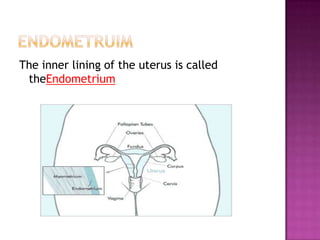
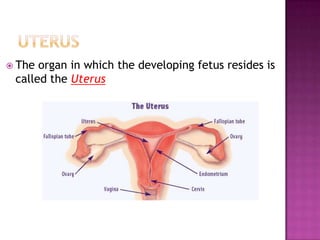
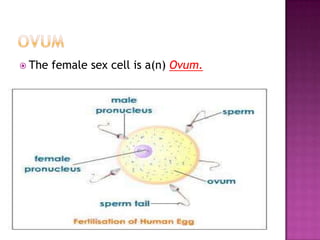
The document summarizes key aspects of the female reproductive system studied in gynecology. It describes the uterus as the organ that houses the developing fetus, and the endometrium as the inner uterine lining that is shed during menstruation if pregnancy does not occur. It also defines the ovum (egg) as the female gamete that can be fertilized by sperm to form a zygote and embryo. Major conditions treated by gynecologists are also listed.