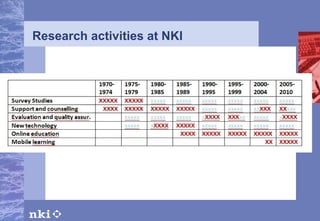
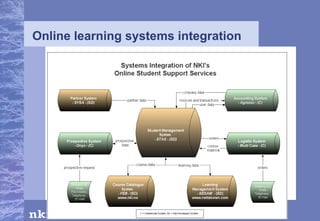
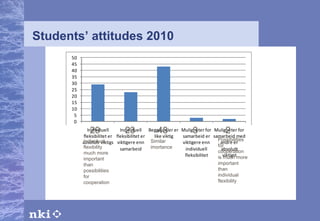
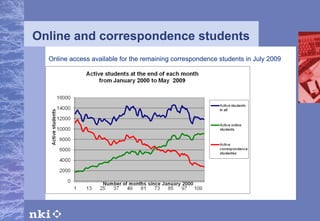
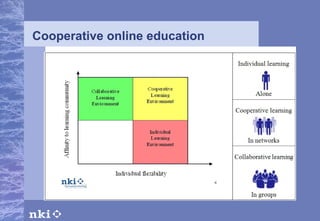
The document summarizes research conducted by the NKI Internet College, a leading provider of online distance education in Norway. NKI has 40 years of experience in distance education research and has explored topics like dropout rates, effects of different teaching techniques, and personalizing instruction at scale. The document outlines NKI's four generations of online learning systems and innovations. It also discusses adapting learning materials to individual students' needs, though current materials are not individually customized. The AM-Learning project's focus on automatic individualization of learning messages based on language ability aligns with NKI's research goals.