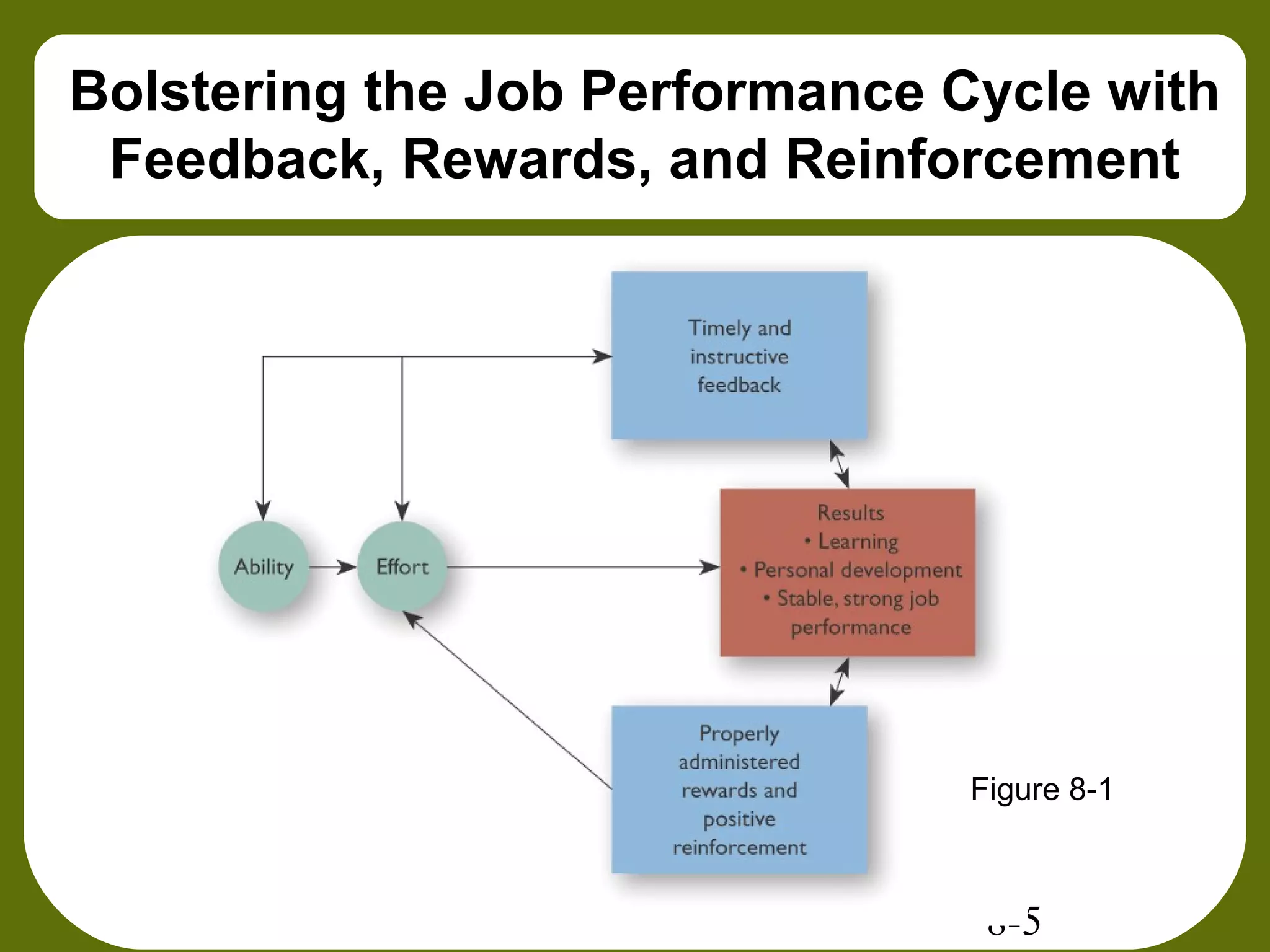
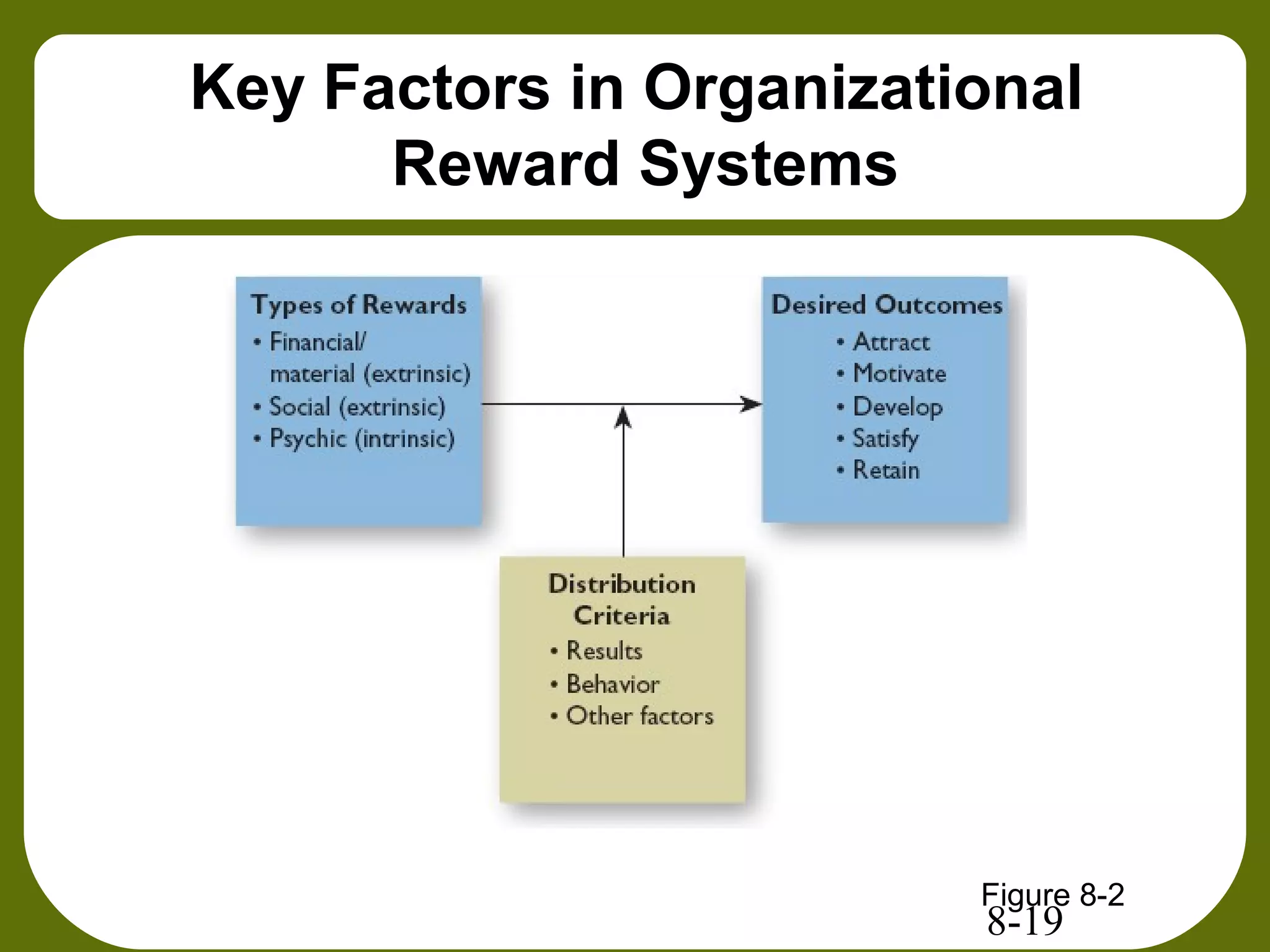
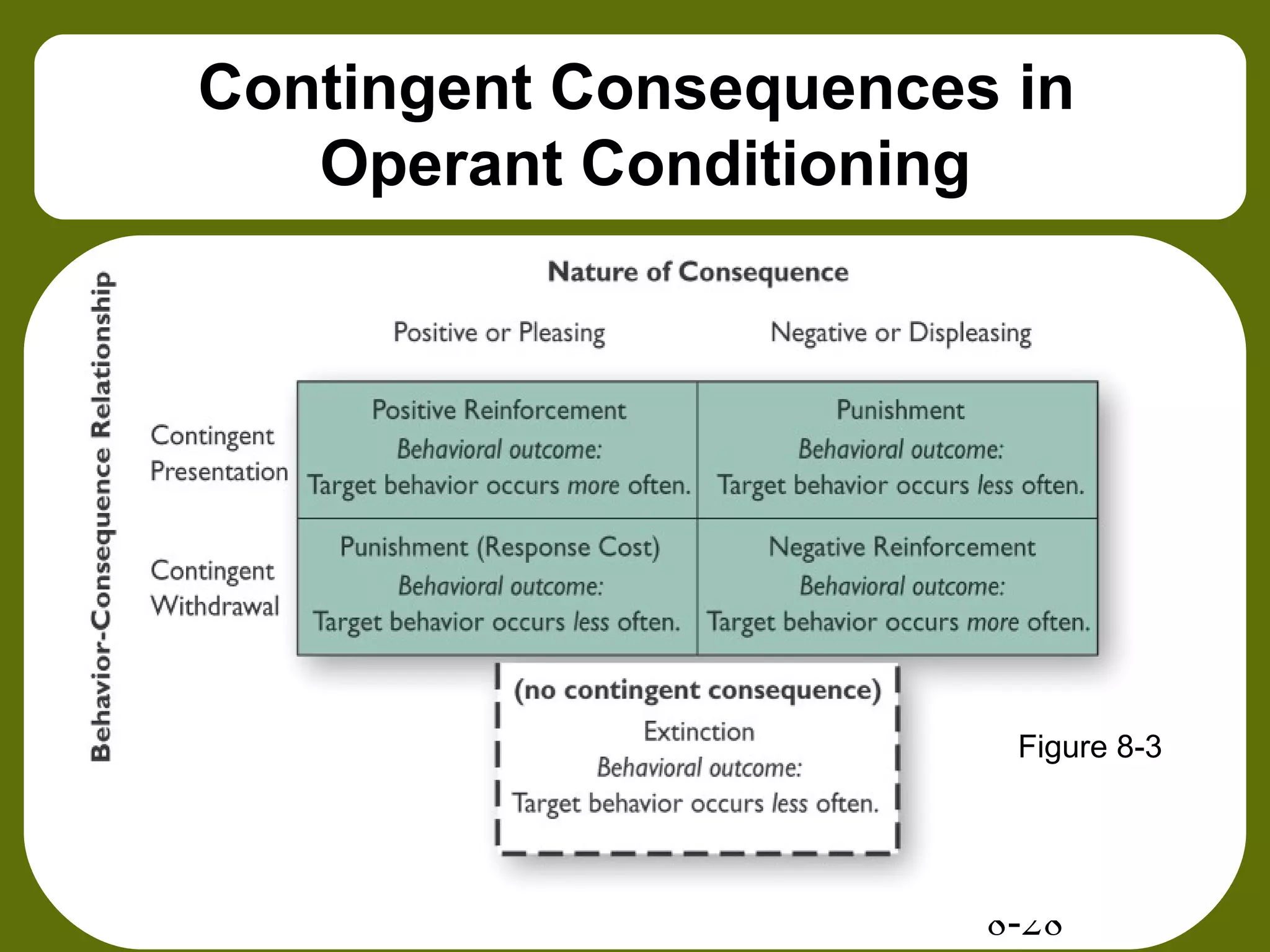
This document provides an overview of feedback, rewards, and positive reinforcement for improving job performance. It discusses the functions and sources of feedback, as well as tips for providing effective feedback. Intrinsic and extrinsic rewards are defined, and it is noted that rewards often fail to motivate due to various factors. The concepts of positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, punishment, and extinction from behavioral psychology are explained. Methods for effectively shaping behaviors through reinforcement schedules and contingencies are also outlined.