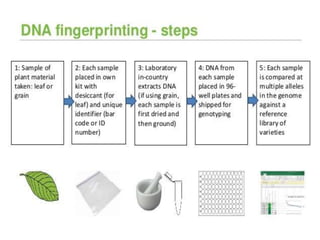
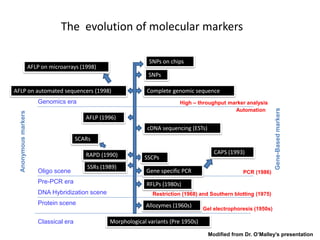
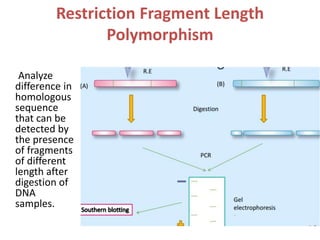
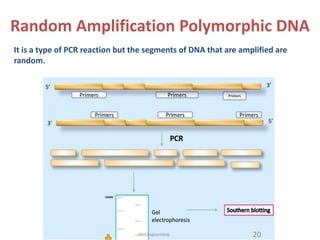
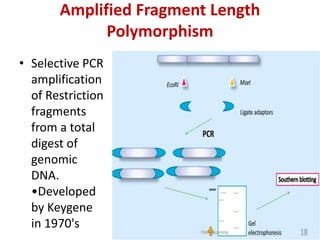
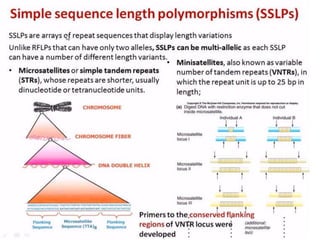
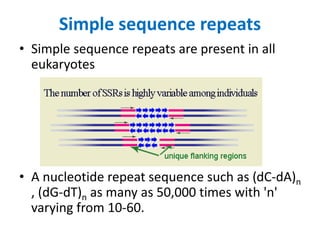
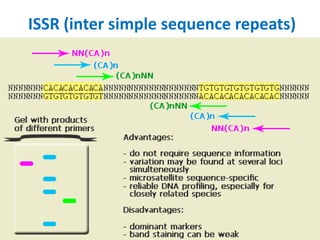
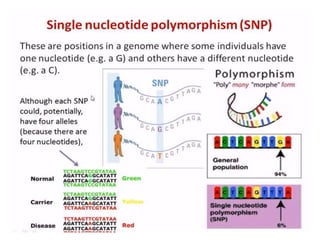
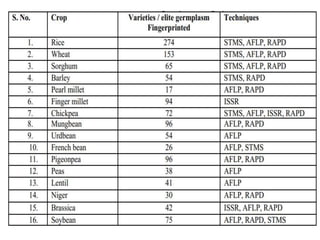
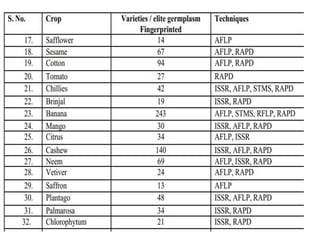
DNA fingerprinting is a technique used for identification by extracting and identifying the base pair pattern of an individual's DNA. Alec Jeffreys developed DNA fingerprinting in 1984 at Leicester University. The evolution of molecular markers progressed from morphological variants pre-1950s to anonymous markers, gene-based markers such as allozymes in the 1960s, RFLPs in the 1980s, SNPs, and complete genomic sequences. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analyzes differences in homologous sequences detected by fragments of different lengths after DNA digestion. Random amplification polymorphic DNA and amplified fragment length polymorphism are types of PCR that amplify random or restriction fragments, respectively. Simple sequence repeats are repetitive nucleotide sequences that vary in length and are used for