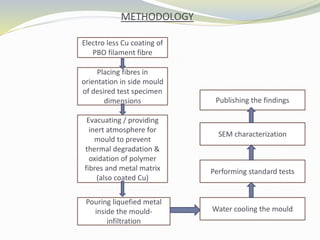
This document presents the design and development of a metal reinforced fibre composite. The project aims to fabricate a new composite made of PBO fibres reinforced in an aluminum-magnesium eutectic alloy matrix. The composite will be produced using vacuum liquid metal melt infiltration. The goals are to improve properties like strength, stiffness, impact resistance, and reduce density compared to the metal alloy alone. Testing will characterize the mechanical properties and microstructure of the composite.