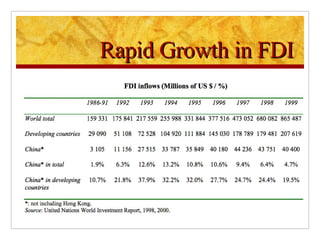
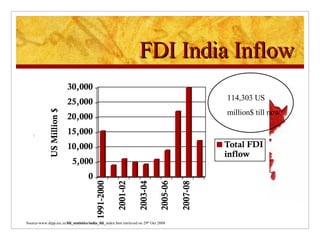
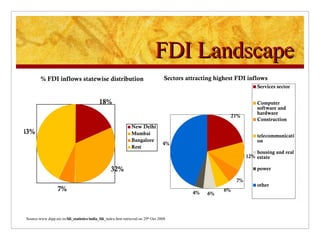
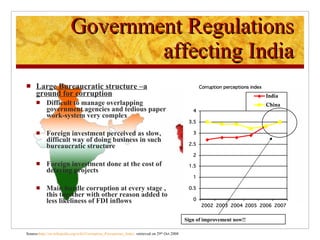
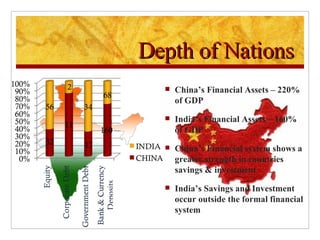
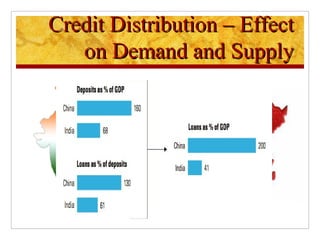
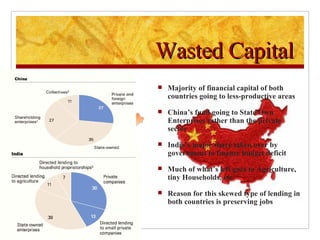
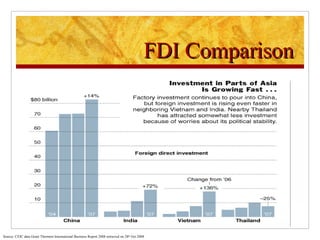
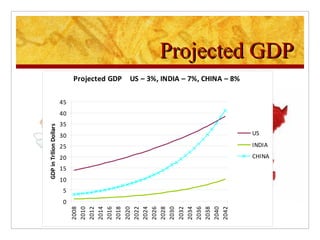
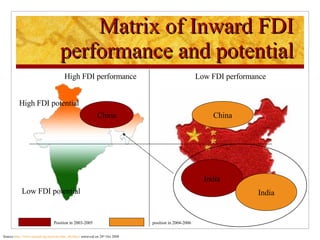
The document compares foreign direct investment (FDI) in China and India, discussing their histories and government regulations. It notes that China rapidly grew its FDI through reforms in the 1970s-80s, while India imposed many restrictions until liberalizing in the 1990s. Key differences are that China attracted more manufacturing FDI while India focused on services, and India faces infrastructure and bureaucratic hurdles more than China. Both countries could improve FDI by reducing barriers and inefficiencies.