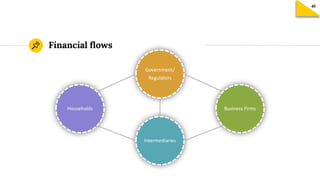
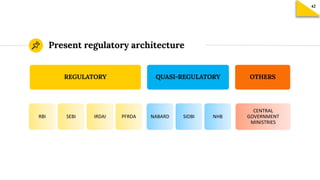
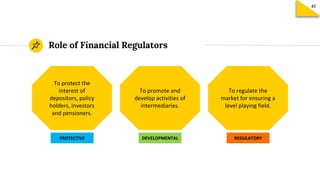
The document discusses the structure and key components of India's financial system. It outlines the main financial institutions, instruments, and markets. It also describes the key functions of a financial system in facilitating resource transfer, transactions, and risk management across sectors. Several regulatory bodies that oversee different aspects of the financial system are mentioned, including RBI, SEBI, and IRDAI. Their main roles are described as protective, developmental, and regulatory. Key financial markets like money market, capital market, and forex market are defined. Depositories like NSDL and CDSL and their role in facilitating electronic holding and transactions of securities are summarized. The primary and secondary markets are distinguished, with stock exchanges providing a platform for trading but