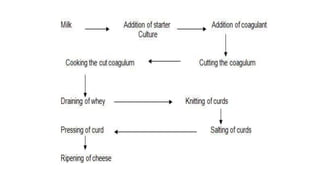
This document discusses various fermented milk products including cheese, yogurt, buttermilk, acidophilus milk, and kefir. It provides details on the production processes and microorganisms involved for each product. Cheese production involves coagulation of milk proteins followed by separation of curds and whey. Most cheeses then undergo ripening through microbial activity. Yogurt is produced by incubating milk with starter cultures at elevated temperatures to produce lactic acid. Buttermilk and acidophilus milk also involve lactic acid bacterial cultures. Kefir uses kefir grains containing various microbes. The document categorizes cheeses and describes characteristics of common types.