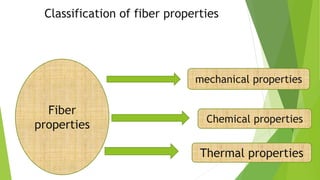
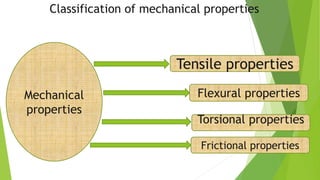
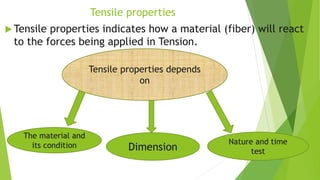
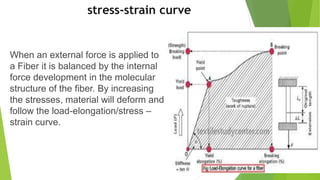
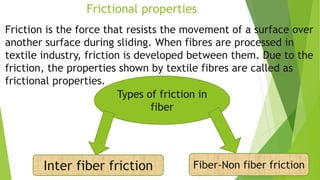
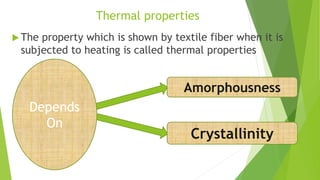
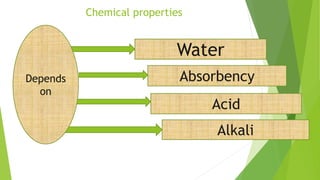
This presentation discusses the properties of fibers used in textiles. It begins with an introduction of the presenters and defines a textile fiber as having strength, flexibility, and sufficient length to be spun. The document then categorizes fiber properties into mechanical, chemical, and thermal properties. Under mechanical properties, it focuses on tensile properties like stress-strain curves, and frictional properties. For chemical properties, it discusses water absorbency, interaction with acids and alkalis. Thermal properties depend on the amorphous and crystalline regions of fibers which influence properties like absorbency when heated.