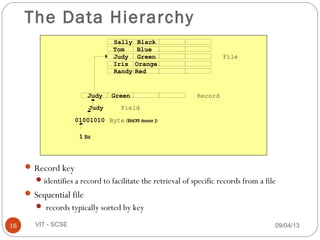
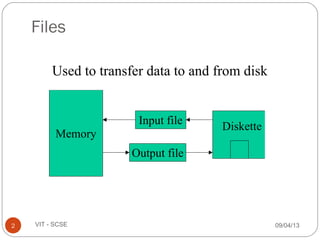
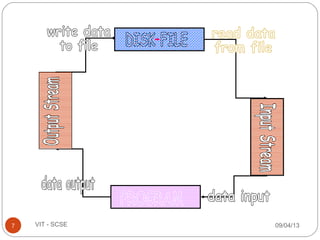
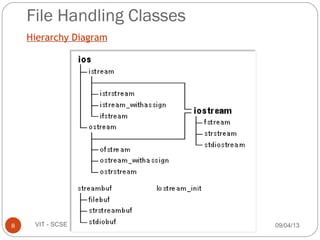
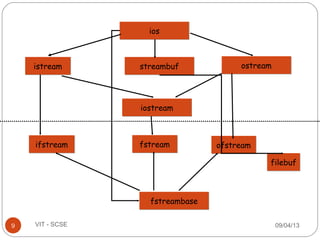
The document discusses files and streams in C++. It defines files as sequences of bytes that end with an end-of-file marker. Streams are used to connect programs to files for input and output. There are standard input and output streams (cin and cout) as well as file streams that use classes like ifstream for input and ofstream for output. Files can be accessed sequentially or randomly - sequential files are read from start to finish while random access files allow direct access to any record.







![09/04/1314 VIT - SCSE
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream.h>
#include <fstream.h>
void main() {
char infname[101];
char outfname[101];
char buffer[101];
cout << ”File to copy from: ";
cin >> infname;
ifstream in(infname);
if (!in) {
cout << "Unable to open " << infname
<< endl;
exit(0);
}
cout << "File to copy to: ";
cin >> outfname;
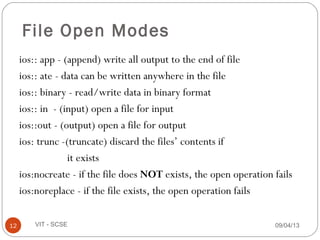
ofstream out(outfname,ios::out |
ios::noreplace);
if (!out) {
cout << "Unable to open " <<
outfname << " -- already exists!" <<
endl;
exit(0);
}
in.getline(buffer,100);
while (!in.eof()) {
out << buffer << endl;
in.getline(buffer,100);
}
in.close();
out.close();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/17filesandstreams-130903232400-/85/17-files-and-streams-14-320.jpg)