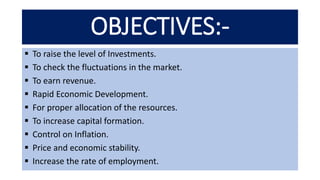
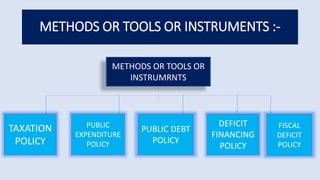
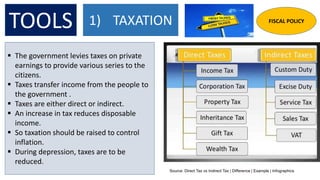
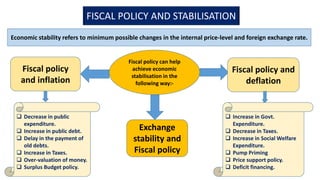
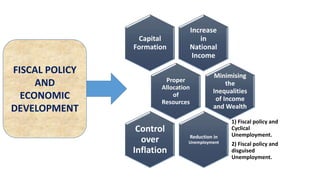
The document presents information on fiscal policy, including definitions, objectives, tools, and how it can be used for economic stabilization and development. Fiscal policy refers to the government's use of taxing and spending tools to influence macroeconomic variables and achieve goals like economic growth and stability. The key tools of fiscal policy discussed are taxation policy, public expenditure policy, public debt policy, deficit financing policy, and fiscal deficit policy.