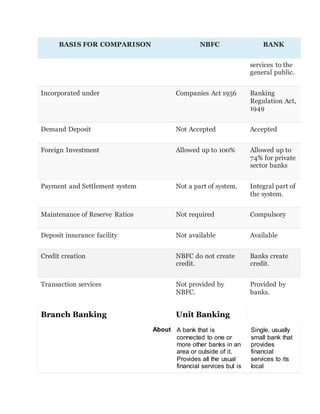
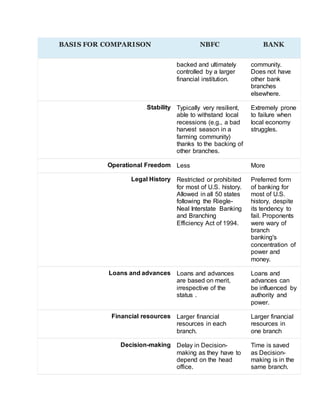
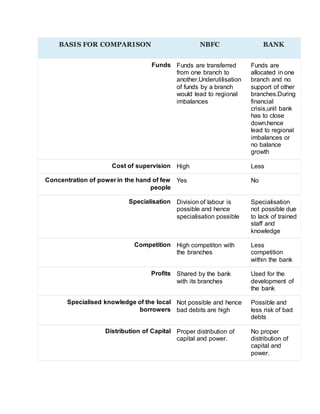
1. NBFCs provide banking services without a bank license and are incorporated under the Indian Companies Act, while banks are registered under the Banking Regulation Act and aim to provide banking services to the public.
2. NBFCs cannot accept demand deposits, have a higher limit of allowed foreign investment, and are not part of the banking payment and settlement system or required to maintain reserve ratios like banks.
3. Unlike banks, NBFC customers do not receive deposit insurance and the NBFC is not involved in credit creation or providing transaction services.