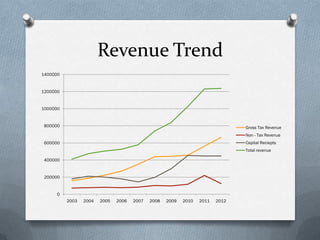
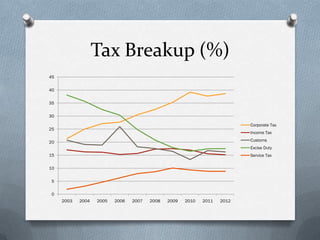
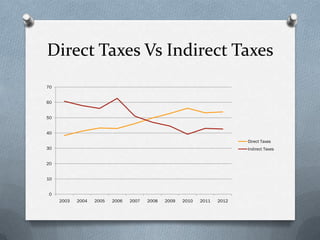
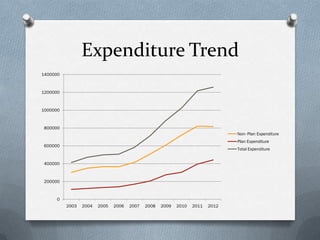
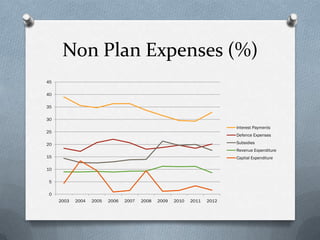
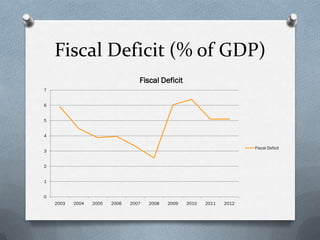
Fiscal policy is the government's use of spending and tax policies to influence the economy. The Indian government uses fiscal policy to achieve objectives like economic development, resource mobilization, and regional balanced growth. Key aspects of India's fiscal policy include reliance on indirect taxes and deficit financing. While fiscal policy aims to accelerate growth, reduce inequality and ensure stability, India's mounting public debt and black money pose challenges.