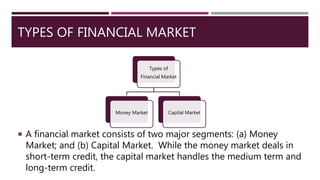
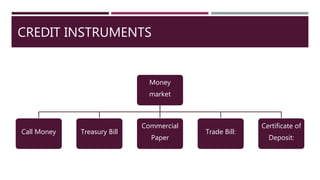
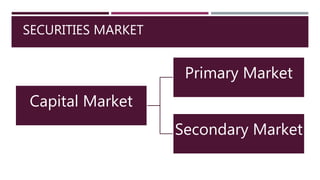
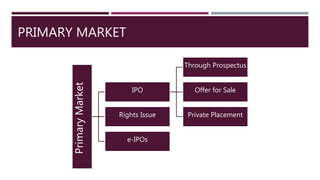
The document provides a comprehensive overview of financial markets, defining investment and explaining its significance. It categorizes financial markets into money markets for short-term funds and capital markets for medium to long-term funds, and outlines the roles of primary and secondary markets, including stock exchanges in India. Additionally, it highlights the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and its regulatory functions to protect investors and ensure market integrity.