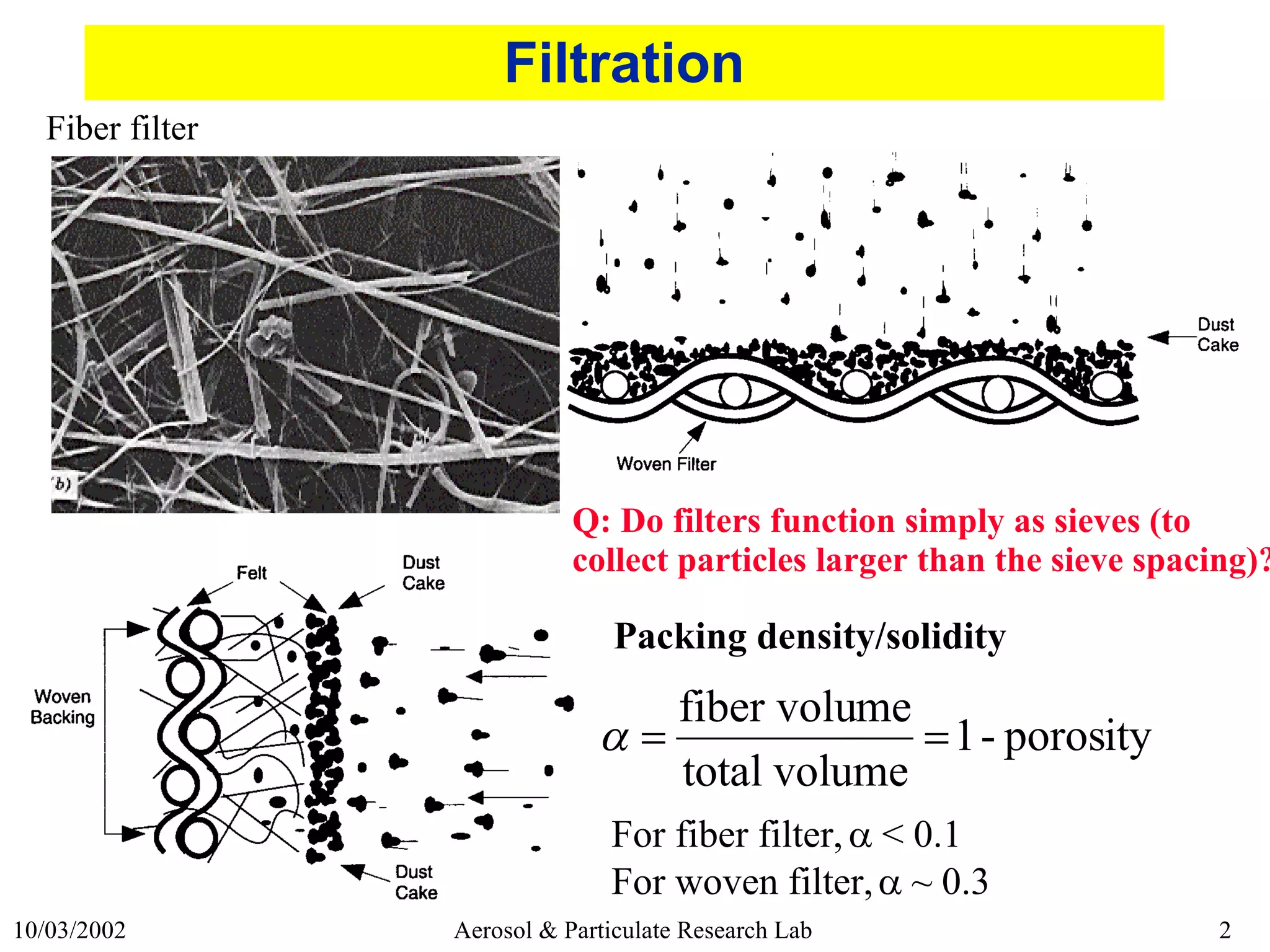
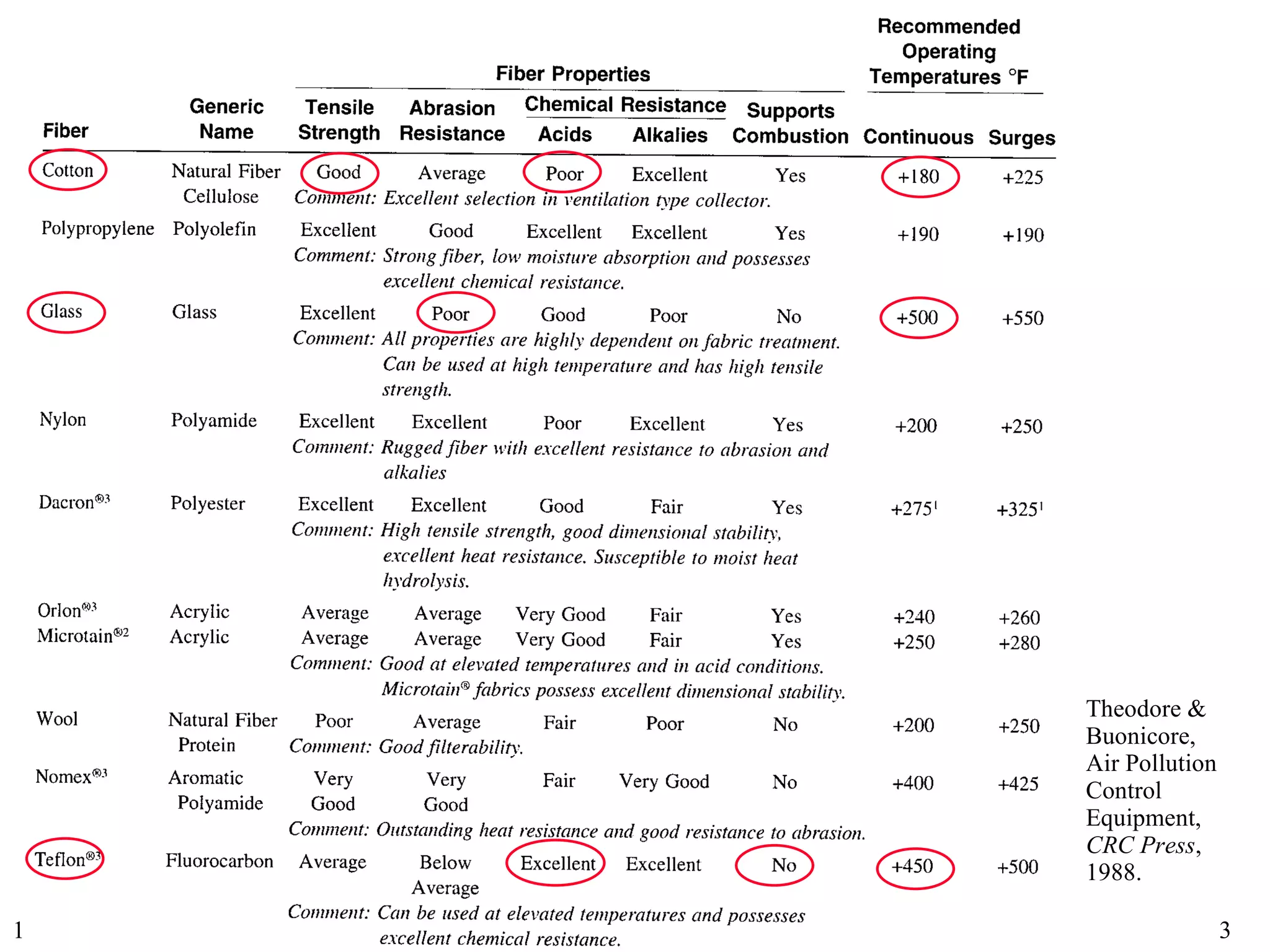
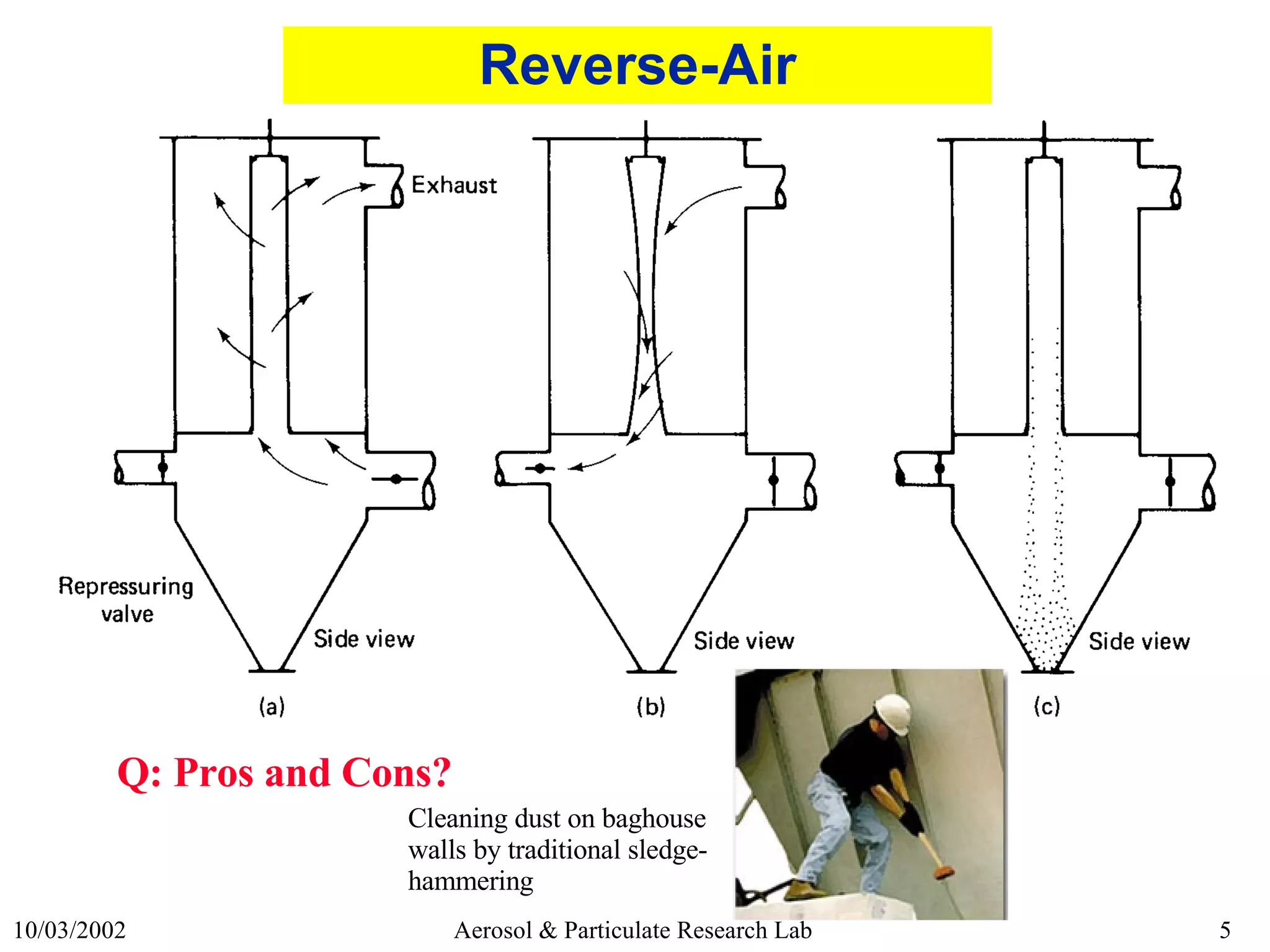
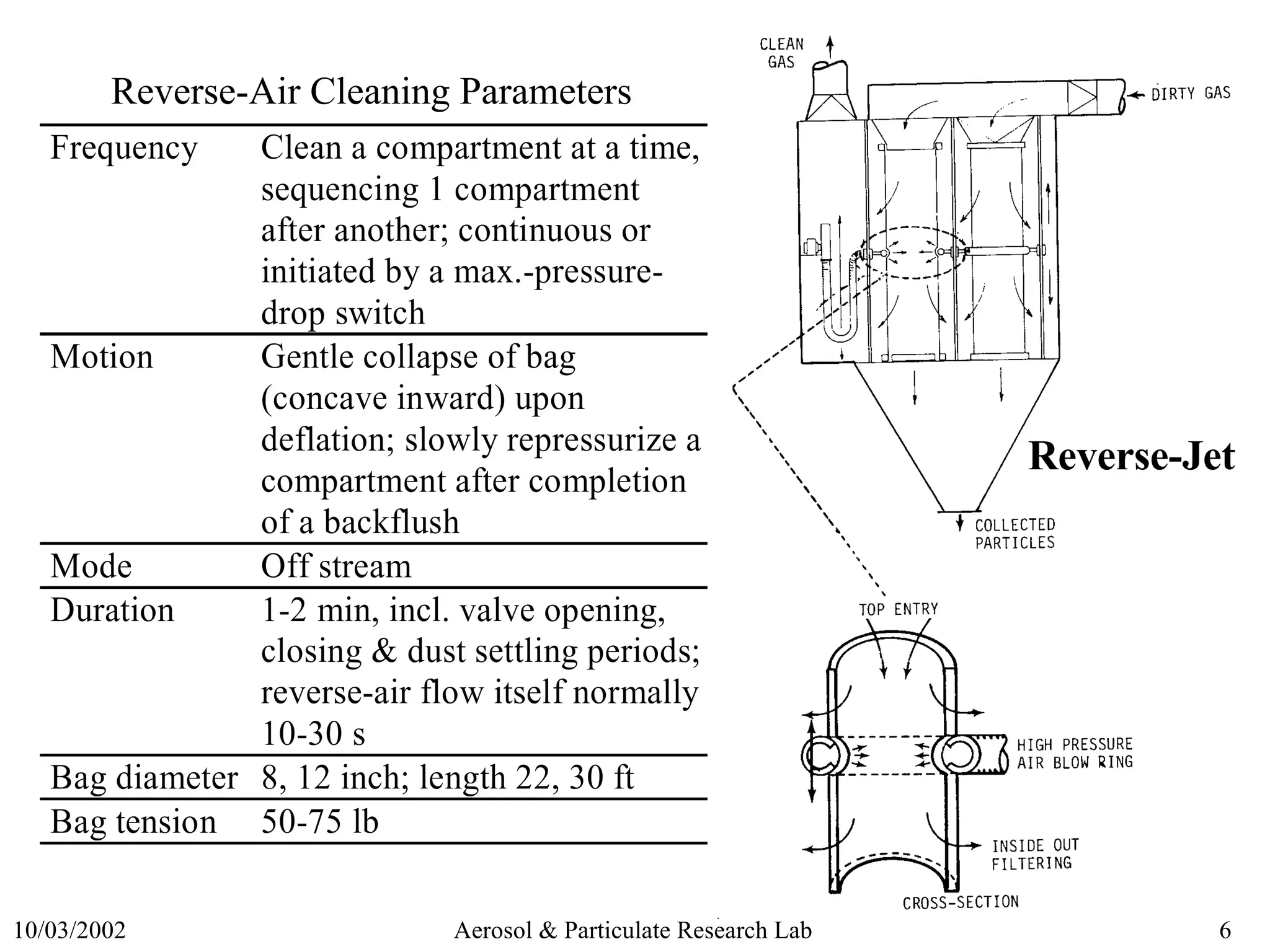
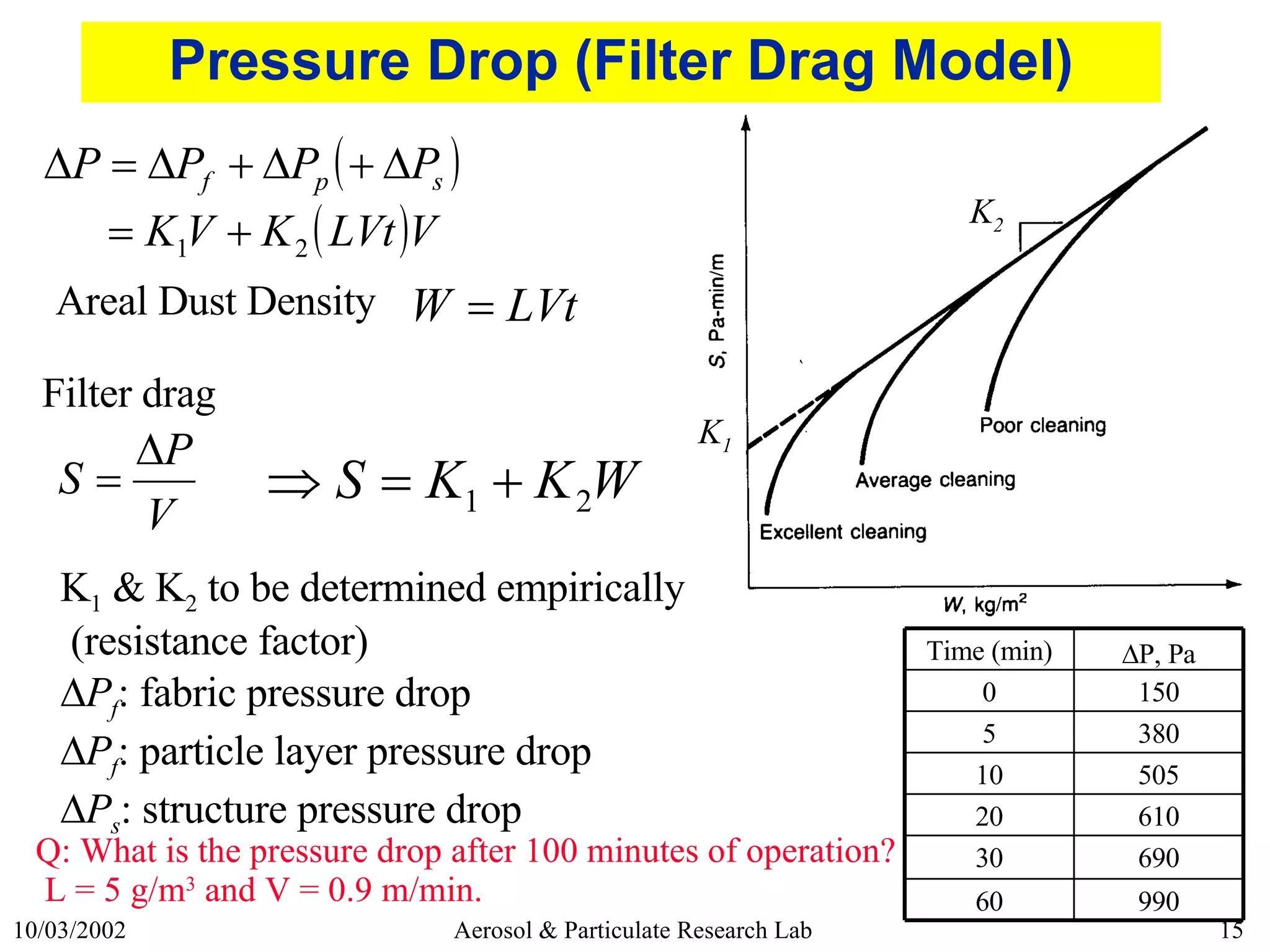
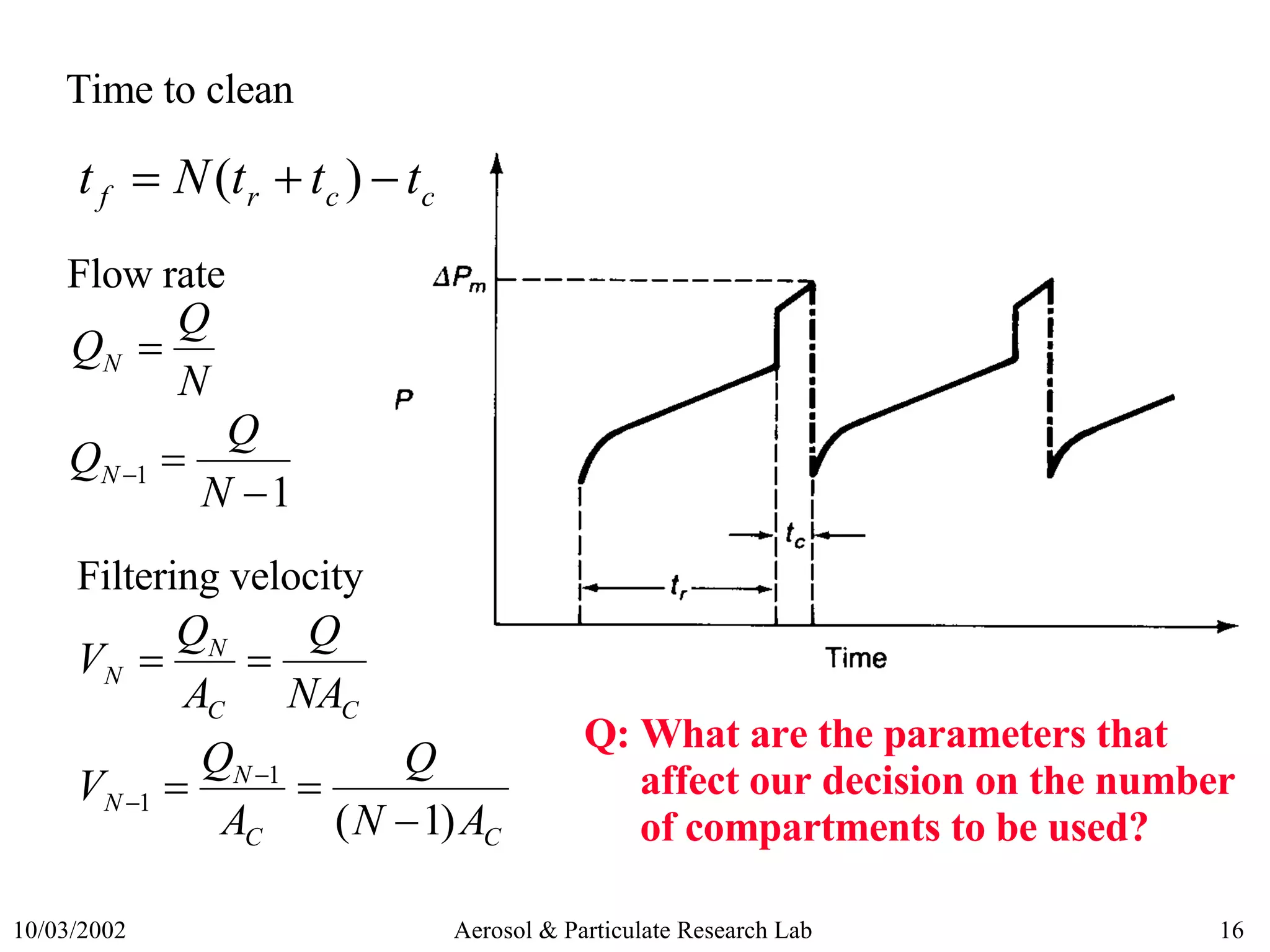
This document discusses various topics related to fabric filter design and operation including:
1) Fabric selection factors such as packing density and fiber type.
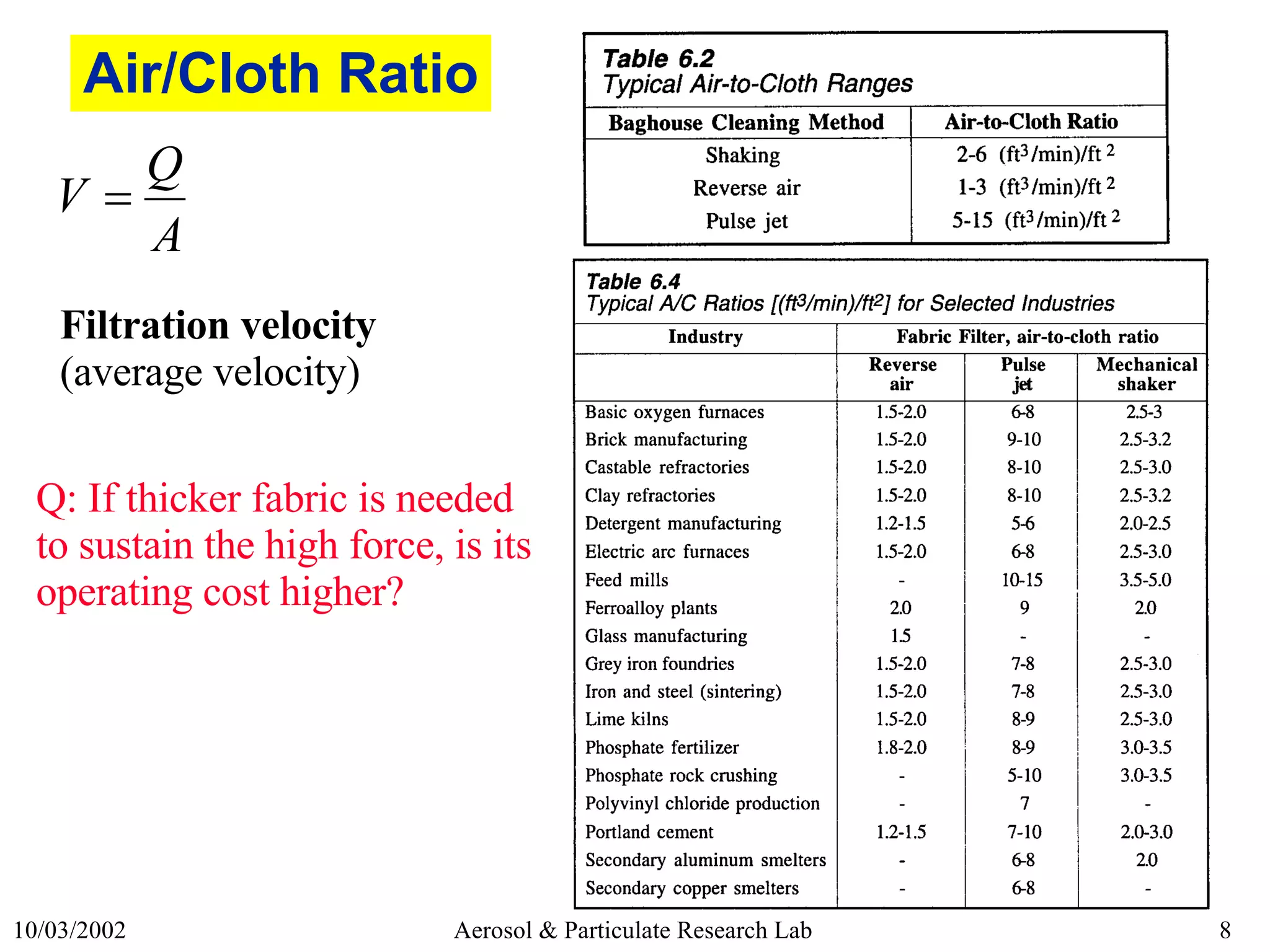
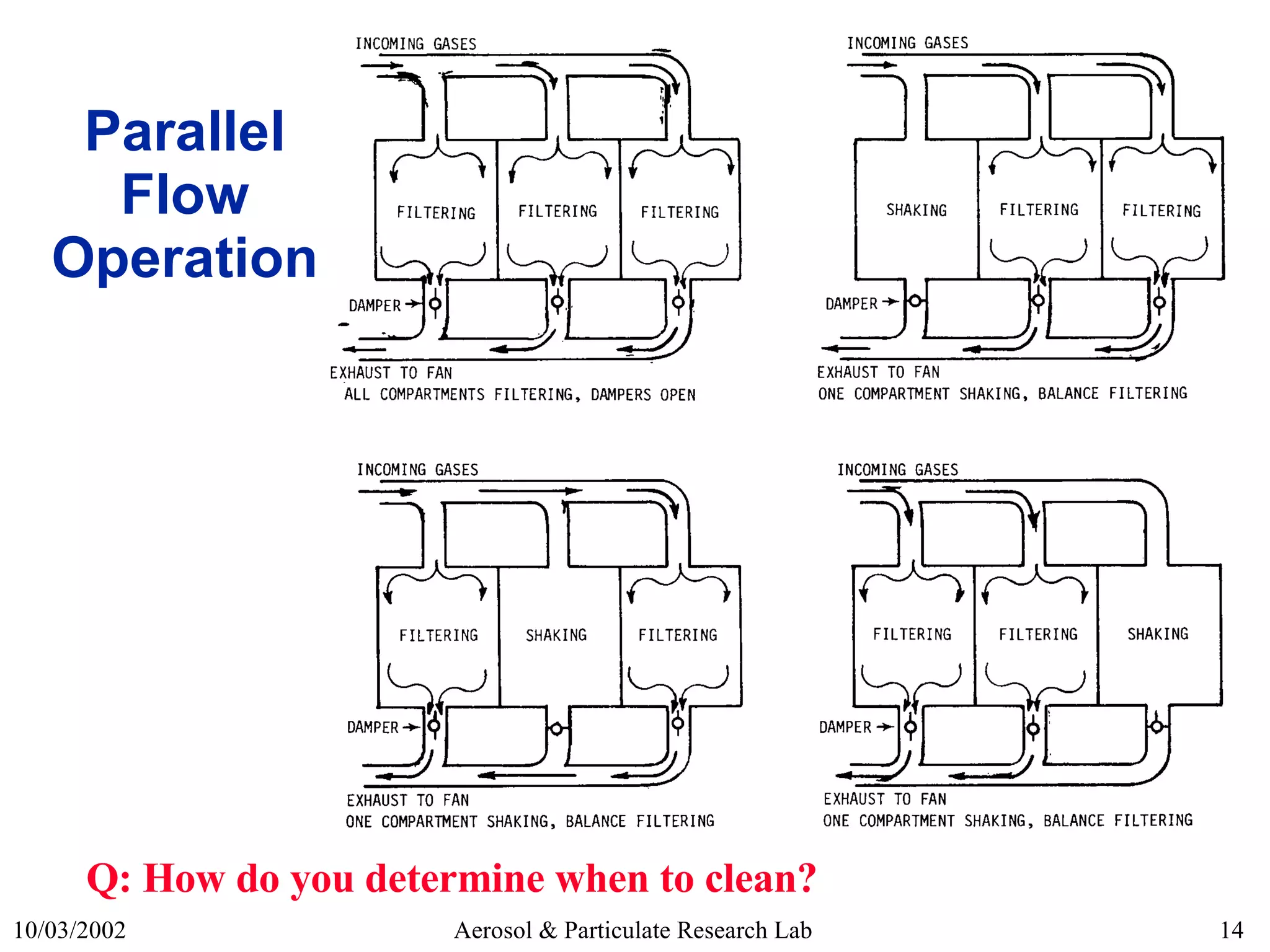
2) Common cleaning methods like shaker, reverse-air, and pulse-jet cleaning and their pros and cons.
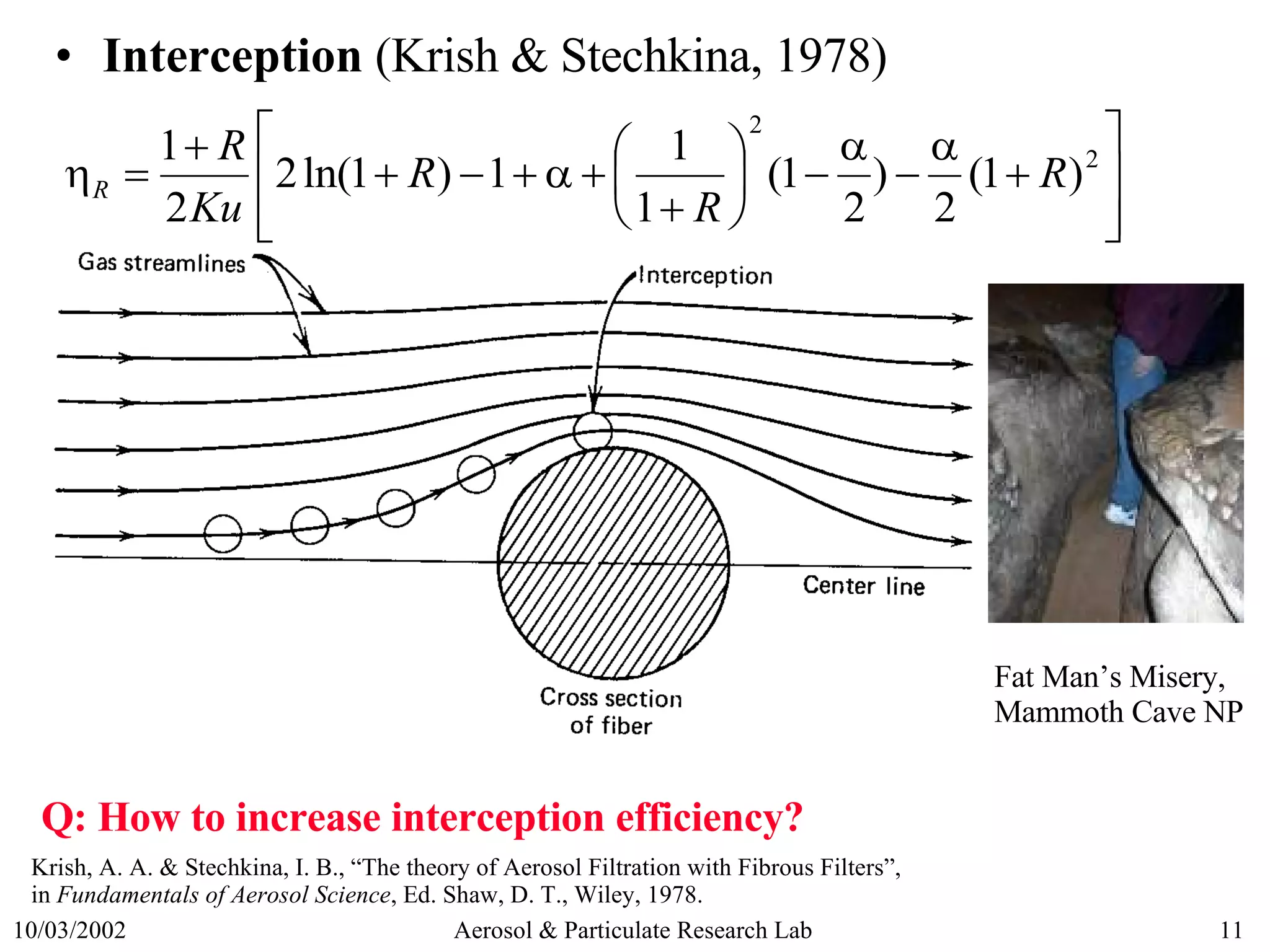
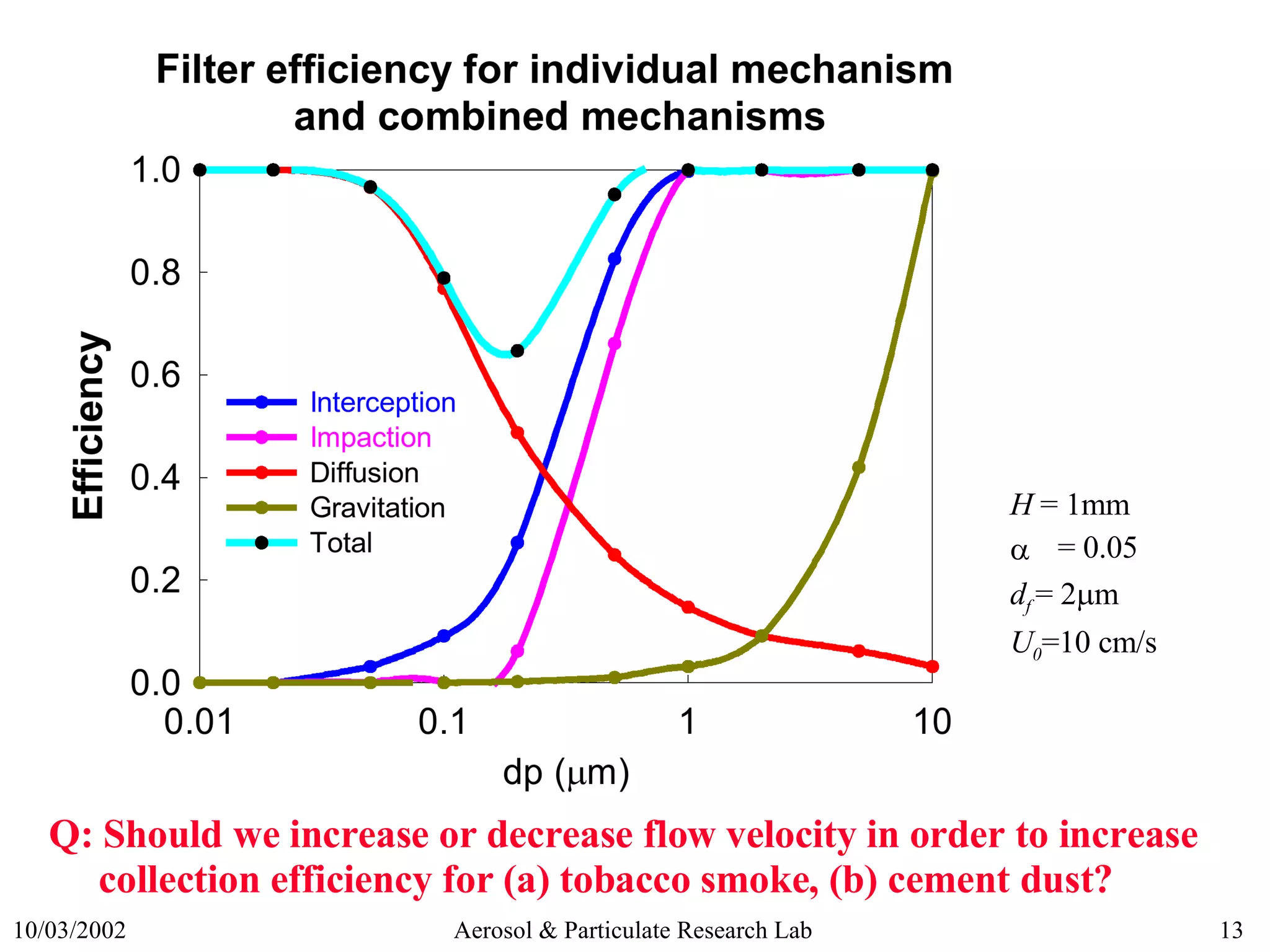
3) Key filtration mechanisms like diffusion, impaction, and interception and how efficiency is affected by particle size.
4) Parameters that influence pressure drop over time like dust loading and filter drag coefficients.
5) Design considerations for factors like compartmentalization and cleaning cycle timing.