the proposed project such as pisciculture, types of fish production including spawning, seed and fish farming. It also discusses culture and capture fisheries. The document further provides details on the proposed project including location, land, buildings, layout, machinery, production process, utilities, raw materials, manpower, products, market, costs, profitability, capital requirements and break even analysis.