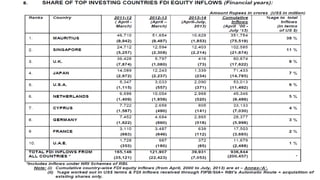
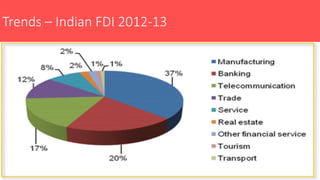
Foreign direct investment (FDI) into India was introduced in 1991 to boost the economy. FDI refers to investment made by companies or individuals in one country into business interests located in another country. India permits FDI through various routes like joint ventures, capital markets, and private placements. Key sectors that allow 100% FDI include insurance, telecom, petroleum, housing, and power. While FDI provides benefits like new jobs and technology, it also poses risks such as loss of domestic savings and political influence from foreign firms. Debates continue around allowing large foreign retailers like Walmart into India due to concerns over small retailers.