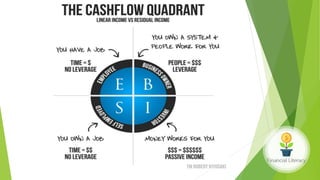
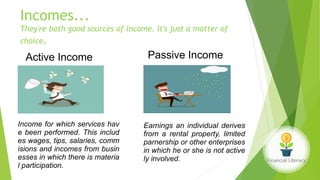
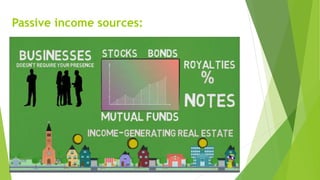
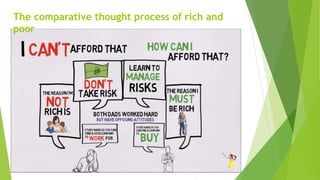
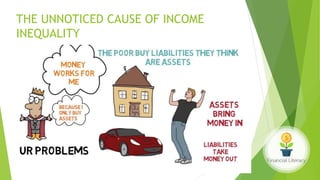
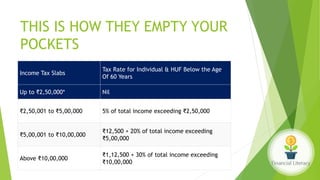
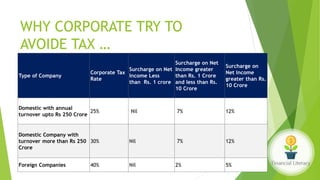
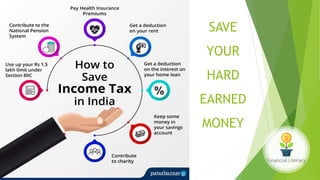
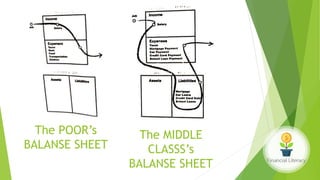
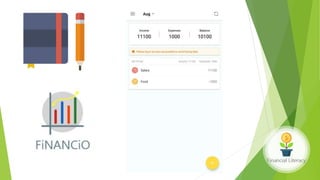
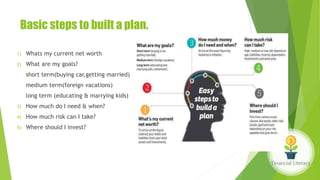
The document emphasizes the importance of financial literacy for achieving financial freedom and provides guidance for effective personal finance management, including budgeting, saving, investing, and retirement planning. It highlights the disparity in financial literacy among demographics, such as millennials, and critiques corporate tax strategies and their implications on individual finances. The text promotes various investment avenues and government schemes aimed at enhancing financial literacy and security, while outlining principles for saving and managing finances effectively.