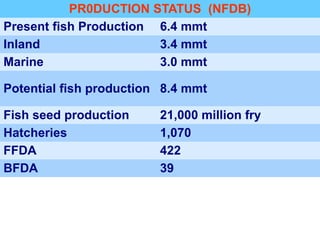
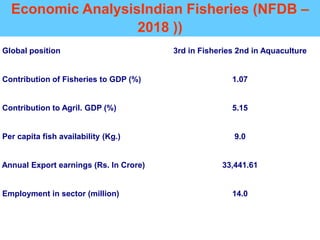
This document discusses the components and process of an indigenous fish feed manufacturing plant. It notes that the plant would have components like weigh scales, elevators, mixers, grinders, screens, and pelletizers to process ingredients into fish feed. The mixing, cooking, conditioning and pelletizing process is described. Additional components like dust collectors and control panels are also mentioned. The document provides context on the need for more localized fish feed production in India.