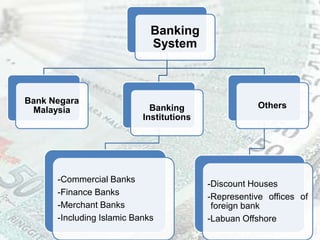
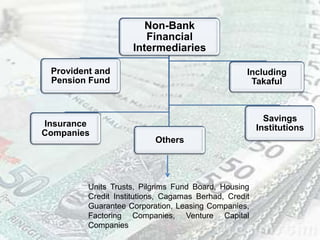
This document provides an overview of Malaysia's banking and financial system. It discusses the various types of banking institutions like commercial banks, Islamic banks, finance companies, and merchant banks that are regulated by Bank Negara Malaysia. It also outlines the roles of non-bank financial intermediaries such as insurance companies, provident funds, savings institutions and capital market institutions. Finally, it provides brief descriptions of the functions of these different financial entities in Malaysia.