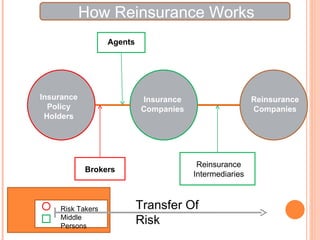
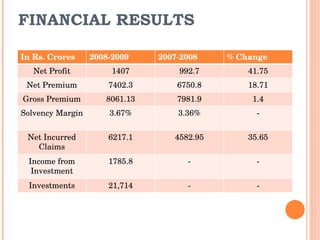
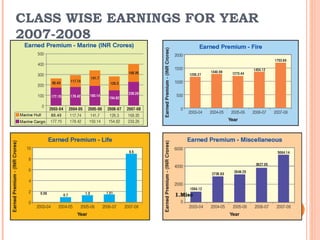
Reinsurance involves insurance companies insuring each other's risks. There are two main types of reinsurance - facultative, which applies to individual risks, and treaty, which applies to a company's entire book of business. Reinsurance can be proportional, where the reinsurer takes a share of each policy, or non-proportional, where the reinsurer covers losses over a certain amount. The reinsurance market in India is dominated by GIC, the sole domestic reinsurer, which reinsures a portion of policies with international reinsurers. Some challenges for reinsurers in the Indian market include higher premium rates and a lack of desirable quotes from Indian reinsurers for small deals.