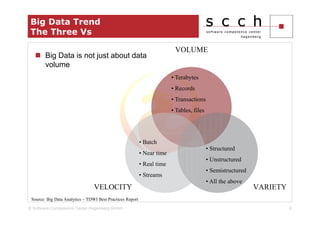
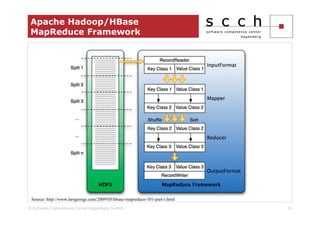
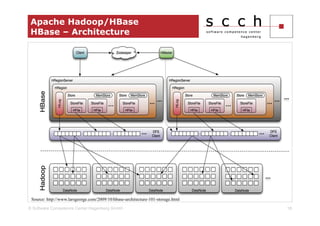
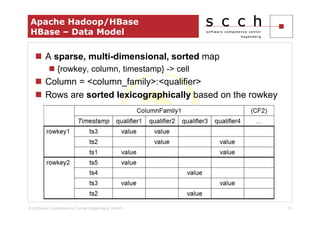
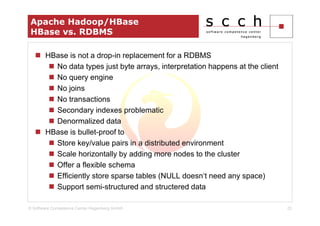
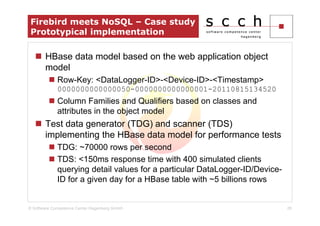
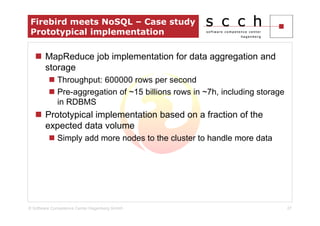
The document discusses the transition from traditional relational database management systems (RDBMS) to NoSQL solutions, particularly focusing on Apache HBase, to address scalability challenges posed by big data. It highlights the growing data volumes and unstructured data that necessitate a shift towards distributed systems like HBase, which allows for efficient data handling and storage. A case study of implementing HBase for a solar collector condition monitoring system is presented, demonstrating its capacity to manage vast amounts of measurement data effectively.