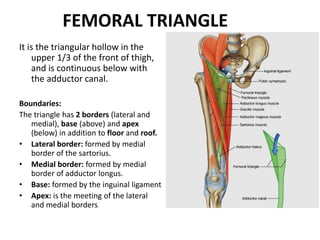
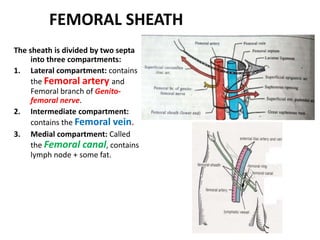
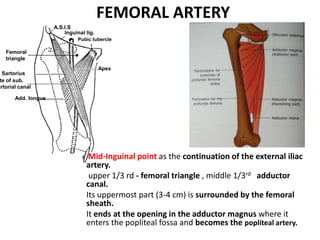
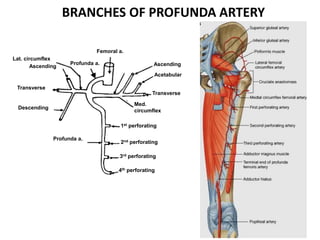
The document describes the femoral triangle region of the upper thigh. The femoral triangle contains the femoral artery and vein as well as the femoral nerve. The femoral artery enters the triangle and continues down the thigh, branching into superficial and deep branches. The femoral vein lies posterior to the artery and drains into the external iliac vein. The femoral canal is prone to femoral hernias.