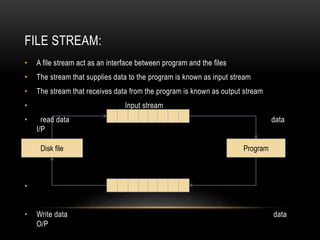
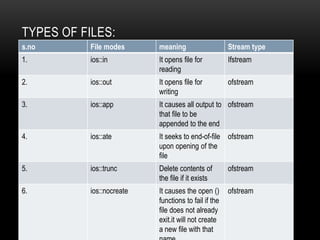
This document discusses files and file streams in C++. It covers the different stream classes like fstream, ifstream, and ofstream used for file input/output. It describes opening and closing files, reading/writing characters and objects to files, and different file modes. Example programs are provided to demonstrate reading from and writing to files using functions like get(), put(), read(), and write().









![#include <fstream.h>
Void main()
{
char ch;
ifstream infile (“out.txt”);
while (infile)
{
infile.get (ch);
cout << ch;
}
infile . Close();l
}
#include <fstream.h>
void main()
{
ofstream outfile (“out.txt”);
char str[]=“This is a text file”;
int i=0;
while (str[i])
outfile.put (str [i++]);
outfile.close ();
}
EXAMPLE PROGRAMS:
To create a file using put() To read a file using get()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesinc-201111133121/85/Files-in-c-12-320.jpg)


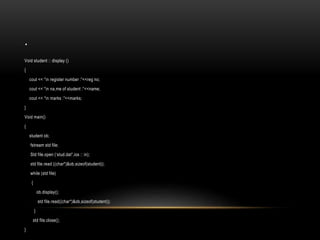
![PROGRAM TO CREATE A STUDENT FILE:
#include<fstream.h>
Class student
{
private :
int regno,mark;
char name [20];
public :
void getdata ();
};
void student :: getdata ()
{
cout <<“n enter reg.number :”;
cin >> reg no;
cout <<“n enter name of students”;
gets (name);
cout <<“nenter marks:”;
cin >> marksw;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesinc-201111133121/85/Files-in-c-15-320.jpg)