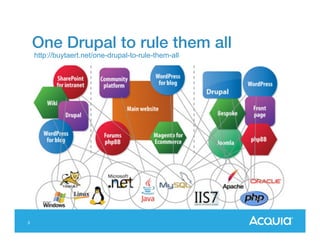
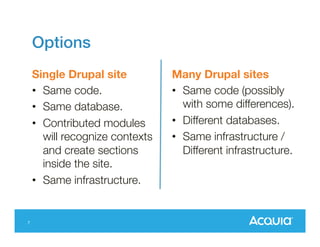
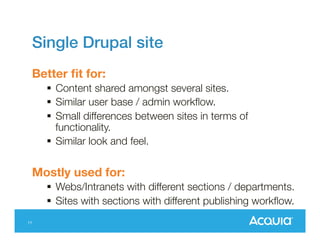
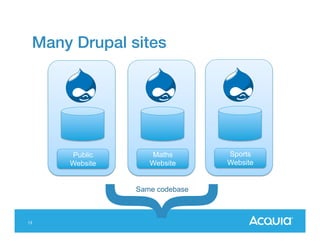
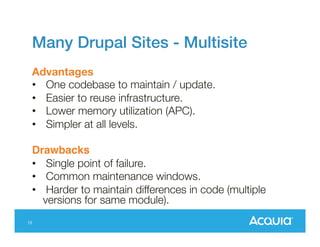
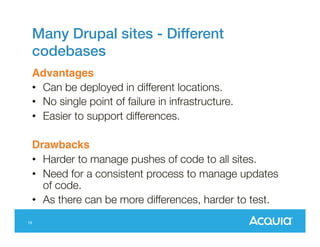
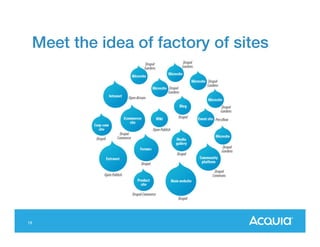
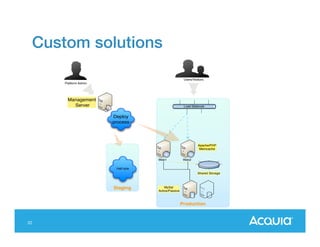
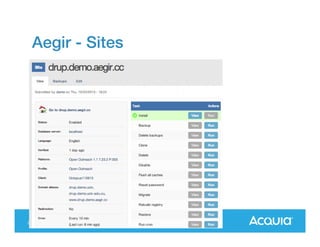
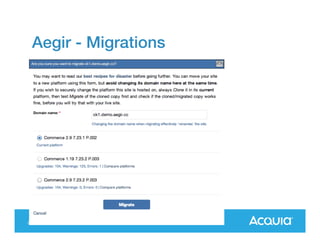
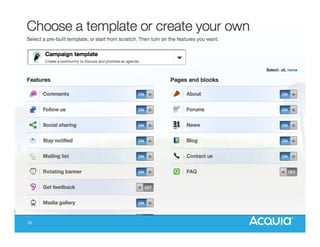
The document presents a discussion on managing a Drupal platform for multiple sites, highlighting the challenges and solutions for single and multiple site configurations. It explores the advantages and drawbacks of single Drupal sites versus multisite installations, emphasizing the need for minimal downtime and shared features. Various custom solutions and services, including Aegir, Drupal Gardens, and Acquia Cloud Site Factory, are mentioned as potential tools to effectively manage such environments.