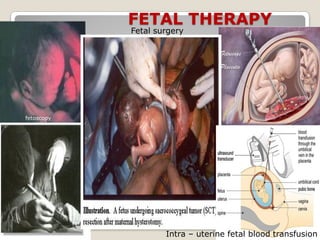
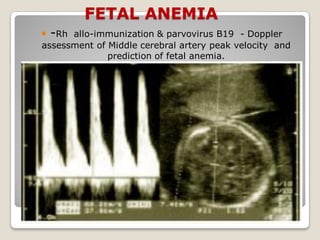
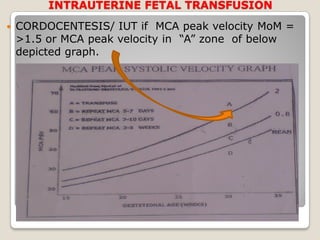
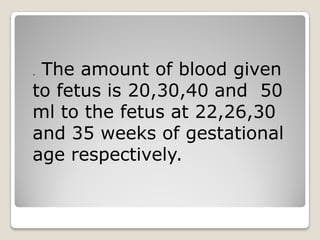
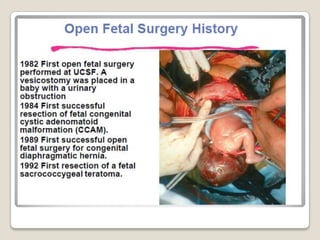
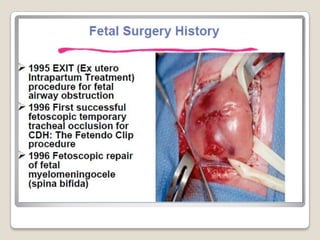
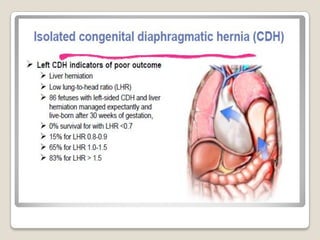
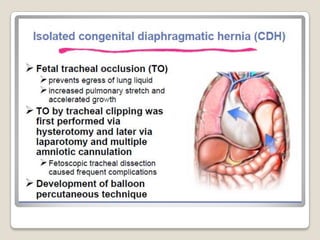
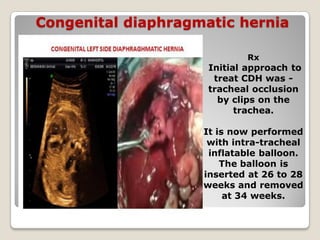
This document provides an overview of perinatology and fetal therapy. It discusses various pharmacological and surgical fetal therapies used to treat conditions such as cardiac arrhythmias, complete atrioventricular block, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, fetal anemia, twin-twin transfusion syndrome, congenital diaphragmatic hernia, and pleural effusions. Invasive fetal therapies discussed include intrauterine blood transfusion, fetoscopy, laser coagulation of vessels, and intra-amniotic gene transfer. Fetal therapy requires a multidisciplinary team and tools such as ultrasound, MRI, and fetoscopes to properly diagnose and treat conditions in-utero.